Paenibacillus polymyxa DX32 and application thereof in inhibiting pathogenic fungi of pestalotiopsis plants
A technology of Paenibacillus polymyxa and Pseudomonas spp., applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of no inhibition of Paenibacillus polymyxa, and achieve a good inhibitory effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
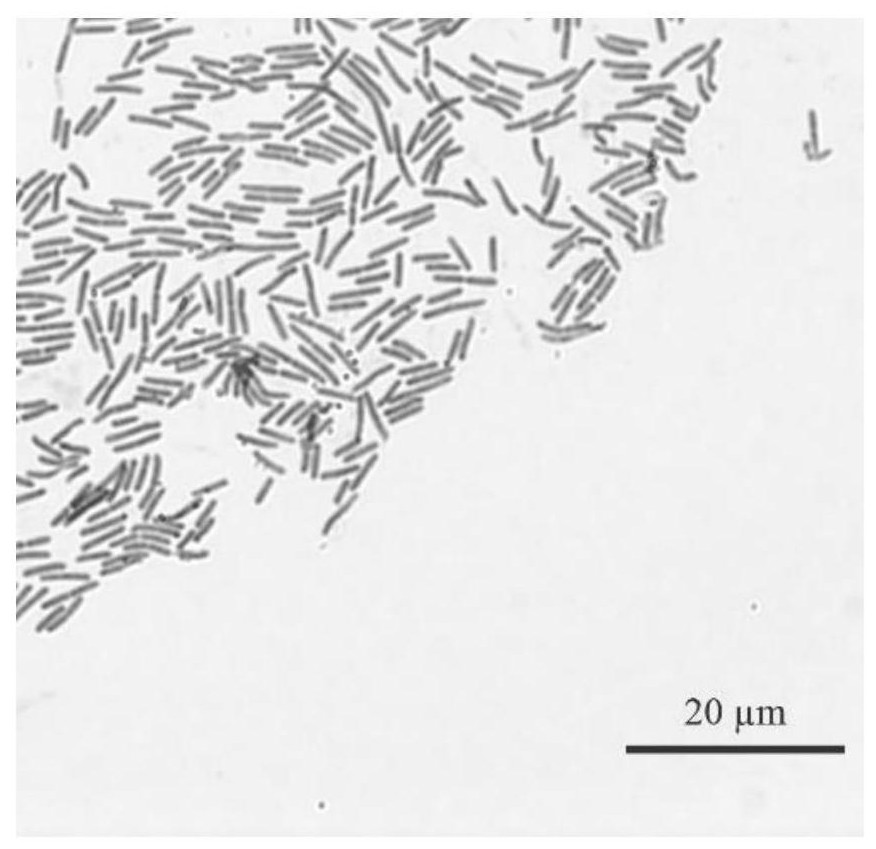
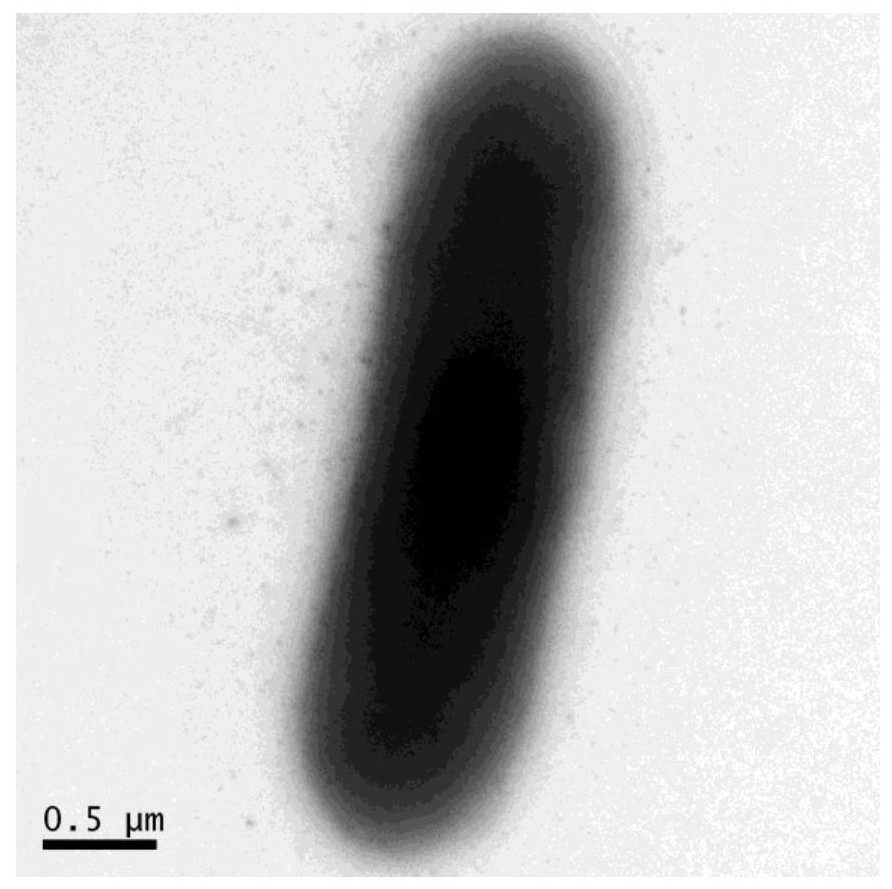
[0021] This example illustrates the isolation and characterization of Paenibacillus polymyxa DX32.
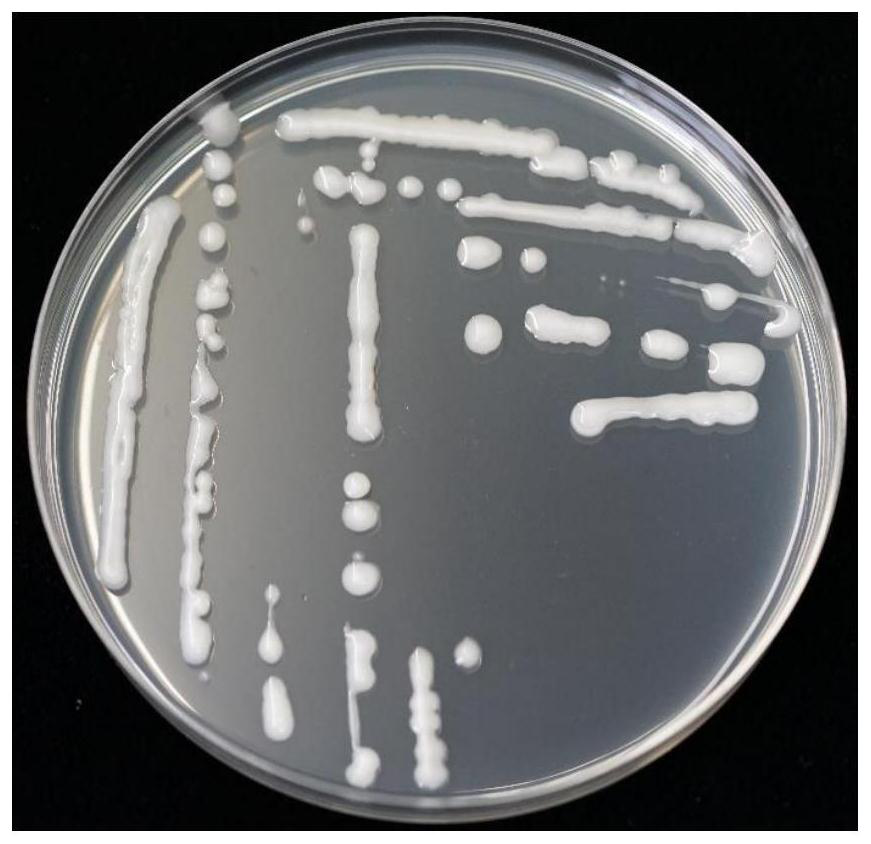
[0022] In the Fritillaria plantation in Daxi Village, Pan'an County, Zhejiang Province, non-susceptible plants were selected from the high-incidence area of Botrytis cinerea, uprooted and put into sampling paper bags. The paper bags were marked and brought back to the laboratory for isolation of plant endophytic fungi. Pick the fritillaria leaves, rinse them with sterile water, drain them, put them in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 3 minutes, take them out, wash them with sterile water for 3 times, and then dry them in a sterile environment. After 5 hours, dry the fritillary leaves Cut the leaves with sterilized scissors, about 2mm×2mm in size, pick them up on NA solid medium plates with tweezers, and cultivate them in the dark at 28°C in an incubator. After the colony grows, use an inoculation loop to dip the bacterial colony onto a new NA solid medium plate for streak ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] This example illustrates the determination of the physiological and biochemical characteristics of Paenibacillus polymyxa DX32.
[0027] Use BIOLOG GENIII (operated according to the kit instructions) to measure the physiological and biochemical characteristics indicators such as the utilization of the only carbon source. strain DX 32 See Table 1 for the sole carbon source utilization and chemical substance tolerance of BIOLOG GENIII plates.
[0028] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of the DX32 strain, such as the utilization of the only carbon source, determined by the BIOLOG GENIII plate
[0029]
[0030]
[0031] Note: +, positive; -, negative; w, weakly positive.
[0032] As can be seen from the results in Table 1, the antagonistic strain DX of the present invention 32Dextran, D-maltose, D-trehalose, D-cellobiose, gentiobiose, sucrose, D-turanose, stachyose, D- raffinose, α-D-lactose, D-melibiose, β-Methyl-D glucoside, D-salicin, N-Acet...
Embodiment 3
[0034] This example illustrates the confrontation growth test between Paenibacillus polymyxa DX32 and the common pathogenic fungus of the genus Discotrichum spp.
[0035] Adopt confrontation growth method to measure the antagonistic strain DX of the present invention 32 Inhibitory effect on the common pathogenic fungus of the genus Discoides spp. Use a hole puncher to take a 5mm cake of the tested strain and place it on the 1 / 3 of the diameter of the PDA plate, pick DX 32 A single colony of the bacterial strain reaches the symmetrical 1 / 3 of the PDA plate containing the bacterial cake, and the DX is measured after 5 days of constant temperature cultivation at 28°C 32 The size of the inhibition zone between the test strain and the colony, and record the data, no DX 32 The PDA plate containing bacteria cake was used as blank control.
[0036] Table 2 bacterial strain DX32 of the present invention and the bacteriostatic zone size (mm) of confrontation growth of common Discotri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com