An ultrasensitive method for the analysis of trace polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water
A polybrominated diphenyl ether, trace technology, applied in analytical materials, chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as hindering practical application and poor chemical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Example 1 Preparation of TpPa-1, TpPa-1 coated fiber and solid phase microextraction device
[0078] (1) Synthesis of TpPa-1
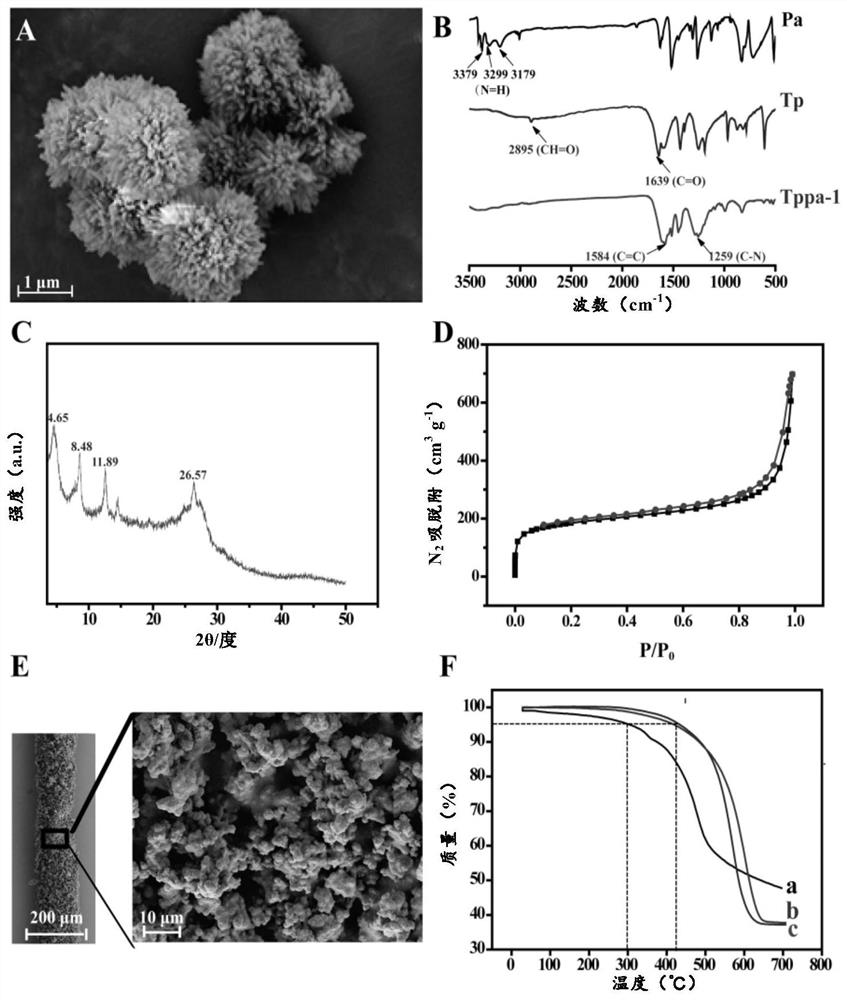
[0079] In a 25mL hydrothermal reactor, add 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzene-1,3,5-tricarbaldehyde (Tp) (126mg, 0.60mmol), p-phenylenediamine (Pa-1) (96mg, 0.90mmol), 1.5mL of mesitylene, 1.5mL of 1,4-dioxane and 0.5mL of 3M aqueous acetic acid. Then, sonicate for 10 min to form a homogeneous mixture. Next, nitrogen gas was introduced thereinto for 30 minutes in order to remove oxygen in the reaction. Finally, the reaction kettle was heated in an oven at 120° C. for 3 days. The red reaction precipitate was centrifuged to obtain a red solid, which was washed with anhydrous acetone (5-6 times), and then the solid was dried in an oven at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain 80% (178 mg) of a deep red powder, which was TpPa-1, and was used Coated fibers were prepared below.
[0080] (2) Preparation of TpPa-1 coated fiber
[0081] Soak one end of the stainless ...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2 Detection of five kinds of PBDEs in water by solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
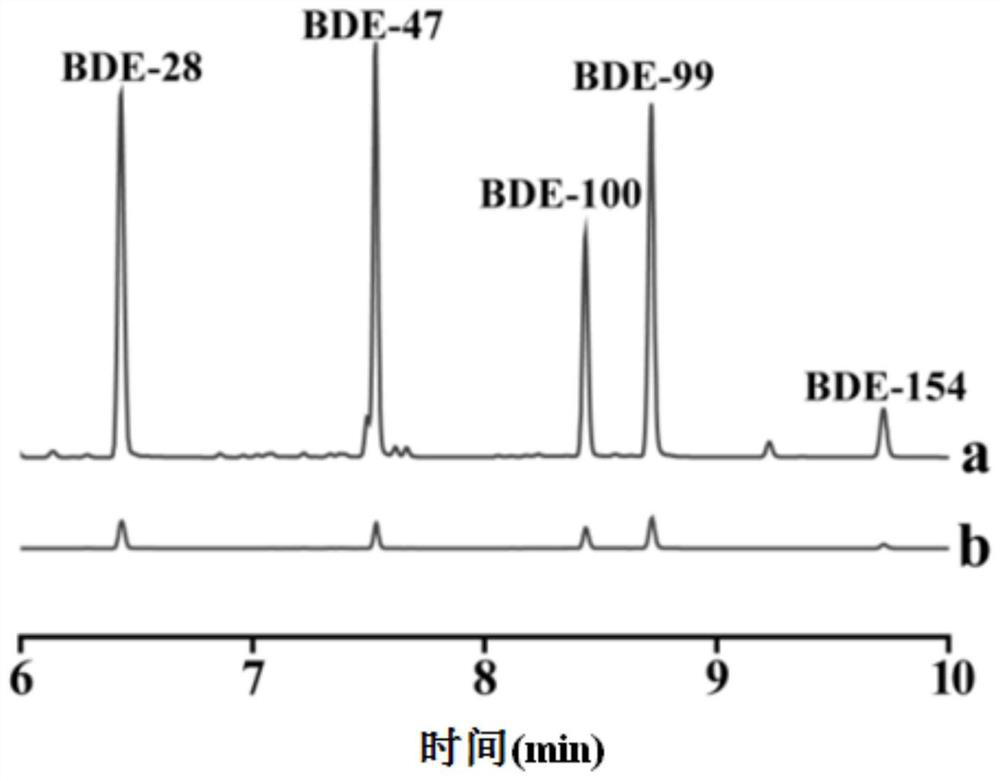
[0088] 5 PBDEs: BDE-28, BDE-47, BDE-100, BDE-99 and BDE-154.
[0089] Detection method: The SPME device (comprising TpPa-1 coated fibers) prepared in Example 1 was inserted into a headspace vial containing 10 mL of sample solution. The TpPa-1 coating is completely immersed in the sample solution, and the temperature and speed are controlled by heating the magnetic stirrer, and the ionic strength is adjusted by adding NaCl. After the extraction is completed, the solid-phase microextraction device is placed in the gas sampling port for high-temperature desorption and sample injection. Among them, the solid-phase microextraction device needs to be aged under nitrogen protection at 280°C for 30 minutes before each extraction.
[0090] Condition parameters are: 0% (w / v) NaCl; extraction time: 40 min; extraction temperature: 70°C; desorption temperatur...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3 Condition Optimization of Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography Detection Method
[0094] According to the above detection method, the parameters in the extraction process and the desorption process are optimized to screen out better experimental conditions. The optimization process is as follows:
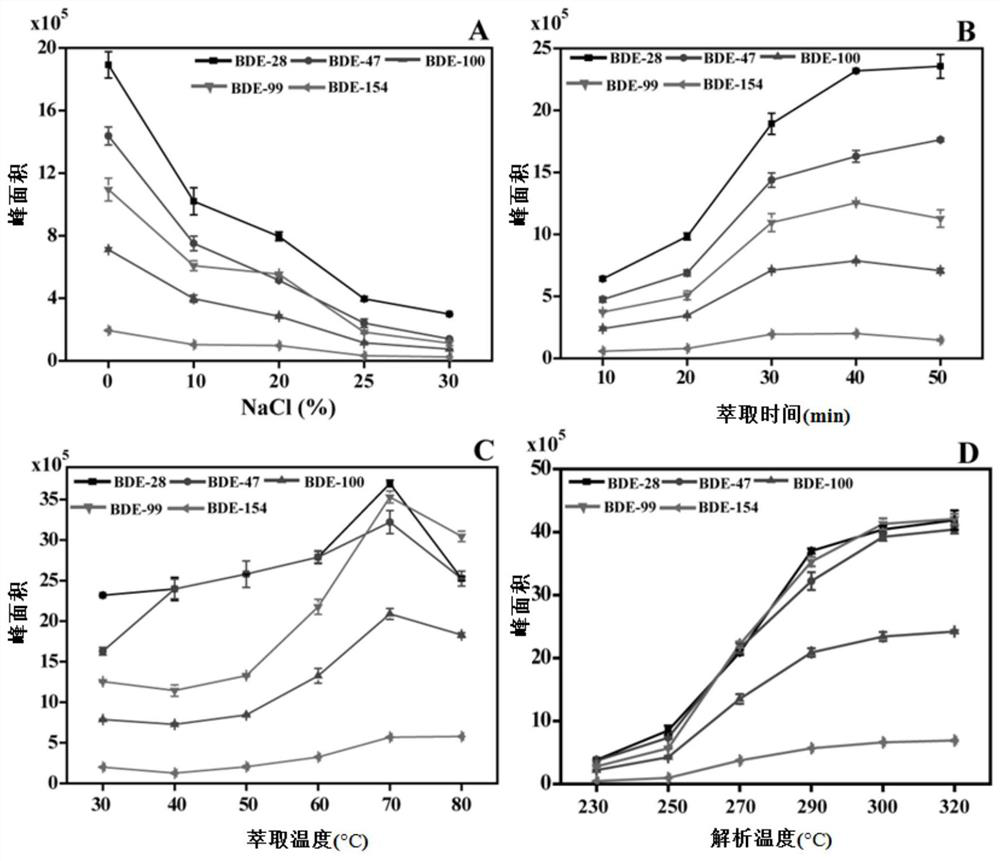
[0095] 1. Single factor method to optimize the conditions of solid phase microextraction
[0096] Based on the TaPa-1 coated fiber prepared in Example 1 and the solid-phase microextraction device assembled therefrom, the PBDEs (i.e. BDE-28, BDE-47, BDE-100, BDE-99) in the enrichment and detection water and BDE-154) SPME method for optimization. In order to obtain higher extraction efficiency, the present embodiment utilizes TaPa-1 coating fiber to extract the concentration in the water sample to be 50ng L -1 The PBDEs (the concentration of the five PBDEs are the same), the experimental parameters in the SPME extraction process and desorption process we...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com