A kind of method of carboxylic acid continuous preparation amides
A technology of amides and carboxylic acids, which is applied in the field of continuous preparation of amides from carboxylic acids, can solve the problems of low automation level, large safety hazards, and difficult removal, and achieve the effects of avoiding the formation of carcinogens, high safety, and low online volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The preparation of embodiment 1 benzamide
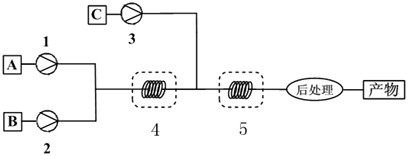
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, after dissolving benzoic acid with dichloromethane, add catalyst concentrated nitric acid as material A, dissolve BTC with dichloromethane as material B, and dissolve ammonium bicarbonate in water as material C. Material A and material B pass through the first The infusion pump 1 and the second infusion pump 2 are transported into the tubular reactor I4, and the temperature of the tubular reactor I4 is controlled by a water bath to 40°C. After a residence time of 5 minutes, the acyl chloride reaction is carried out to generate benzoyl chloride, and then benzoyl chloride Enter the tubular reactor II 2 together with the material C delivered by the infusion pump 3, control the temperature of the tubular reactor II 2 to 10°C through a water bath, and carry out the amination reaction after a residence time of 3 minutes, and control the flow rate through the pump to make benzoic acid and nitric acid...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The preparation of embodiment 2 o-chlorobenzamide
[0025] After dissolving o-chlorobenzoic acid with chloroform, add catalyst concentrated phosphoric acid as material A, dissolve phosphorus oxychloride in chloroform and dissolve as material B, ammonia as material C; material A and material B pass through the first infusion respectively The pump 1 and the second infusion pump 2 are transported into the tubular reactor I4, and the temperature of the tubular reactor I4 is controlled by a water bath to be 50°C. After a residence time of 15 minutes, the acyl chloride reaction is carried out to generate o-chlorobenzoyl chloride, and then o-chlorobenzoyl chloride Benzoyl chloride enters the tubular reactor II 2 together with the material C transported by the amination reagent delivery device 3, and the temperature of the tubular reactor II 2 is controlled by a water bath to 60°C, and the amination reaction is carried out after a residence time of 5 minutes. The flow rate is c...
Embodiment 3
[0026] The preparation of embodiment 3 p-chlorobenzamide
[0027] Raw material p-chlorobenzoic acid and concentrated sulfuric acid are dissolved in toluene as material A, thionyl chloride is used as material B, and ammonia water is used as material C; material A and material B are transported into the pipeline through the first infusion pump 1 and the second infusion pump 2 respectively. Type reactor I 4, the temperature of tubular reactor I is controlled by a water bath to be 120°C, acid chloride reaction is carried out after 15min residence time to generate acid chloride, and then enters tubular reactor II together with material C delivered by infusion pump 3, through The water bath controls the temperature of the tubular reactor II to 0°C, and the amination reaction is carried out after a residence time of 0.1 min. The flow rate is controlled by the pump so that the feed molar flow ratio of p-chlorobenzoic acid, sulfuric acid, thionyl chloride, and ammonia water is: 1:0.005...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com