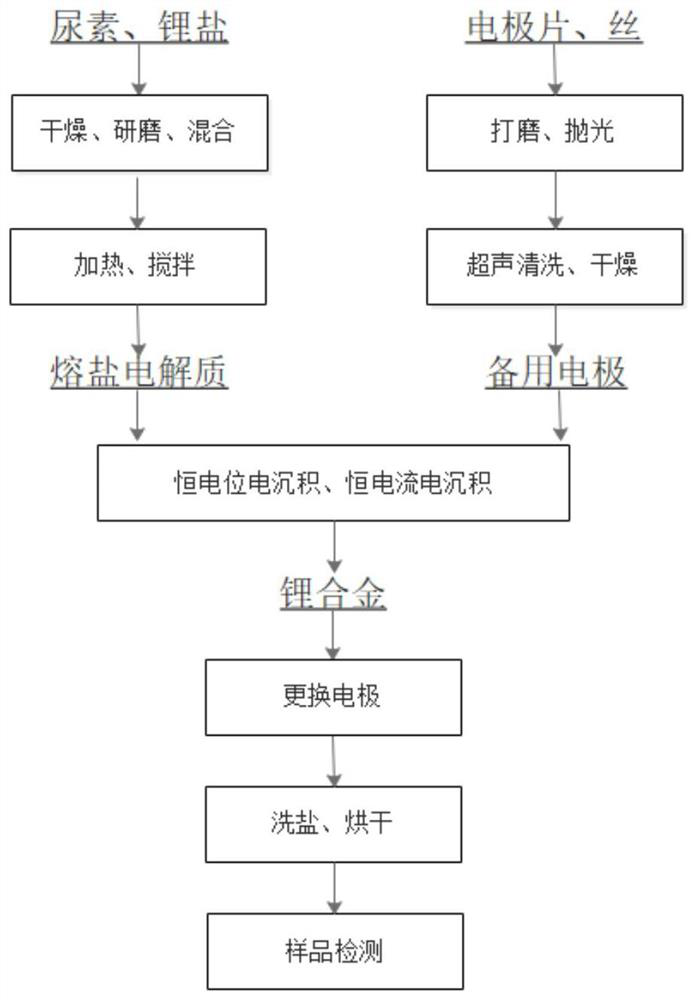
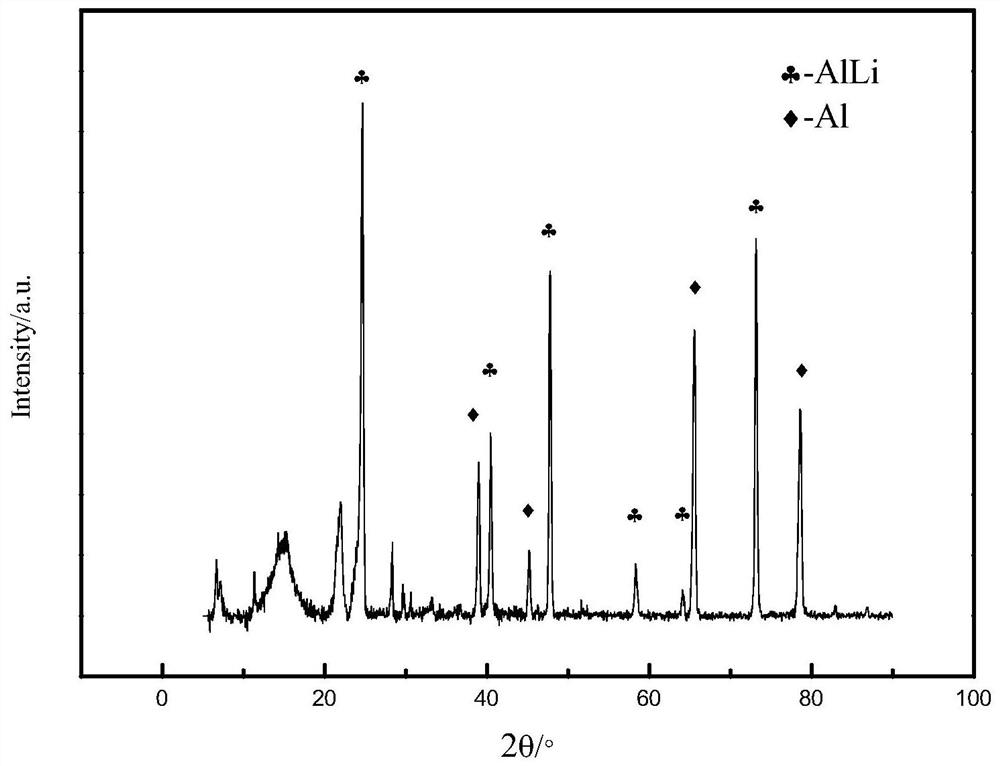
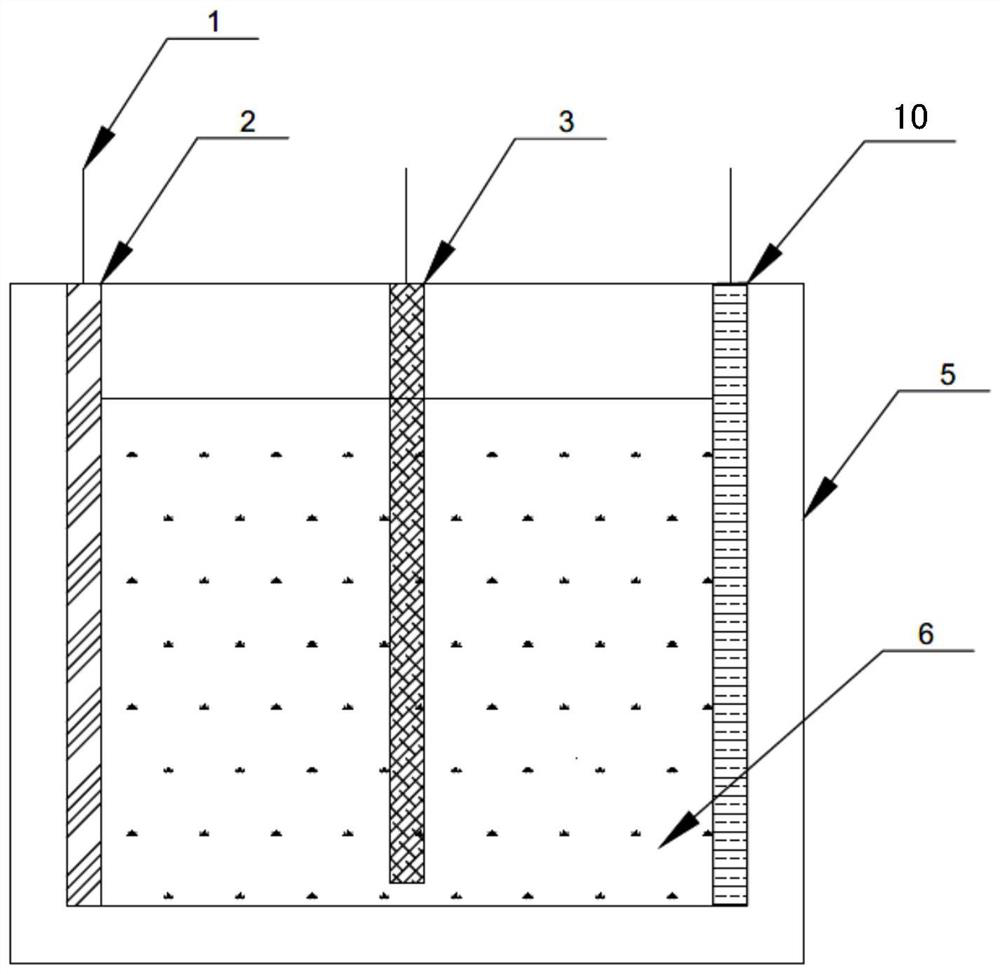
A kind of preparation method of high Li content lithium alloy
A lithium alloy and content technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of high Li content lithium alloys, can solve problems such as solvent destruction, and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, reducing costs and low prices.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Under an argon atmosphere, mix urea powder and lithium salt powder, heat to 100°C under stirring, and continue stirring until a transparent liquid is obtained as a molten salt electrolyte; wherein the molar ratio of urea powder to lithium salt powder is 3; The lithium salt powder is lithium chloride;
[0049] The molten salt electrolyte is placed in the electrolytic cell, and under the condition of argon atmosphere, constant potential electrodeposition is carried out. The electrolytic cell is a single-chamber electrolytic cell with a structure such as image 3As shown, the single-chamber electrolytic cell body 5 is provided with a single-chamber electrolytic cell cathode plate 3, a single-chamber electrolytic cell first anode plate 2 and a reference electrode plate 10, and the single-chamber electrolytic cell cathode plate 3 is located in the single-chamber electrolytic cell In the middle part of the body 5, the first anode plate 2 and the reference electrode plate 10 o...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0053] (1) urea powder and lithium salt powder are mixed and heated to 80°C under stirring conditions, the molar ratio of urea powder and lithium salt powder is 5; the lithium salt powder is lithium fluoride;
[0054] (2) The material of the cathode plate is magnesium, and the material of the anode plate is platinum; the electrodeposition temperature is 80°C, the electrolysis time is 2h; the cathode potential is -0.5V;
[0055] (3) After the cathode plate is taken out, place it in ethylene carbonate, soak it at a temperature of 80°C for 3 hours, then dry it for 24 hours at a vacuum degree of ≤50Pa and a temperature of 80°C, and make a lithium alloy with a high Li content on the surface of the cathode plate , containing Li16.54% by mass percentage, and the rest is magnesium.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0058] (1) urea powder and lithium salt powder are mixed and heated to 120°C under stirring conditions, the molar ratio of urea powder and lithium salt powder is 2; the lithium salt powder is lithium bromide;
[0059] (2) The material of the cathode plate is copper, and the material of the anode plate is tungsten; the temperature of electrodeposition is 120°C, the electrolysis time is 0.5h; the cathode potential is -0.3V;
[0060] (3) After taking out the cathode plate, place it in ethylene carbonate, soak it for 2.5 hours at a temperature of 80°C, and then dry it for 24 hours at a vacuum degree of ≤50Pa and a temperature of 90°C to make lithium with a high Li content on the surface of the cathode plate. The alloy contains Li17.23% by mass percentage, and the rest is copper.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com