Extracellular expression L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase engineering bacterium constructing method and application thereof
A technology of aspartic acid and construction method, which is applied in the field of construction of engineering bacteria expressing L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase extracellularly, can solve the problems of low product concentration, long production cycle, and insufficient enzyme activity, and achieve The effect of high product purity, cost saving and simplified extraction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] An engineering bacterium expressing L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase extracellularly and a construction method thereof, the steps of the construction method include: cloning a highly active L-aspartate α-decarboxylase gene, and cooperating with the signal peptide gene Express and transform Escherichia coli competent cells, and construct signal peptide-mediated extracellular secretion engineering bacteria of L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase. Specifically:
[0035] According to the gene sequence information of PanD in the whole genome of B. tequilensis (LGRW01000001) and the cloning vector pET20b, upstream and downstream primers containing adapters (indicated in italics) and restriction endonuclease sites (indicated in bold) were designed. The upstream primer is pelB-PanD -F: 5'- cccagccggcgatgg ccatggatatgtatcgaacaatgatgagc-3'; downstream primer is pelB-PanD-R:5'- gtggtggtggtggtg ctcgagctacaaaattgtacgggcggg-3'. The genomic DNA of B. tequilensis PanD37 (CGMCC NO:10506)...
Embodiment 2
[0037] An engineering bacterium expressing L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase extracellularly and a construction method thereof, the steps of the construction method include: cloning a highly active L-aspartate α-decarboxylase gene, and cooperating with the signal peptide gene Express and transform Escherichia coli competent cells, and construct signal peptide-mediated extracellular secretion engineering bacteria of L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase. Specifically:
[0038] The gene encoding the signal peptide torA of trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase was synthesized (Genebank number: BAA36139.1), and amplified using primers F-torA: 5′-AAccatgggcatgaacaataacgatctctttc-3′ and R-torA: 5′-ATCCATGGCCGCTTGCGCCGCAGTC-3′, The torA coding gene and plasmid pET20b were double digested with NdeI and NcoI respectively, and then the two were ligated to construct the plasmid pET20b-torA with torA signal peptide; according to the gene sequence information and Plasmid vector pET20b-torA designed up...
Embodiment 3
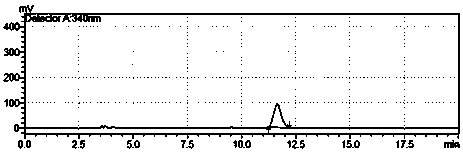
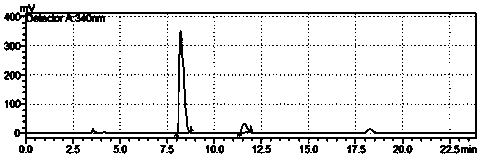
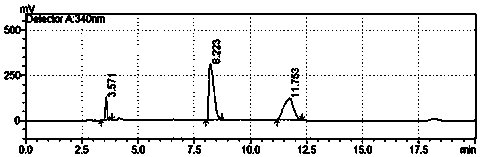
[0049] The method for extracellularly expressing L-aspartic acid α-decarboxylase fermentation broth to convert L-aspartic acid to produce β-alanine, the steps are:
[0050] (1) Insert the genetically engineered bacteria E. coli BL21(DE3) / pT20b-pelB-panD constructed in Example 1 into the LB slant medium containing 100 mg / L ampicillin and cultivate it at 37°C for 16 hours, wherein the LB medium formula is: Yeast powder 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, NaCl 5g / L, agar 20g / L, pH7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 30min;
[0051] (2) 50mL of LB liquid medium in a 500mL triangular flask, add 100mg / L ampicillin, connect to 1 ring of slant seed culture medium for 7 hours at 37°C and 200r / min, and the liquid LB medium formula is; yeast powder 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, NaCl 5g / L, pH7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 30min;
[0052] (3) Put 3.0 L medium into a 5 L fermenter, insert the seed solution into the fermentation medium with 5% seed volume, adjust the speed and ventilation to control the dissolved oxygen va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com