Microbial population sensing signal quenching bacteria and application thereof as biocontrol bacteria
A quorum sensing signal and signal technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve the problems of degradation characteristics and quenching mechanisms that need to be studied, and the types are limited, so as to protect crops and human beings Healthy, environmentally friendly, and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Isolation and screening of Burkholderia cepacia bacterial strain F25
[0041] 1. Isolation and purification of bacterial strains
[0042] (1) Soil sample collection: The sweet potato field soil cultivated for many years was collected as the microbial source.
[0043] The soil samples were collected on March 16, 2017 from the sweet potato field soil cultivated all year round in Nanhai District and Shunlugang, Foshan City, Guangdong Province. The soil from the surface layer to the depth of 5 cm was sampled, bagged, and preserved as a microbial source for strain isolation.
[0044] (2) Enrichment culture of strains: Prepare MSM medium, put 50 mL of MSM medium into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask for sterilization, add DSF mother solution under aseptic conditions after cooling (the concentration of the mother solution is 100mM, methanol is the solvent ), so that the final mass concentration of DSF was 0.01mM, and at the same time, 5 g of soil samples were added, and af...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Identification of Burkholderia cepacia strain F25
[0056] 1. Morphological identification of strain F25
[0057] (1) Colony morphological characteristics: Streak the above strain F25 on LB solid medium and culture at 30°C for 48 h. Such as figure 1 As shown, the color of the colony is yellow-green, and the colony is slightly raised, indicating that it is smooth and opaque with neat edges. Strain F25 was diffusely turbid and aerobic in LB broth.
[0058] (2) Morphological characteristics of bacteria: such as figure 2 As shown, the cells are rod-shaped, or short spherical, with a size of (0.5-1.0)×(0.3-0.5) μm.
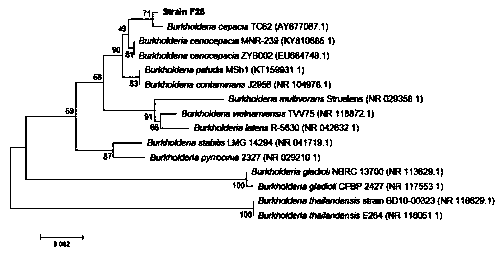
[0059] 2. Phylogenetic analysis of strain F25
[0060] 16S rDNA sequence and phylogenetic analysis: the genome of the strain F25 was extracted as a template, and the 16S rDNA PCR amplification of the strain was carried out using bacterial universal primers 27F (AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) and 1492R (GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT), and the 16S rDNA gene sequenc...
Embodiment 3
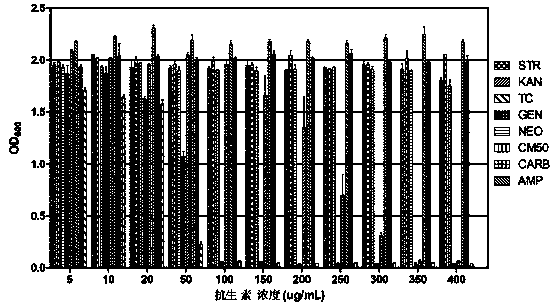
[0062] Antibiotic susceptibility analysis of embodiment 3 bacterial strain F25
[0063] In order to better study the biocontrol potential of the bacterial strain F25 obtained in Examples 1 and 2, we studied the antibiotic sensitivity of the bacterial strain F25. The result is as Figure 4As shown, the resistance of the strain F25 to gentamicin (GEN), neomycin sulfate (NEO), carbenicillin (CARB), ampicillin (AMP) and streptomycin (STR) reached 400 μg / mL or more, the resistance to kanamycin (KAN) reaches 200 μg / mL, and the resistance to tetracycline (TC) and chloramphenicol (CM) reaches 50 μg / mL. This result is helpful for selecting appropriate antibiotics as a reference in follow-up studies.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com