Porous biomass microspheres used for treating heavy metal sewage and preparation method of porous biomass microspheres
A biomass and microsphere technology, applied in the field of biomass, can solve the problems of single heavy metal element adsorption and single adsorption, and achieve the effect of excellent specific surface area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
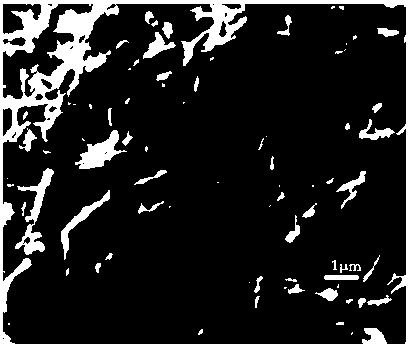
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Preparation of porous biomass microspheres hybridized with inorganic materials:
[0033] 1) Modification of sorghum stalks:
[0034] a) Pulverizing process: dry the sorghum stalks and pulverize them until the particle size is below 200 mesh to obtain sorghum stalk biomass particles;
[0035] b) Acid-base treatment process: 100g sorghum stalk biomass particles are placed in 200ml 3wt% phosphoric acid aqueous solution and stirred and soaked for 30min, then placed in 200ml 5wt% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution at 50°C for 10min, filtered and washed with tap water until The filtrate becomes neutral to obtain acid-base modified biomass particles;
[0036]c) Oxidation process: place the acid-base modified biomass particles in an aqueous potassium permanganate solution with a concentration of 5 wt%, and oxidize them at 10-20° C. for 1-2 hours to obtain an oxidized biomass dispersion; the potassium permanganate The dosage is 0.10 times of the weight of sorghum stalk bioma...
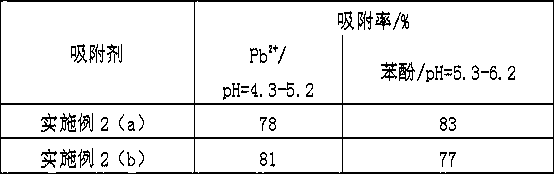
Embodiment 2
[0043] The influence of embodiment 2 different drying temperatures on the specific surface area of porous biomass microspheres
[0044] (a) Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the drying temperature in the preparation process of the porous biomass microspheres hybridized with inorganic materials is 20-30°C, and the rest of the preparation process and raw material ratio are exactly the same as in Example 1;
[0045] (b) Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the drying temperature in the preparation process of the porous biomass microspheres hybridized with inorganic materials is 80-90°C, and the rest of the preparation process and raw material ratio are exactly the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
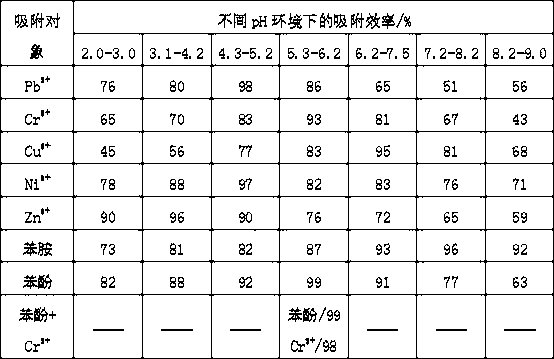
[0047] Porous biomass microspheres hybridized with inorganic materials are used to absorb heavy metals in aqueous solution. The specific method is as follows, respectively prepare Pb 2+ 、Cr 2+ 、Cu 2+ 、Ni 2+ or Zn 2+ The aqueous solution of chloride, the molar concentration is 60mmol / L; Prepare the aqueous solution of aniline and phenol respectively, and the molar concentration is also 60mmol / L in addition; The porous biomass microsphere of the inorganic material hybridization that prepares with embodiment 1 is adsorbent (add 1.0g of adsorbent per liter of aqueous solution), place it in an aqueous solution of heavy metals or organic substances (aniline or phenol) at room temperature 20-30°C, use hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH of the system to a certain range, and then carry out stirring and adsorption for 2 hours , filter, adopt ultraviolet detector to test the concentration in aniline and phenol in the filtrate, adopt atomic absorption to measure the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com