An improved compound microbial inoculant and its application in increasing the yield of Angelica sinensis
A technology of compound microbial agent and microbial fertilizer, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, chemicals for biological control, etc., can solve problems such as urea burning seedlings and ammonium salt poisoning that have not been considered, and promote the absorption of rich Accumulate, promote the conversion into ammonium nitrogen, enhance the effect of activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1 Determination of microbial phosphorus solution, nitrogen fixation and nitrification
[0044] 1. Qualitative detection of phosphorus dissolving ability
[0045] Different strains were inoculated on NBRIP inorganic phosphorus solid medium, and cultured at a constant temperature of 28 °C for 2 to 5 days. effect.
[0046] 2. Quantitative detection of nitrogen fixation activity
[0047] Take 5ml of purified bacterial liquid and inoculate it into sterilized 50ml of Axubi nitrogen-free medium, 200r·min -1 , 30 ℃ shaking culture for 72h, measure the turbidity OD 600 .
[0048] Determination of nitrogenase activity of the strain by acetylene reduction method: transfer 5ml of the above fresh bacterial liquid into a 20ml headspace bottle and seal it, extract 2ml of gas from the bottle, inject an equal volume of acetylene, continue to cultivate for 24h, use a gas chromatograph The amount of ethylene produced was detected. Gas chromatographic analysis conditions: ...
Embodiment 2
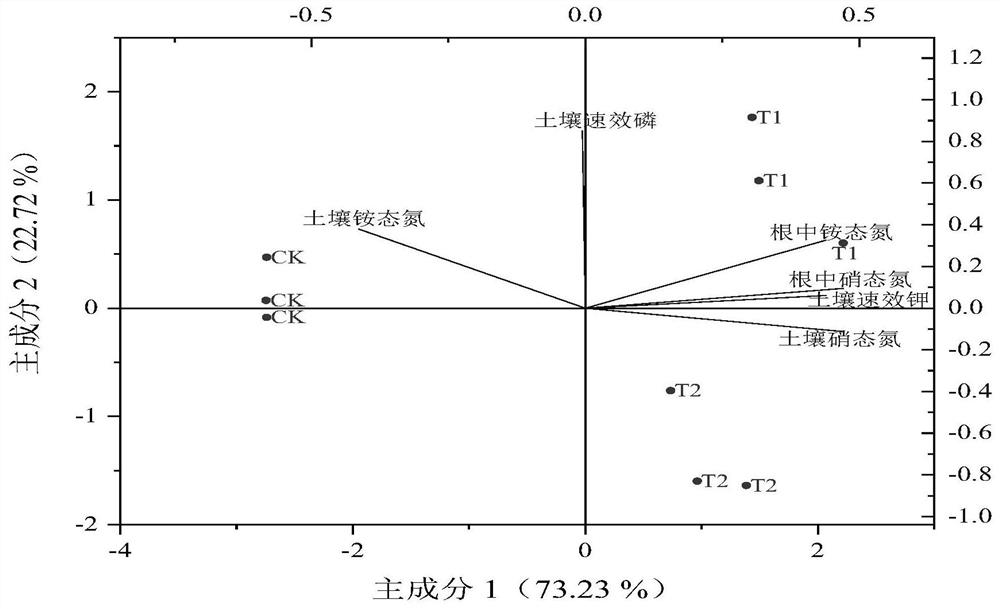
[0058] The influence of embodiment 2 different treatments on the yield-related indexes of Angelica sinensis
[0059] After harvesting, the number of adventitious roots was calculated by conventional methods, the diameter, head length and body length of Angelica were measured with vernier calipers, and the fresh weight of each plant was weighed by electronic scales.
[0060] The results are shown in Table 2. Compared with CK, the adventitious root number, reed head diameter, reed head length, body length and average fresh weight of angelica were basically unchanged after treatment with CBS4 single bacteria. The number of adventitious roots, diameter of reed head, reed head length, body length and average fresh weight per plant all increased. Compared with the CK group, the number of adventitious roots, the diameter of the head, the length of the head, the length of the head, and the average fresh weight per plant increased by 14.30% and 19.74%, respectively, after being treated...
Embodiment 3
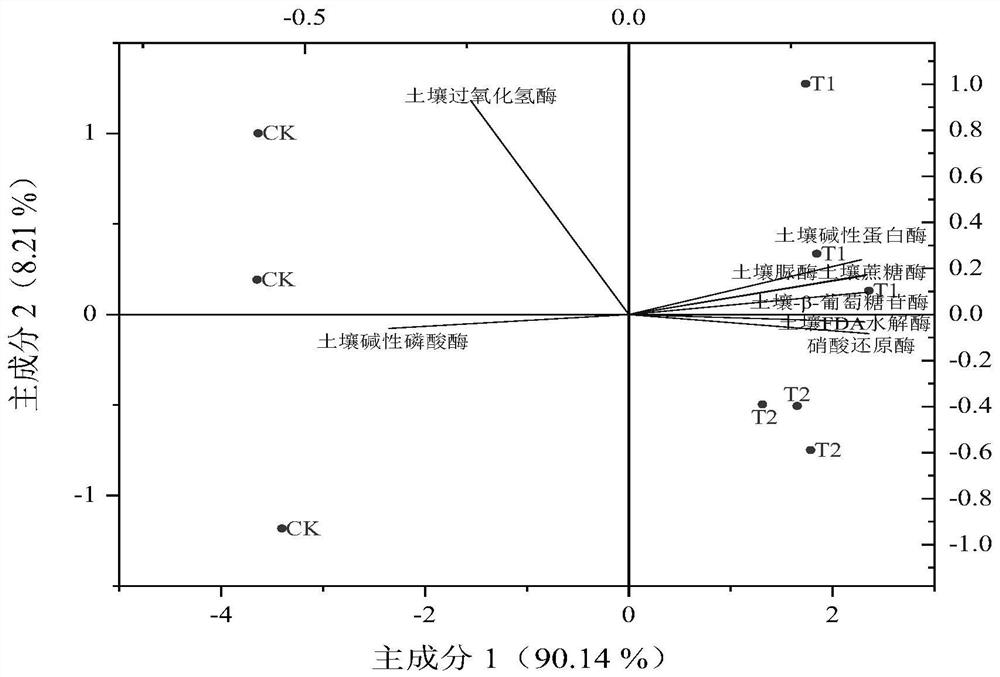
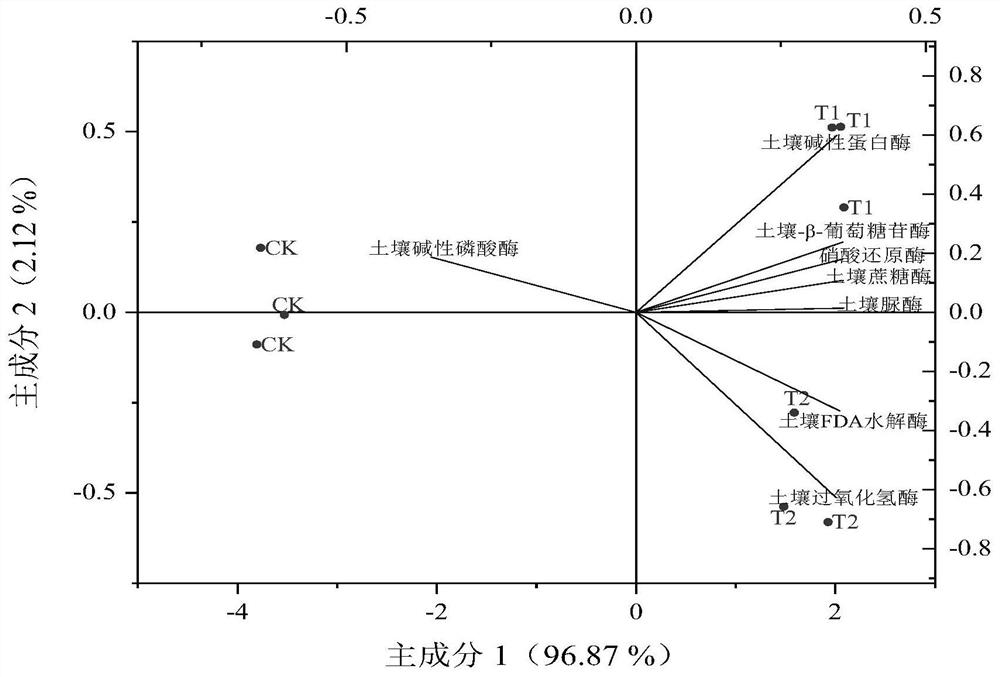
[0064] Embodiment 3 Angelica rhizosphere soil enzyme activity assay
[0065] Determination of rhizosphere soil urease (S-UE), soil sucrase (S-SC), soil FDA hydrolase, soil β-glucosidase (S-β-GC), soil alkalinity at different stages of Angelica sinensis according to the method described in the kit Protease (S-ALPT), soil alkaline phosphatase activity (S-AKP / ALP), soil catalase (S-CAT) activity, each sample was repeated three times, and the average value was calculated.
[0066]The effects of different treatments on rhizosphere soil enzyme activities are shown in Table 3. Compared with the CK group, the treatment of T1 and T2 compound inoculants (S2 and S3 periods) all increased the levels of FDA hydrolase, soil invertase, soil-β-glucosidase, soil urease, soil alkaline protease in the rhizosphere soil of Angelica sinensis. The results showed that the two compound inoculants could improve the microbial activity of the rhizosphere soil and the transformation ability of organic ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com