Gasification slag magnesium-nickel alloy hydrogen storage composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material and gasification slag technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrogen, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, unsuitable application conditions for dissociation temperature and speed, and low reaction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The raw materials are as shown in Table 1:
[0033] Table 1
[0034] raw material purity(%) Average particle size (μm) Average pore size (μm) mass (g) Magnesium powder 99.8 5 - 850 nickel powder 99.8 4 - 50 Gasification slag 99 80 7 100
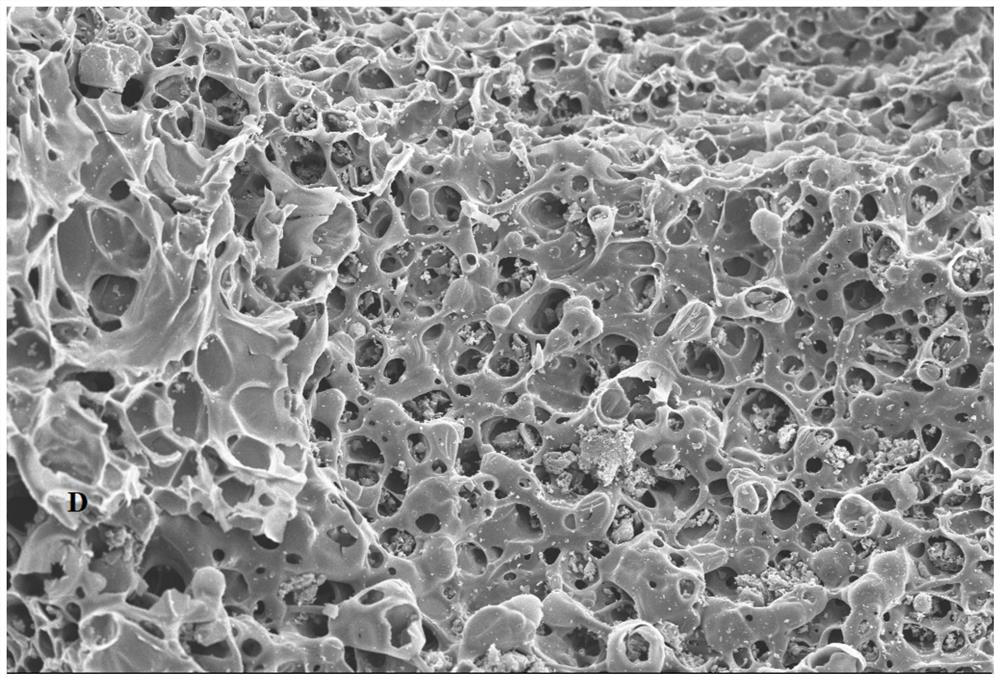
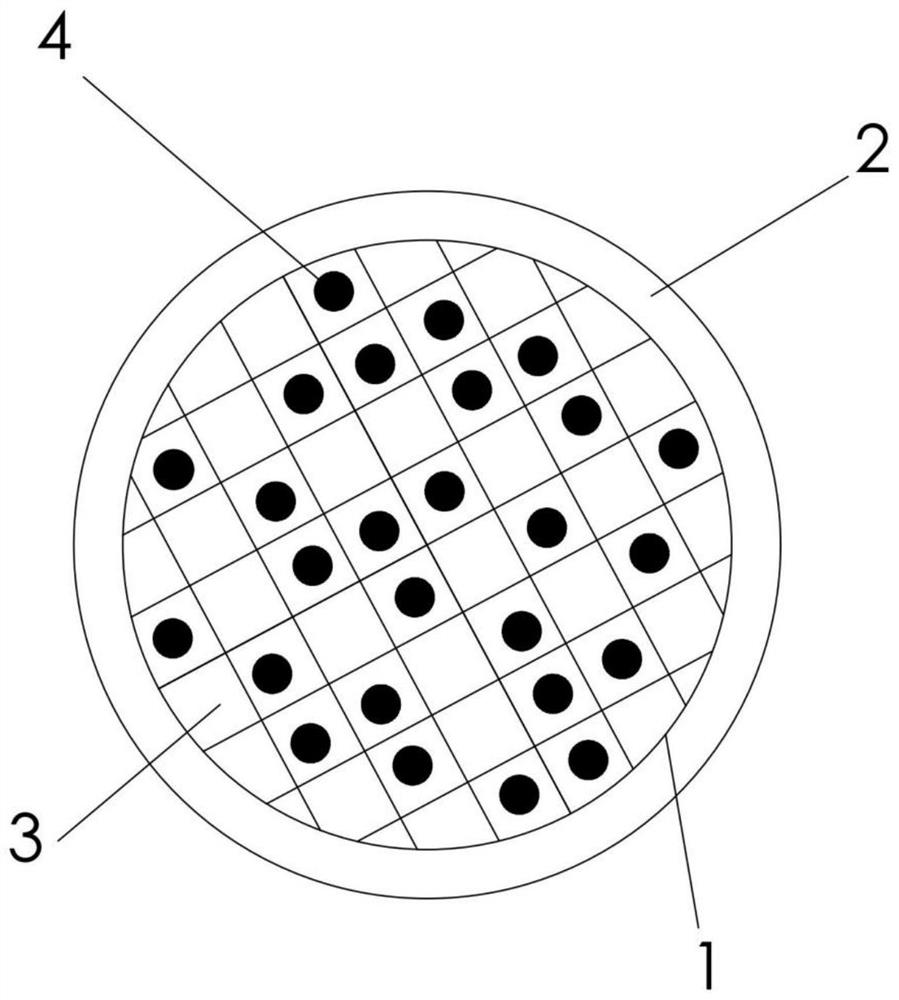
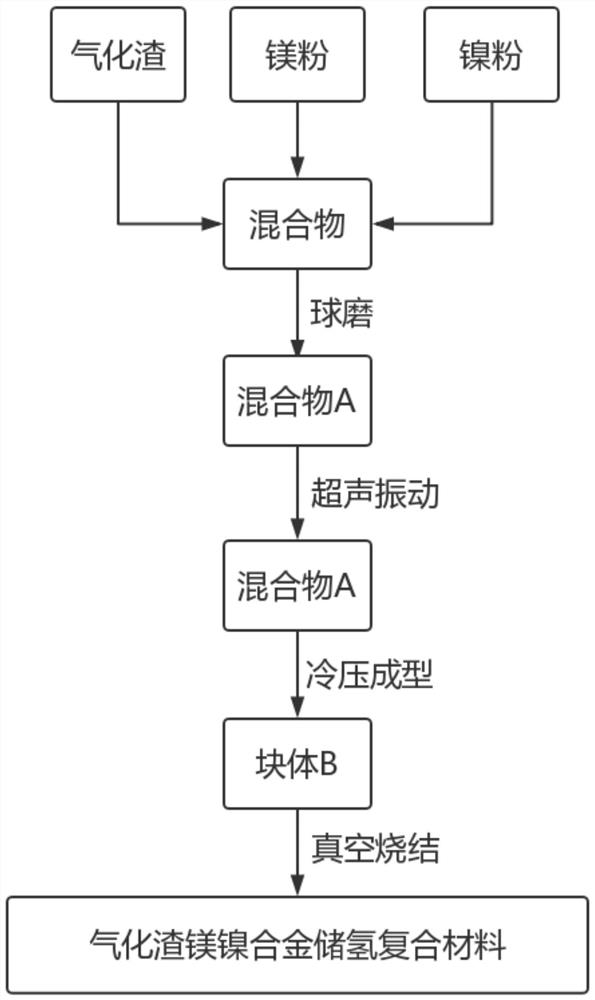
[0035] The raw materials in Table 1 were uniformly mixed by ball milling, the ball milling time was 4h, and the mixture A was obtained by ultrasonic vibration, and the mixture A was ultrasonically vibrated for 0.5h, and then the mixture A was pressed into a block B, and B was placed in a graphite crucible ; Put the graphite crucible into the vacuum atmosphere sintering furnace, and the vacuum pressure is 1.0×10 -1 Pa; 0.5MPa inert gas atmosphere, sintering at 550°C for 1h, and after cooling, a gasification slag magnesium-nickel alloy hydrogen storage composite material was obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0037] The raw materials are as shown in Table 2:
[0038] Table 2
[0039] raw material purity(%) Average particle size (μm) Average pore size (μm) mass (g) Magnesium powder 99.8 4 - 800 nickel powder 99.8 3 - 60 Gasification slag 99 100 6 140
[0040] The raw materials in Table 2 were uniformly mixed by ball milling, the ball milling time was 5h, and the mixture A was obtained by ultrasonic vibration, and the mixture A was ultrasonically vibrated for 0.8h, and then the mixture A was pressed into a block B, and B was placed in a graphite crucible ;Put the graphite crucible into the vacuum atmosphere sintering furnace, and vacuum the pressure to 6.0×10 -2 Pa; 0.9MPa inert gas atmosphere, sintering at 575°C for 1.6h, and cooling to obtain gasification slag magnesium-nickel alloy hydrogen storage composite material.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The raw materials are as shown in Table 3:
[0043] table 3
[0044] raw material purity(%) Average particle size (μm) Average pore size (μm) mass (g) Magnesium powder 99.8 3 - 740 nickel powder 99.8 2 - 70 Gasification slag 99 130 5 190
[0045] The raw materials in Table 3 were uniformly mixed by ball milling, the ball milling time was 6 hours, and the mixture A was obtained by ultrasonic vibration, and the mixture A was ultrasonically vibrated for 1 hour, and then the mixture A was pressed into a block B, and B was placed in a graphite crucible; Put the graphite crucible into the vacuum atmosphere sintering furnace, and the vacuum pressure is 5.5×10 -2 Pa; 1.1MPa inert gas atmosphere, sintered at 600°C for 2h, and obtained vaporized slag magnesium-nickel alloy hydrogen storage composite material after cooling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com