Linked furan-based n-type conjugated polymer and its application in organic photoelectric device
A conjugated polymer, polymer technology, applied in the direction of electric solid devices, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low absorption coefficient and insufficient absorption spectrum, and achieve improved absorption coefficient, wide absorption spectrum and absorption. coefficient, effect of high electron mobility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A representative synthetic route is as follows:
[0034]
[0035] (1) Monomers M1 and M5 were synthesized according to the method disclosed in the literature [Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(34):8904-8915.].
[0036] (2) Monomers M2, M3, M4, M6, and M7 were synthesized according to the method disclosed in the literature [Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(5): 1405-1418.].
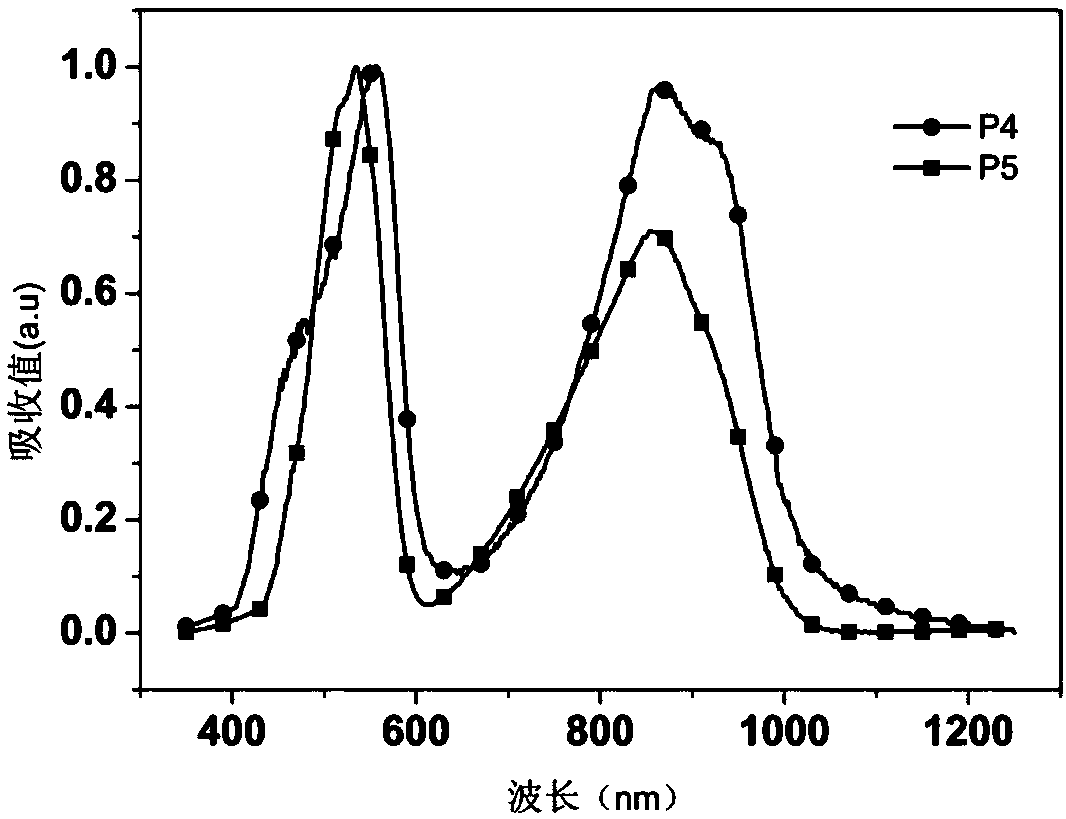
[0037] (3) Synthesis of polymers P1, P2, P3:
[0038] Add monomer M1 (0.5mmol) and monomer M2 (0.5mmol) into a 25mL two-necked flask, pass through nitrogen protection, and add 8mL of toluene. Add 5mg Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 , After reacting at 95°C for 12h, the polymer was precipitated with methanol and washed three times. A dark polymer P1 was obtained with a yield of 90.7%.
[0039] Add monomer M1 (0.5 mmol) and monomer M3 (0.5 mmol) into a 25 mL two-necked flask, pass through nitrogen protection, and add 12 mL of toluene. Add 7mg Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 , After reacting at 95°C for...
Embodiment 2
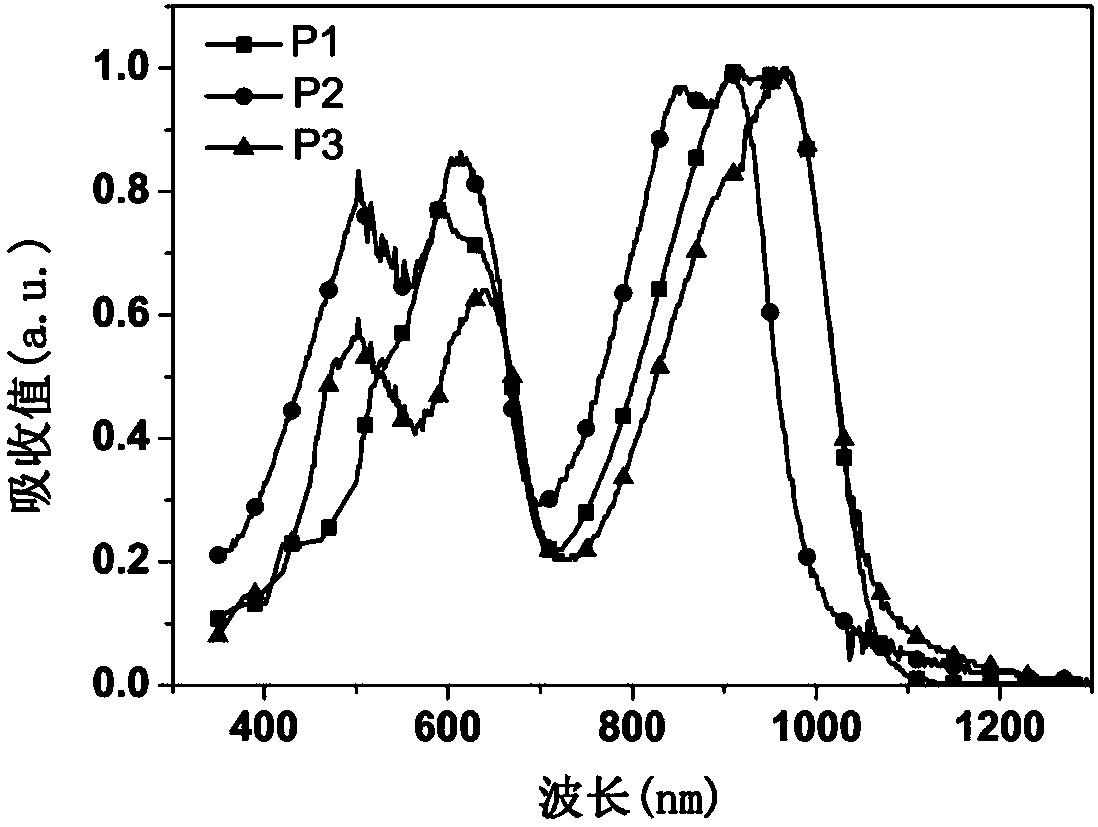
[0046] Using the conjugated polymers P1, P2, and P3 synthesized in Example 1 (the AB components in the structure are the same) as electron acceptors in organic photovoltaic devices (ITO cathode / cathode interface layer / active layer / anode-machine interface layer / anode) middle application
[0047] Pre-cut the ITO conductive glass with a square resistance of 20 ohms / cm2 into 15mm×15mm square pieces. Use acetone, special detergent for micron-sized semiconductors, deionized water, and isopropanol to clean ultrasonically in sequence, blow nitrogen whistle, and place in a constant temperature oven for later use. Spin-coat a layer of 5nm thick PFN-Br on ITO, then spin-coat active layer materials PTB7-Th / P1, PTB7-Th / P2, PTB7-Th / P3 with a thickness of 110nm, and finally evaporate MoO 3 and Al electrodes. All preparations were carried out in a glove box under a nitrogen atmosphere. The current-voltage curves of the fabricated flip-chip devices are as follows: Figure 4 The relevant da...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Using the conjugated polymers P1, P2, and P3 synthesized in Example 1 (with the same AB components in the structure) as electron acceptors in organic photovoltaic devices (ITO anode / anode interface layer / active layer / cathode interface layer / cathode) middle application
[0050] Pre-cut the ITO conductive glass with a square resistance of 20 ohms / cm2 into 15mm×15mm square pieces. Use acetone, special detergent for micron-sized semiconductors, deionized water, and isopropanol to clean ultrasonically in sequence, blow nitrogen whistle, and place in a constant temperature oven for later use. Spin-coat a layer of PEDOT:PSS with a thickness of 20 nm on the ITO, and then spin-coat the active layer materials PTB7-Th / P1, PTB7-Th / P2, and PTB7-Th / P3 with a thickness of 100 nm. Then spin-coat a layer of PFN-Br with a thickness of 5nm, and finally evaporate Al electrodes. All preparations were carried out in a glove box under a nitrogen atmosphere. The current-voltage curves of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com