Detection primers, detection methods and applications of leaf spot pathogen phoma exigua
A technology for detecting primers and pathogenic bacteria, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of short time consumption and achieve the effects of short time consumption, high precision and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Construction of a specific PCR detection method for Phoma exigua, the pathogen of Panax ginseng leaf spot
[0035] 1. Extraction of pathogenic genomic DNA of Panax ginseng leaf spot disease
[0036] Phoma exigua, the pathogenic bacterium of Phoma exigua, is preserved by the Plant Protection Laboratory of the Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences. After culturing on PDA plates containing cellophane for one week, the total genomic DNA of pathogenic bacteria was extracted by CTAB method.
[0037] 2. Design of specific molecular detection primers
[0038] Using ITS1 and ITS4 primers, the total genomic DNA of the obtained pathogen Phoma exigua was amplified and sequenced by PCR to obtain its ITS sequence. Phoma aliena, Phoma aloes, Phoma neerlandica, Phoma schachtii, Phoma odoratissimi, Phoma helianthi, and fungi such as Magnaporthe oryzae, Rhizoctonia, Anthracnose, Fusarium, Alternaria, Sclerotinia, Aspergillus oryzae, White...
Embodiment 2
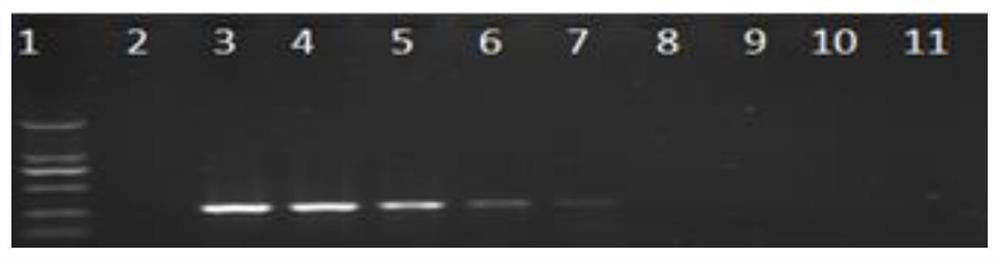
[0055] Example 2 Specific detection for Phoma exigua genomic DNA
[0056] Phoma glaucii, Phoma tanaceti, Phoma herbarum, Phomabellidis, Phoma senecionis, Phoma macrostoma, Phoma aliena, Phoma aloes, Phomaneerlandica, Phoma schachtii, Phoma odoratissimi, Phoma helianthi, and blast fungus, Rhizoctonia anthracnose, Genomic DNA of fungal microorganisms such as Fusarium, Alternaria, Sclerotinia, Aspergillus oryzae, and Sclerotinia spp., and Panax ginseng plants. The genomic DNA of Phoma exigua was used as a positive control, and clear water was set as a negative control. Take the above pathogenic bacteria 1 μL of DNA was used as a template for PCR.
[0057] The reaction system was: 12.5 μL of 2×Taq Master Mix, 1 μL of 10 μM upstream and downstream primers ZJSF / ZJSR, 9.5 μL of double distilled water.
[0058] The amplification reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes, followed by 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 30 seconds, and fin...
Embodiment 3
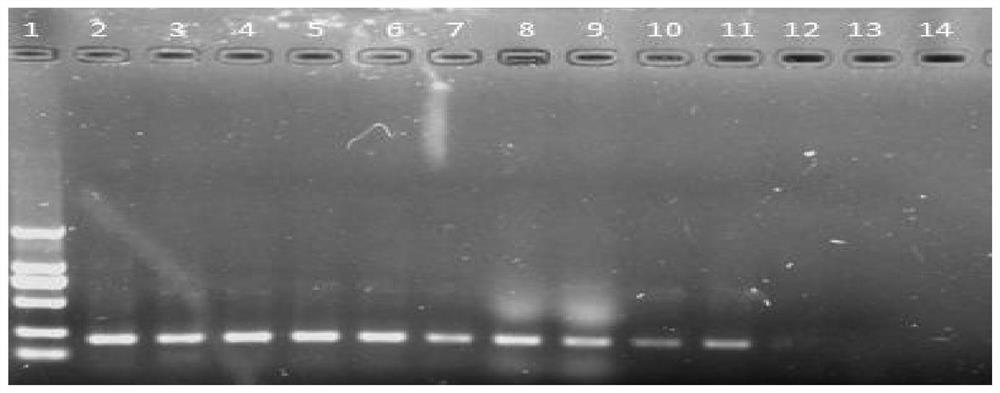
[0061] Example 3 Detection of Phoma exigua Genomic DNA by Conventional PCR
[0062] The Phoma exigua genomic DNA was sequentially diluted to a total of 9 concentration gradients of 100ng / μL, 10ng / μL, 1ng / μL, 100pg / μL, 10pg / μL, 1pg / μL, 100fg / μL, 10fg / μL, 1fg / μL, and then Perform PCR.
[0063] The total volume of the PCR reaction system is 25 μL, and the reaction system is: 12.5 μL of 2×Taq Master Mix, 1 μL of 10 μM upstream and downstream primers ZJSF / ZJSR, 9.5 μL of double distilled water.
[0064] The amplification reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes, followed by 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 30 seconds, and finally extension at 72°C for 3 minutes.
[0065] Take 7 μL of the amplification product, use 1% (mass / volume) agarose gel, add 100 μL (mass volume ratio) of Goldview I nucleic acid stain to 100 mL of agarose gel, electrophoresis at a voltage of 120 V for 20 minutes, and image on the gel Take pictures under the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com