Efficient traceless gene knockout method for saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and gene knockout, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of peculiar smell of wine, lower probability of ideal transformants, influence on the flavor and quality of wine, etc., and achieves the effect of reducing isoamyl alcohol content and excellent flavor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
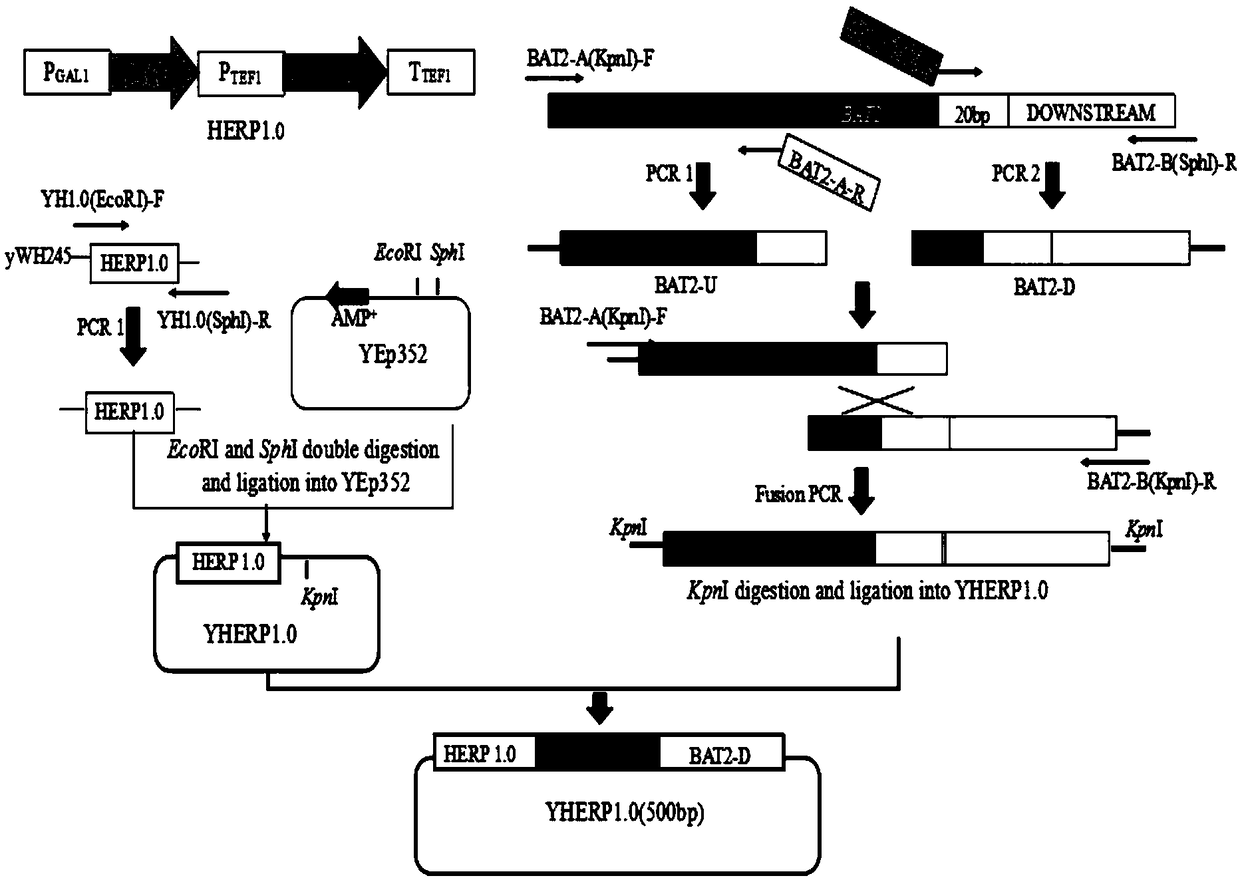
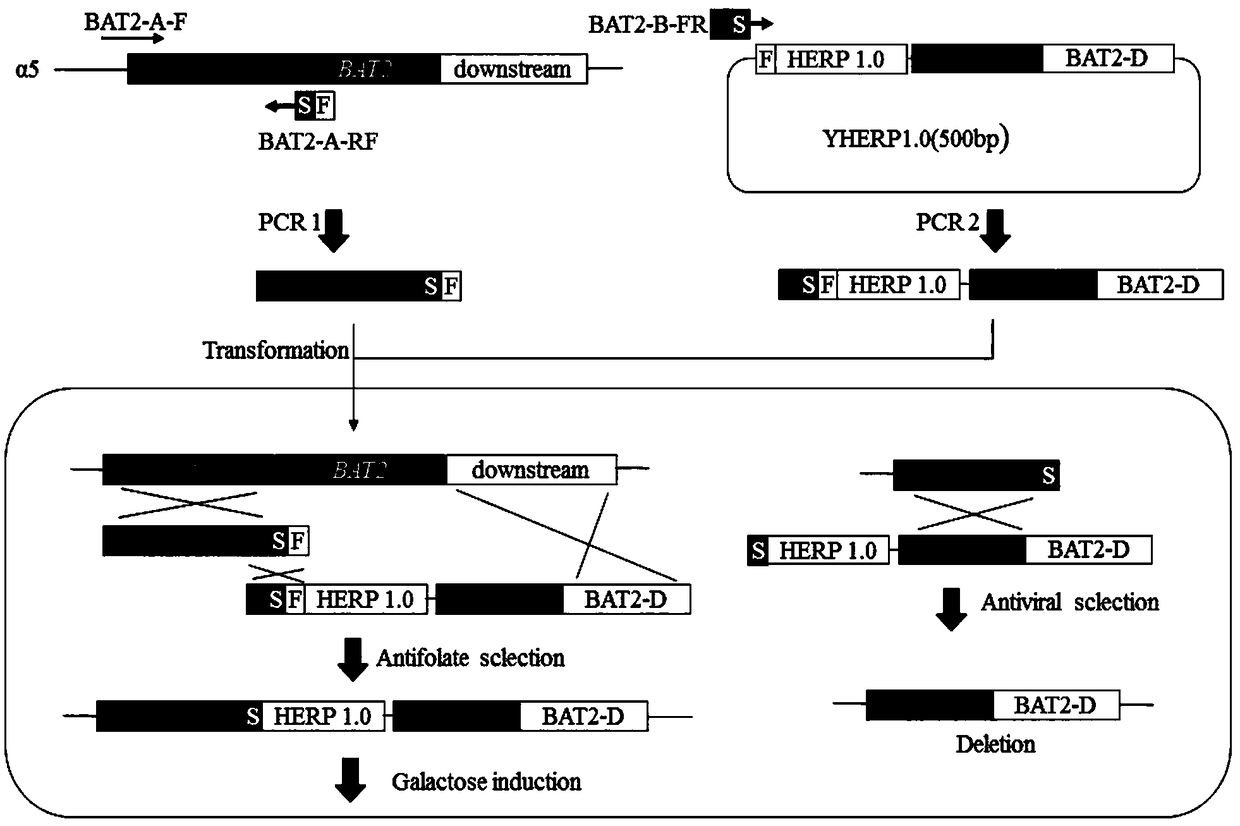
[0032] Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the seamless knockout of amino acid transaminase encoding gene BAT2
[0033] The starting strain used in this example is haploid α5 of CICC32315. (For the source of the fragment HERP1.0, see William G. Alexander, Drew T. Doering and Chris Todd Hittinger, High-Efficiency Genome Editing and Allele Replacement in Prototrophic and Wild Strains of Saccharomyces. Genetics, Vol. 198, 859-866 November 2014). The Escherichia coli DH5α was purchased from Takara Company. The YPD medium is a general complete medium; the components of the screening medium YPGly+AF are 5% glycerol, 2% peptone, 1% yeast extract powder, 200mg / mL aminomethylfolate, 5mg / mL sulfonamide, 5 μg / mL thymidine, 50 μg / mL hypoxanthine; the composition of the yeast synthetic medium (SC) is 2% glucose, 0.17% YNB, 0.5% ammonium sulfate, complete amino acid mixture solution, and the solid medium contains 2% imported agar powder.
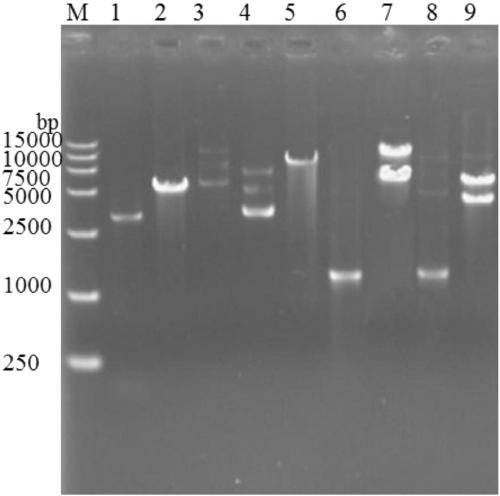
[0034] According to the yeast genome da...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Determination of Growth Curves of Hα5(500)ΔH and α5 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain Hα5(500) without Scarless BAT2
[0057] Pick a single colony of Hα5(500)ΔH and α5 and inoculate it in 50mL YEPD liquid medium, culture at 30°C with shaking at 180rpm for 24 hours, take the expanded culture and inoculate it into three bottles of 50mL YEPD medium according to the inoculum size of 1:100 , shake culture under the same conditions, and take the bacterial cell culture suspension 0.5 mL, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 1min, then resuspend the sludge with deionized water. Calibrate the zero point of the 7200 visible spectrophotometer with deionized water, and measure the OD of the bacterial solution colorimetrically at a wavelength of 600nm 600 value. The absorbance value (OD) of bacterial solution at each time point 600 ) is the ordinate, and taking the culture time as the abscissa, the growth curve of each bacterial strain is drawn, and the growth curve is as follows: Figur...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Corn mash fermentation experiments of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains Hα5(500)ΔH and α5 without trace knockout of BAT2
[0060] The recombinant strain Hα5(500)ΔH and the starting strain α5 were respectively subjected to corn thick mash fermentation experiments, and the fermentation process roadmap is as follows:
[0061] Corn flour soaking→liquefaction→saccharification→fermentation with bacteria→weighing for weight loss→distilling alcohol→determination of fermentation indicators
[0062] Process conditions:
[0063] Soaking conditions: 60-70°C, soaking for 20 minutes; liquefaction conditions: 85-90°C, adding high-temperature resistant α-amylase, liquefying for 90 minutes; saccharification conditions, 55-60°C, adding glucoamylase, saccharifying for 20 minutes.
[0064] Ingredients: corn flour 60g, water 130mL, high temperature resistant α-amylase 2×10 4 U / mL, 30μL, glucoamylase 1×105 U / mL, 90μL, 7.5×10 2 U / mL acid protease 1.2mL: nutrient salt 1mL (MgSO 4 150g / L, KH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com