Cuprous sulfide nano material for electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
A technology of cuprous sulfide and nanomaterials, which is applied in the field of nanomaterials and electrochemical sensing, can solve the problems of electrochemical sensors without cuprous sulfide nanomaterials, and achieve the effects of fast detection speed, convenient operation and low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Synthesis of Cuprous Sulfide Nanomaterials
[0034] Mix 2.50 mmol of ammonium diethyldithiocarbamate with 20 mL of dodecanethiol and 34 mL of oleic acid in a three-necked flask. solution in nitrogen (N 2 ) was heated to 110 ° C under flowing, and then a suspension composed of 2 mmol copper acetylacetonate and 3 mL oleic acid was injected rapidly. Then, the solution is rapidly heated to 180° C., and kept at this temperature for 10-30 minutes (it is necessary to ensure that the airtightness of the device is good before all reactions, and pass N 2 The apparatus was vented of air and all solutions used were anhydrous to avoid any possible oxidation). After the reaction, there will be Cu 2-x The solution of S nanocrystals was naturally cooled to 120° C., then taken out from the flask, and centrifuged at 20,000 rpm for 10 minutes. Discard the supernatant, dissolve the pellet in 18.4 mL of toluene and 56 mL of isopropanol, and then centrifuge at 20,000 rpm for 10 minutes. ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Cuprous sulfide modified electrode (Cu 2-x S-GC) preparation
[0037] First, the bare glassy carbon electrode (GC) was polished to a mirror surface with alumina powder (0.1 μm) and alumina powder (0.05 μm) on the suede in turn, rinsed with deionized water twice, rinsed with ethanol and ultrasonically washed for 1 min. Dry and cool for later use. A certain amount of synthesized Cu 2-x Material S (2 mg) was mixed with 50 μL chitosan (1 mg / mL) and 80 μL chloroform, and then 4.0 μL of the mixed solution was dropped on the surface of the treated optical glassy carbon electrode. After drying, the modified electrode was thoroughly rinsed with double distilled water. When not in use, the modified electrode was polished to a mirror surface with aluminum oxide powder on the suede, and then immersed in a phosphate buffer solution (pH7.0, 0.1mol L -1 ), stored at a constant temperature of 4°C.
Embodiment 3
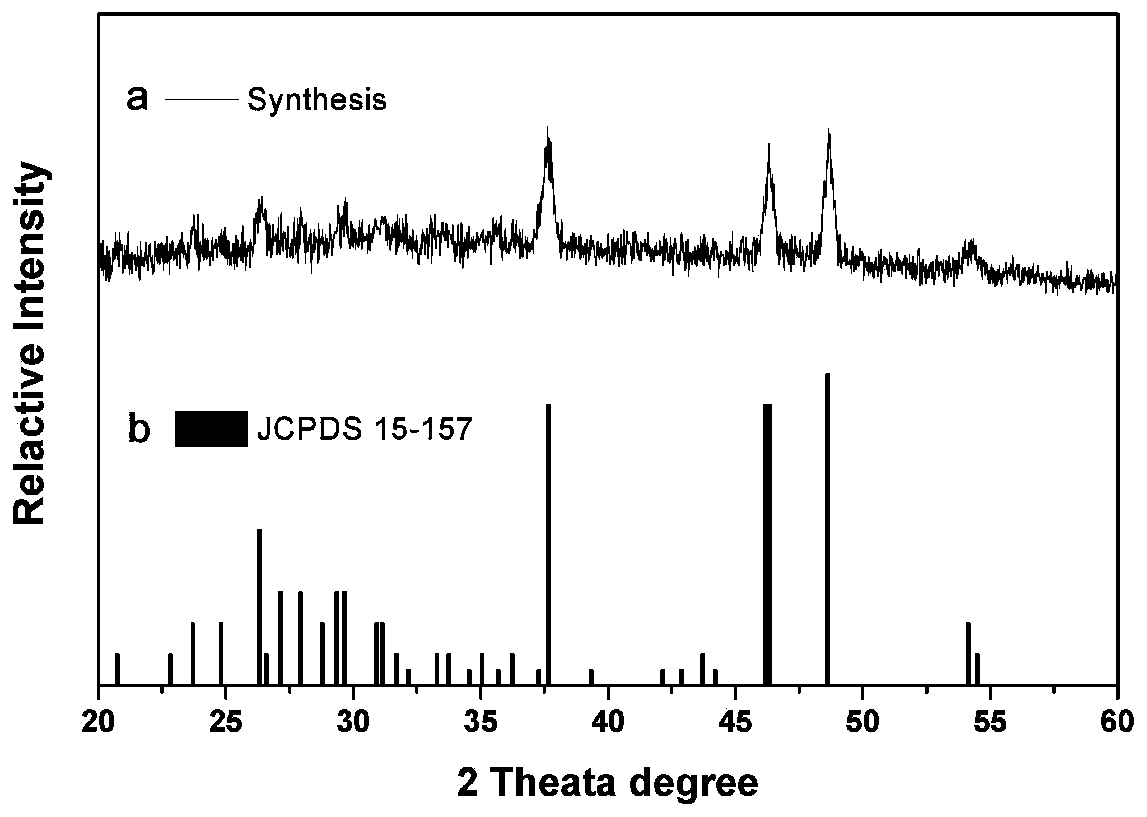
[0039]X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Spectrum Test
[0040] Cu 2-x S nanomaterials were synthesized by thermally injecting acetylacetone and ammonium diethyldithiocarbamate solutions in a mixed solution of dodecanethiol and oleic acid, and Cu with different particle sizes were prepared by controlling different reaction times 2-x S nanoparticles. In order to determine and analyze the phase of nanomaterials, X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used for characterization ( figure 1 ). The test results show that the material prepared by thermal injection is hexagonal chalcocite Cu 1.96 S (JCPDS15-157), the angles, peak heights, and peak shapes of the two peaks are basically the same, and the characteristic diffraction peaks (37.7°, 46.2°, 46.6°, 48.6°) basically overlap. Further comparison of Cu prepared at different synthesis times (10min, 20min and 30min) 2-x The half-width of the diffraction peak of S is stronger. It can be seen that the longer the reaction time, the smaller the half-widt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com