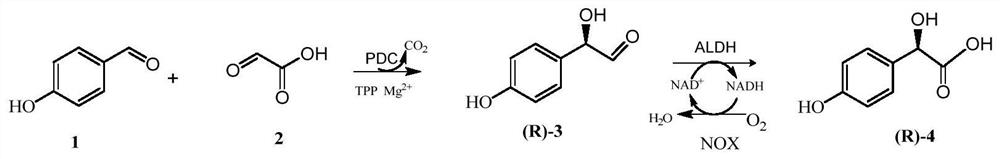
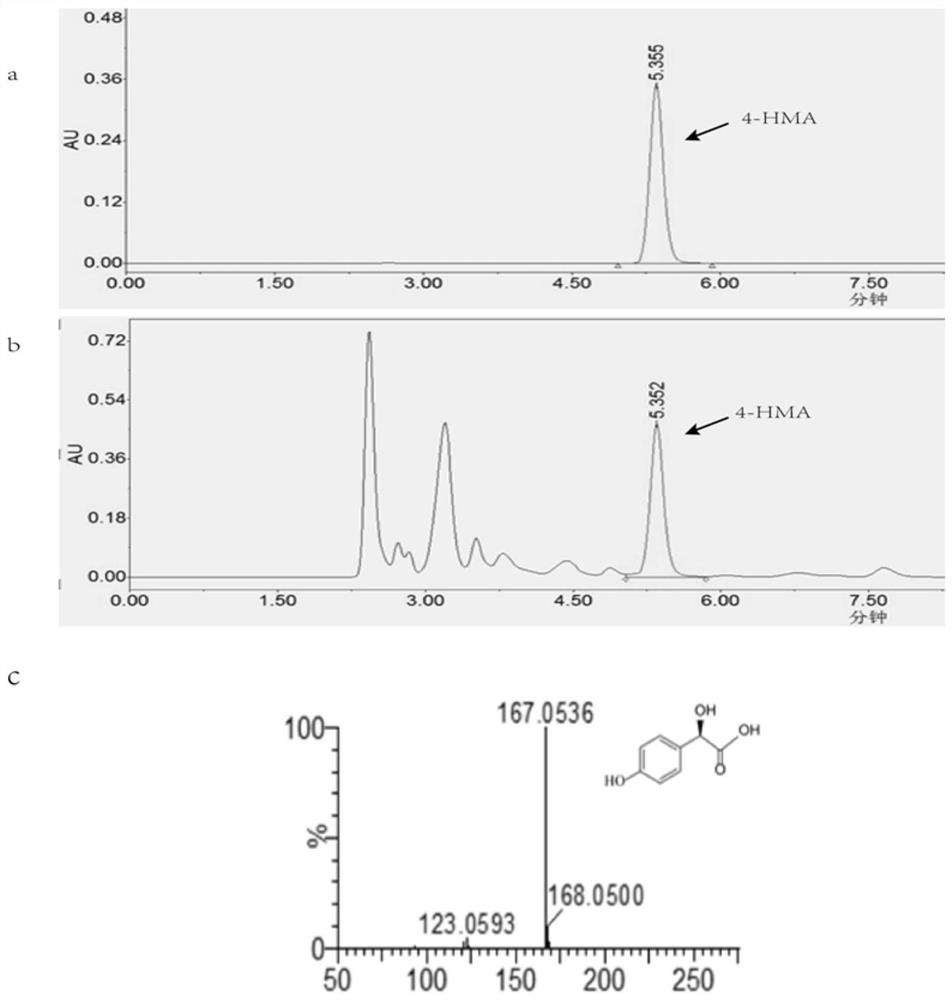
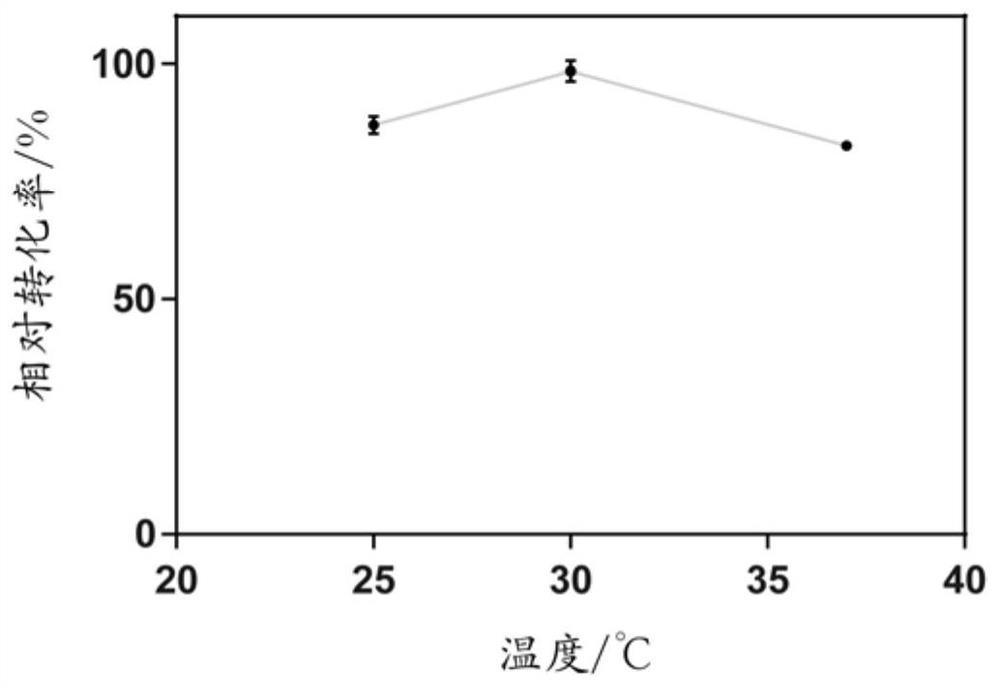
A method for synthesizing p-hydroxymandelic acid
A technology for p-hydroxymandelic acid and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high cost, environmental pollution, equipment corrosion, expensive substrates, etc., and achieves the effects of easy operation, efficient production, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Construction of recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-pdc
[0044] The artificially synthesized pdc gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1) containing BamHI and SalI restriction sites through codon optimization, pdc gene and plasmid pRSFDuet- with restriction endonuclease BamHI and SalI 1 Digest for 3 hours at 37°C, use T 4 Ligase ligated the pdc gene and plasmid pRSFDuet-1 after digestion and gel recovery at 16°C for 10 h, and transformed the ligated product into E.coli JM109 competent cells by chemical transformation method, and cultured it on LB plates containing ampicillin for 12 h. Colonies grown on the plate were verified by PCR. Positive transformants were selected and inoculated in LB medium, cultured at 37°C for 12 hours, and plasmids were extracted. After sequencing verification, the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-pdc was constructed.
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: Construction of recombinant plasmid pETDuet-padA
[0046] Using the genome of Escherichia coli MG1655 as a template, the 5'CG GGATCC AATGACAGAGCCGCATGTA 3' as forward primer, 5' as ACGC GTC GAC TTAATACCGTACACACACCGA 3' is the reverse primer (the underlined part is respectively the restriction site of BamHI and SalI) amplifying and obtaining the padA gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2), using restriction endonucleases BamHI and SalI digested the padA gene and the plasmid pETDuet-padA at 37°C for 3h, and used T 4 Ligase ligated the padA gene and plasmid pETDuet-1 after enzyme digestion and gel recovery for 10 hours at 16°C, and transformed the ligation product into E.coli JM109 competent cells by chemical transformation method, and cultured it on an LB plate containing ampicillin for 12 hours. Colonies grown on the plate were verified by PCR. Positive transformants were selected and inoculated in LB medium, cultured at 37°C for 12 hours, an...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Construction of recombinant plasmid pETDuet-padA-noxE
[0048] Using the genome of Bacillus subtilis 168 as a template, the 5'GGA AGATCT AATGACGAATACTCTGGATGTTT3' as forward primer, with 5' CCG CTCGAG TTACAGCCAAGTTGATACTTTT 3' is the reverse primer (the underlined part is the restriction site of BglII and XhoI respectively) to amplify the noxE gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), and use restriction enzymes BglII and XhoⅠdigested the noxE gene and plasmid pETDuet-padA at 37°C for 3h, and used T 4 The noxE gene and plasmid pETDuet-padA after digestion and gel recovery were ligated with ligase for 10 hours at 16°C, and the ligated products were transformed into E.coli JM109 competent cells by chemical transformation, and cultured on LB plates containing kanamycin for 12 hours , and verify the colonies grown on the plate by PCR. Positive transformants were selected and inoculated in LB medium, cultured at 37°C for 12 hours, and plasmids were ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com