Polypeptide tag and application thereof in in-vitro protein synthesis
A technology of polypeptide labeling and target protein, which is applied in the field of polypeptide labeling and its application in in vitro protein synthesis. It can solve the problems of interfering with the structure and function of the target protein, reducing the efficiency of protein synthesis, and large molecules, so as to increase the expression of the target protein. , small molecular weight and short polypeptide chain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0128] As an embodiment, the source of magnesium ions is a magnesium salt selected from the group consisting of one of magnesium glutamate, magnesium acetate or a combination thereof.
[0129] As an embodiment, the amino acid mixture includes 20 natural amino acids, as well as other unnatural amino acids.
[0130] As an embodiment, the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is 200-12000Da, preferably 400, 600, 800, 2000, 4000, 8000Da. Measured by weight average molecular weight.
[0131] As an embodiment, the energy supply system is selected from the group consisting of one or a combination of glucose, maltose, trehalose, maltodextrin, starch dextrin, phosphocreatine and phosphokinase; preferably, 320 mM malt Dextrin, 6% trehalose.
[0132] As an embodiment, the cell extract is selected from: eukaryotic cells, yeast cells, Kluyveromyces cells, preferably, Kluyveromyces lactis cells. More preferably, it is a K. lactis cell with T7 RNA polymerase integrated into its genome, ...
Embodiment 1
[0135] Example 1 Determining the sequence of the polypeptide tag
[0136] 1.1 The source and determination of the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide tag: there have been public literature reports, and researchers have confirmed through experiments that the first 11 amino acid residues in the N-terminal half-domain of Dunaliella carbonic anhydrase (dca) (see SEQID for the amino acid sequence of NT11 No.: 9; its DNA sequence: see SEQ ID No.: 18) linked to the N-terminal of foreign protein for fusion expression can increase the translation level of YFP (yellow fluorescent protein) and other proteins in BL21(DE3) E.coli cells (Thi Khoa My Nguyen, et al. The NT11, a novel fusion tag for enhancing protein expression in Escherichia coli. 2019; 103(5):2205–2216.). In this example, the amino acid sequence of NT11 is partially deleted or randomly point-mutated, and then the amino acid sequence that can significantly improve the expression of the foreign protein is screened through e...
Embodiment 2
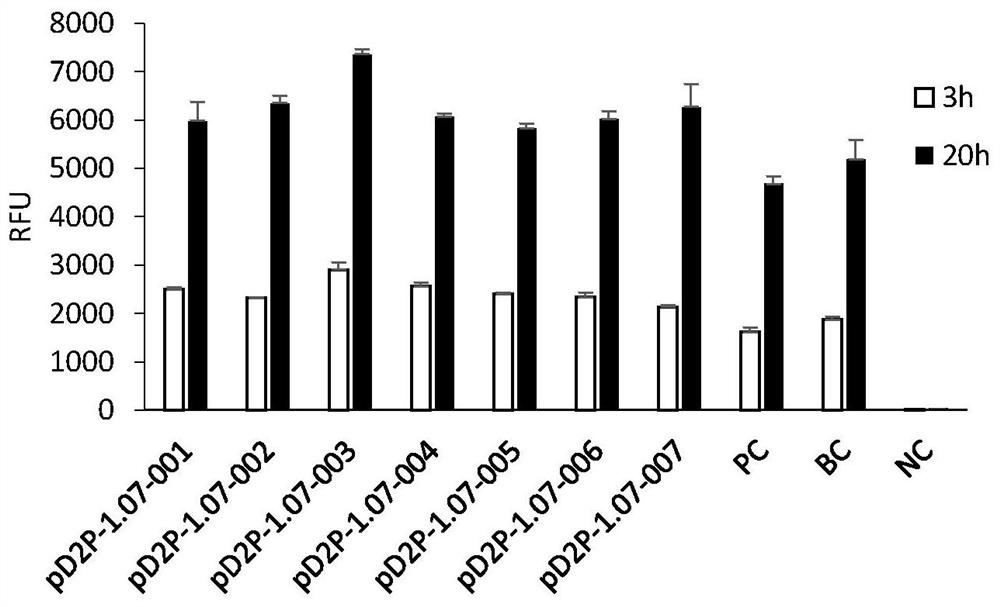
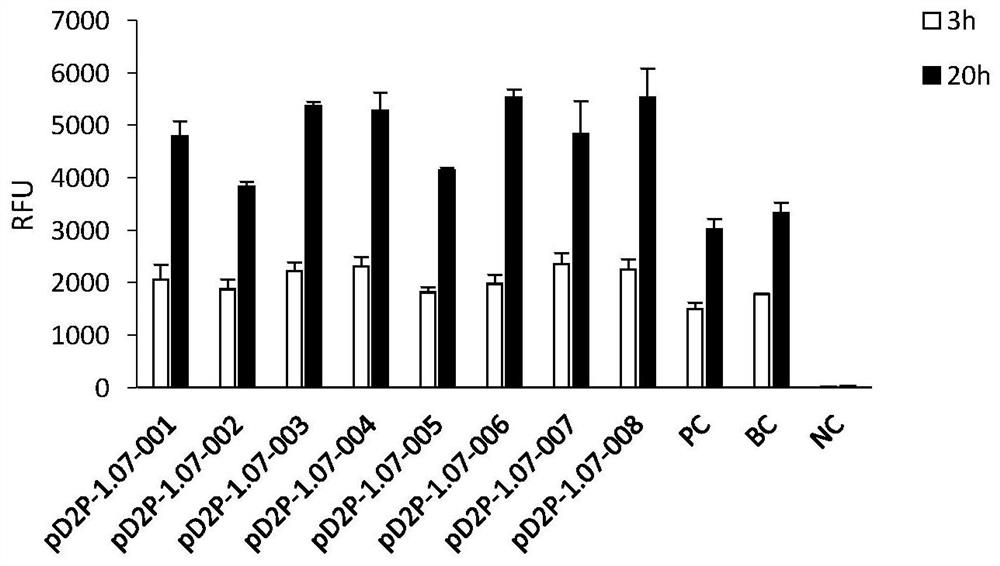
[0149] Example 2 Plasmid construction of eGFP with N-terminal fusion polypeptide tag
[0150] Plasmid construction: Use a pair of primers to connect the coding gene of the polypeptide tag to the N-terminal coding sequence position of eGFP in the pD2P-eGFP plasmid by using a seamless cloning method. For the gene structure, refer to figure 1 . The names of nine of them are: pD2P-1.07-(001-008) and PC (see Table 1). The sequences of the amplification primers of the nine plasmids are as follows: SEQ ID No.: 19-36.
[0151] The specific construction process is as follows:
[0152] Design a pair of primers according to the seamless cloning technique (see Table 2, wherein, the corresponding forward primer with the suffix of PF, and the corresponding reverse primer with the suffix of PR, were respectively based on the above nine plasmids pD2P-1.07-(001-008 ) and PC as the template for PCR amplification, and 5 μL of the amplified product was identified by 1% agarose electrophoresis;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com