Industrial applications of plant cell extracts comprising sod enzymes of extremophilic micro-organisms
A plant cell and extract technology, applied in plant cells, medical preparations containing active ingredients, applications, etc., can solve problems such as pollution, restricted use, anti-UV and poor temperature stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in tomato cell cultures and characterization of cell-derived extracts belonging to the microorganism Sulfolobus solfataricus.
[0097] To express the gene encoding superoxide dismutase (SsSOD) (SEQ ID NO 1) of the extremophile Sulfolobus solfataricus in tomato cells (MicroTom cell line), the binary vector pBI121 modified with the above gene was transferred to the root Agrobacterium carcinoma (LBA4404 trunk) was used for gene transformation of tomato cotyledon (S. lycopersicum).
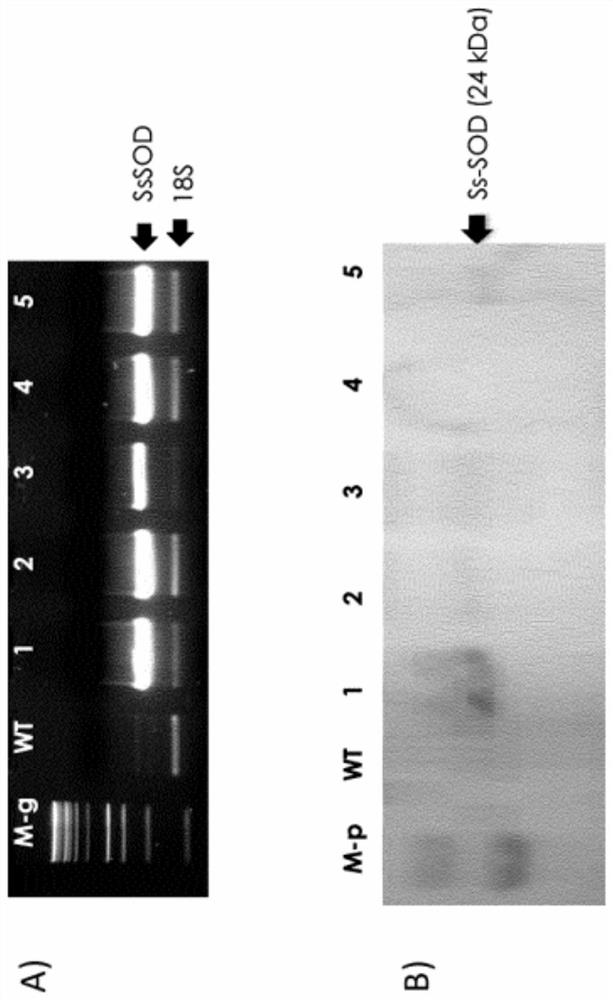
[0098] Infected plant tissue is then transferred to a specific medium for callus induction containing the antibiotic kanamycin for selection of transformed cells. After approximately 6 weeks from gene transformation, abundant calli were regenerated, isolated from remaining plant tissue, transferred to fresh medium, and analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. figure 1 A shows the analysis involving some SsSOD expressing cell lines. Amplification products ...
Embodiment 2
[0159] Expression of SOD in plant cell cultures and characterization of cell-derived extracts belonging to the microbial thermophilic spring-forming archaea.
[0160] Tomato was genetically transformed with the thermophilic springtime archaea SOD (ApSOD) (SEQ ID NO 2) using Agrobacterium tumefanciens as described in Example 1 . Four transformed cell lines were analyzed by RT-PCR using specific primers for ApSOD, and the amplification products were compared with amplified 18S ribosomal RNA obtained in the same reaction (multiplex PCR) ( Figure 4 A). All clones analyzed showed high levels of SOD expression and, as expected, no amplified bands were found in unprocessed tomato cells (wild type, WT) used as a control.
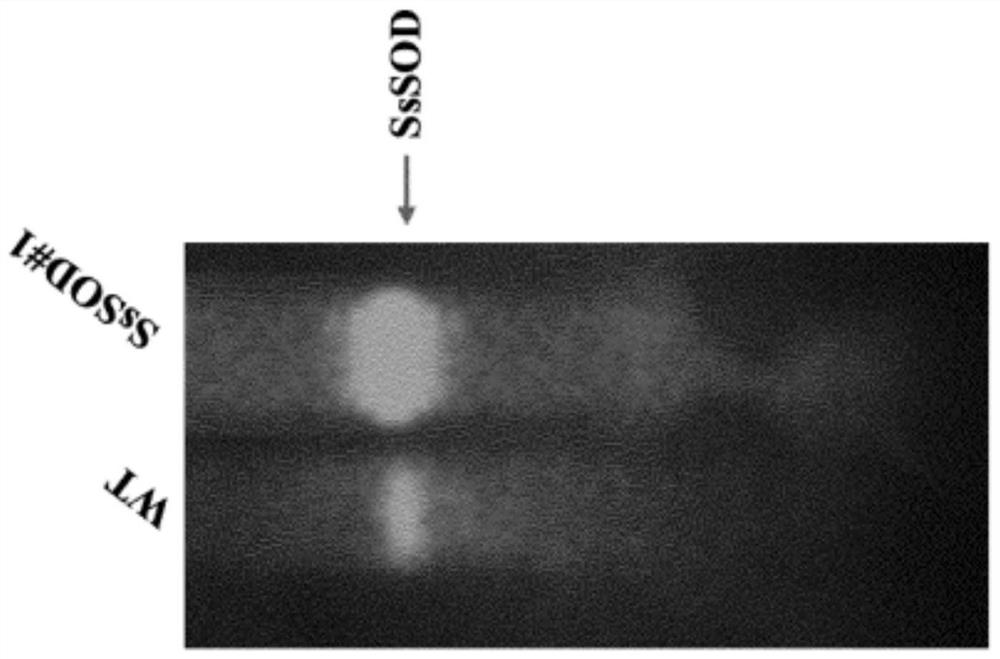
[0161] Western blot analysis indicated that the transgenic cell lines contained detectable amounts of ApSOD protein, whereas in untransformed cell lines, slight hybridization bands were barely visible due to the high similarity between endogenous tomato SOD and ex...
Embodiment 3
[0184] Expression of SOD belonging to the microorganism Deinococcus radiodurans in plant cell cultures and characterization of cell-derived extracts.
[0185] Stable transfer of Deinococcus radiodurans SOD (DrSOD) (SEQ ID NO 3) to tomato by Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
[0186] Calli selected on selective media were analyzed by RT-PCR using specific primers for the SOD transfer sequence. Figure 7 A shows RT-PCR of 5 transgenic cell lines. Amplification products obtained using specific oligonucleotides directed against the DrSOD sequence were normalized to amplified 18S ribosomal RNA obtained in the same reaction (multiplex PCR). All clones analyzed showed high levels of SOD expression. The cell lines were then analyzed in Western blot as Figure 7 In B, the transgenic tomato cell line expresses DrSOD at high levels, whereas a slight band corresponding to endogenous SOD is present in WT cell extracts.
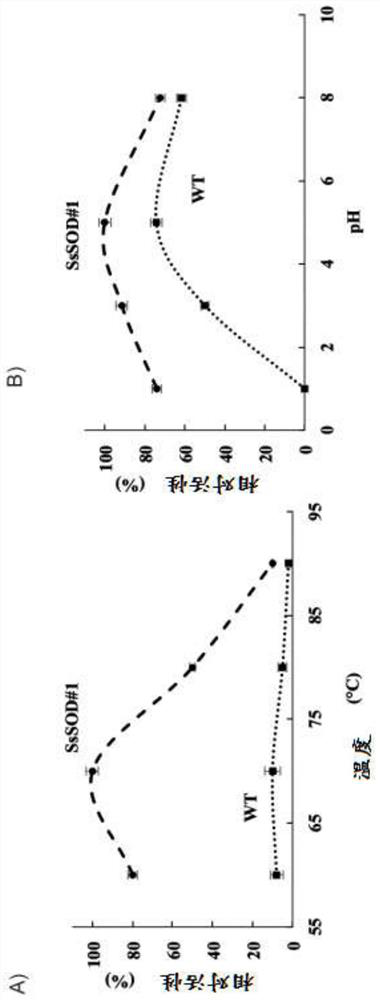
[0187] Cell line 3 extracts containing DrSOD were used to characterize t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com