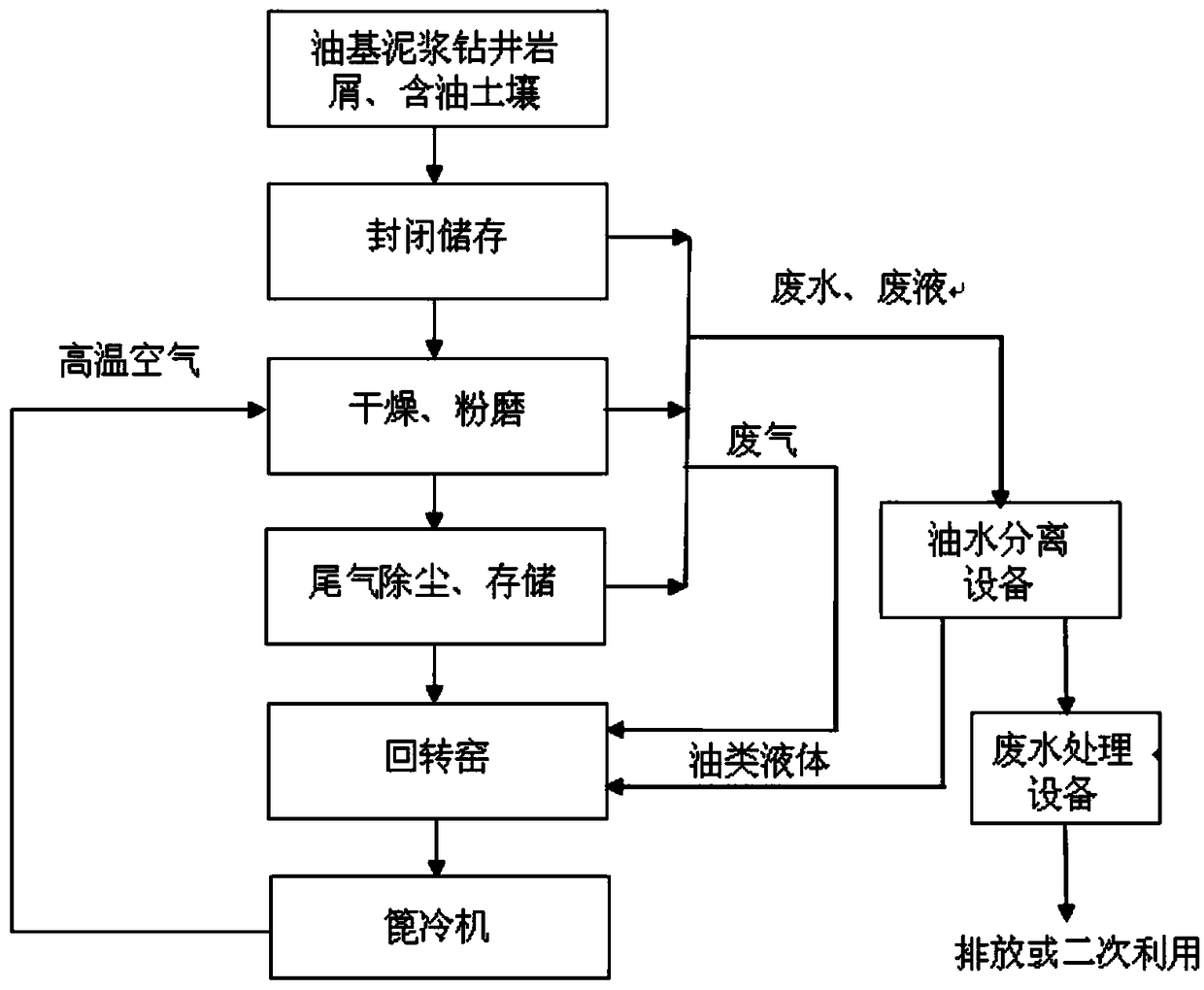
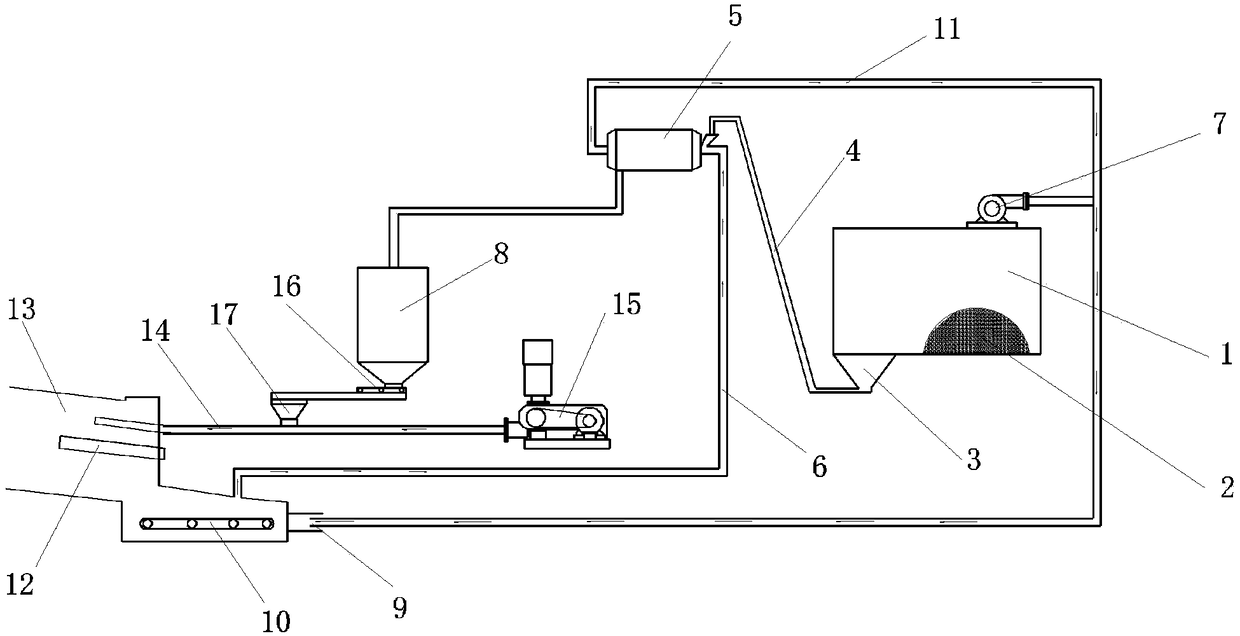
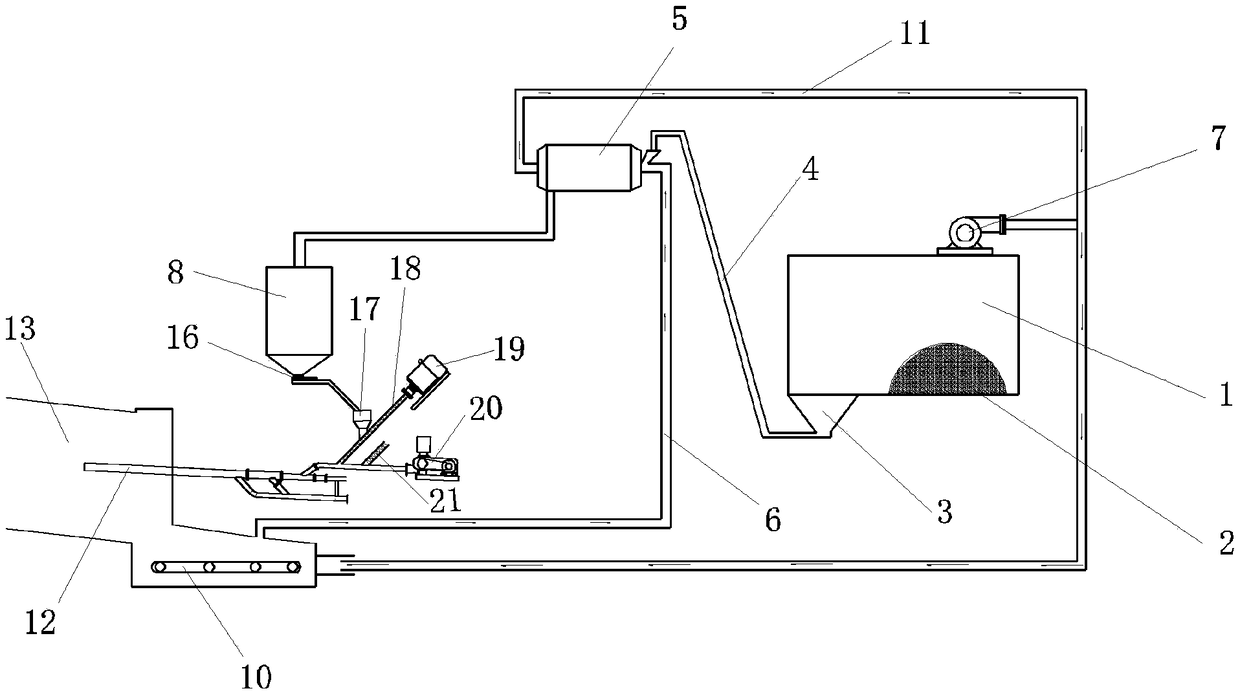
Equipment and method for cooperative treatment of drilling solid waste by using cement kiln
A drilling waste and co-processing technology, applied in combustion methods, cement production, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient mixing of raw materials, ecological environment damage, and fluctuations in cement quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The oil-based mud cuttings in this case were taken from a shale gas drilling well in Sichuan after solid-liquid separation. The chemical composition, phase composition and thermal performance test results are shown in Table 1. Figure 4 and Figure 5 . Wherein Table 1 specifies the chemical composition and content of cuttings; Figure 4 It is the XRD diffraction pattern of the cuttings. The test results show that the cuttings mainly contain mineral phases such as quartz, limestone, dolomite, barite, and mica. Figure 5 It is the result of TG-DSC detection of cuttings. The analysis shows that the weight loss in the temperature range of 200°C is 2.49%, and most of the weight loss of this part is water volatilization. The loss is the decomposition of organic matter, so it can be seen that the water content in the cuttings is small, and most of the loss on ignition is caused by the volatilization of white oil.
[0054] Table 1 The chemical composition and content of oil-...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The oil-bearing soil in this case was taken from polluted soil near a mining platform in Changqing. The chemical composition is shown in Table 2. Its composition is also mainly composed of silicon oxide, aluminum oxide, iron oxide, and calcium oxide, and is close to the composition of drilling cuttings.
[0058] Table 2 Chemical composition and content of oil-bearing soil, unit: %;
[0059] Loss on ignition
Embodiment 3
[0061] The cuttings and cement raw materials in Example 1 are used for batching, and are designed as components of ordinary Portland cement clinker, and are calcined at 1450° C. for 30 minutes. The clinker is mixed with 5% dihydrate gypsum powder and ground into cement. The specific surface area is controlled at 342±10m 2 kg range. See Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 for the specific batching scheme, clinker chemical composition and cement performance.
[0062] Table 3 ingredient scheme
[0063]
[0064] Table 4 Detection of clinker chemical composition, unit: %;
[0065] index
LOSS
SiO 2
Al 2 o 3
Fe 2 o 3
CaO
MgO
SO 3
f-CaO
IR
R 2 o
Cl-
sample
0.31
22.84
3.58
5.16
63.40
2.75
0.73
0.37
0.36
0.41
0.037
standard
≤3.0
/
/
/
/
≤5.0
≤3.5
/
≤0.75
≤0.75
≤0.06
[0066] Table 5 cement physical properties
[0067]
[0068] Accordin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com