A kind of resource processing method of magnesium-containing raw material
A processing method and a resource-based technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of high cost, lack of calcium and magnesium resources, waste and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
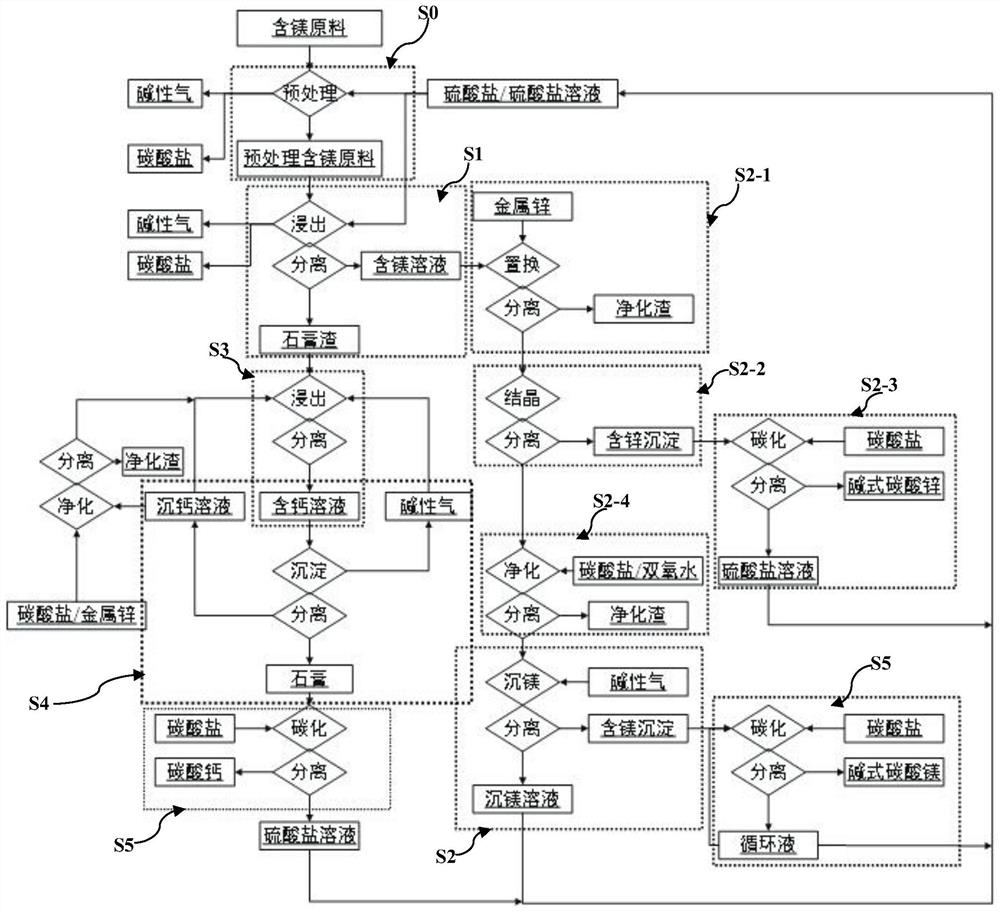
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] (1) Add 1kg of monoethanolamine, 0.25kg of threonine, and 0.2kg of phenylalanine to a 10L reaction kettle, set the volume to about 8.5L, add 1kg of dolomite (containing 12.7% of magnesium and 21.8% of calcium), and heat to 60°C, use sulfuric acid to adjust the pH to less than 4.0, react for 2 hours, filter, and wash with 1L of pure water to obtain 9L of filtrate and gypsum residue;
[0096] (2) transfer the obtained filtrate of step (1) into another reaction kettle, use sodium hydroxide water to adjust the pH value between 9.0-9.1, add 0.5kg of sodium carbonate, and filter to obtain calcium carbonate precipitation and filtrate;
[0097] (3) step (2) gained filtrate is transferred in another reactor, adds sodium carbonate 1.5kg, uses sodium hydroxide to maintain pH value between 9.7-9.9 during, reacts 5h, filters, obtains filtrate and basic magnesium carbonate precipitation;
[0098] (4) step (1) gained gypsum slag is transferred in another 15L reactor, adds 1kg magnesi...
Embodiment 2
[0102] (1) Mix 100g of magnesium smelting waste slag (4.5% magnesium and 50.1% calcium) with 100g ammonium sulfate solid, put it into a tube furnace, use argon to blow, and use two-stage 200ml water to absorb the tail gas. Pretreatment at ℃ for 10 hours to obtain 170g of pretreated magnesium smelting slag and 200ml of ammonia water (ammonia content 11.5%);
[0103] (2) Prepare 1L of 0.1mol / L magnesium sulfate and 0.5mol / L ammonium sulfate solution, add the pretreated magnesium smelting slag obtained in step (1) into the solution, heat to 100°C, react for 0.5h, and filter to obtain 0.95L filtrate and gypsum residue;
[0104] (3) Transfer the filtrate obtained in step (2) into another beaker, add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 11.1-11.2, maintain the reaction temperature at 95°C, and filter for 2 hours to obtain magnesium hydroxide precipitate and sulfate filtrate .
[0105] (4) The magnesium hydroxide precipitate obtained in step (3) is transferred to a beaker, 10...
Embodiment 3
[0109] (1) Add 55.6g of ammonium sulfate and 20g of magnesium sulfate to a 1L beaker, set the volume to 800ml, add 400g of dirty acid neutralization slag (containing 10% zinc, 5.5% magnesium, and 10% calcium), start stirring, and heat to 120 ℃, react for 2 hours, control the reaction pressure to 0.1Mpa, and filter to obtain 700ml of filtrate and gypsum slag;
[0110] (2) Add 10g of zinc powder to the filtrate gained in step (1), react for 5h, and filter to obtain purified residue and filtrate;
[0111] (3) Add the filtrate obtained in step (2) into another beaker, heat and evaporate to 400ml, cool to 0°C, and filter to obtain ammonium zinc sulfate solid and filtrate;
[0112] (4) Transfer the zinc ammonium sulfate solid obtained in step (3) into another beaker, add 500ml of water, use ammonia water to adjust the pH value between 8.0-8.2, pass through carbon dioxide at 100ml / min for 2 hours, filter, and obtain the basic formula Zinc carbonate products;
[0113] (5) The filtra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com