Bowel-relaxing oral liquid and preparation method thereof
An oral liquid, weight percentage technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of easy oxidation, inconvenience in use, difficulty in developing liquid preparations, etc., and achieve the effects of improving safety, avoiding irritation to the intestines, and being beneficial to intestinal health.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1, the preparation of laxative oral liquid
[0030] The preparation of the laxative oral liquid of Experimental Example 1-10 and Comparative Example 1-3 includes the following steps:
[0031] (1) Dissolution: According to the ratio shown in Table 1, weigh purified water and each component, and stir and dissolve at room temperature.
[0032] (2) Filling.
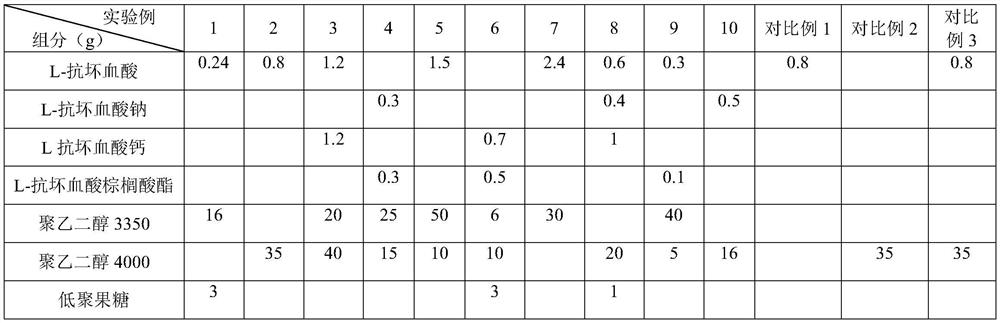
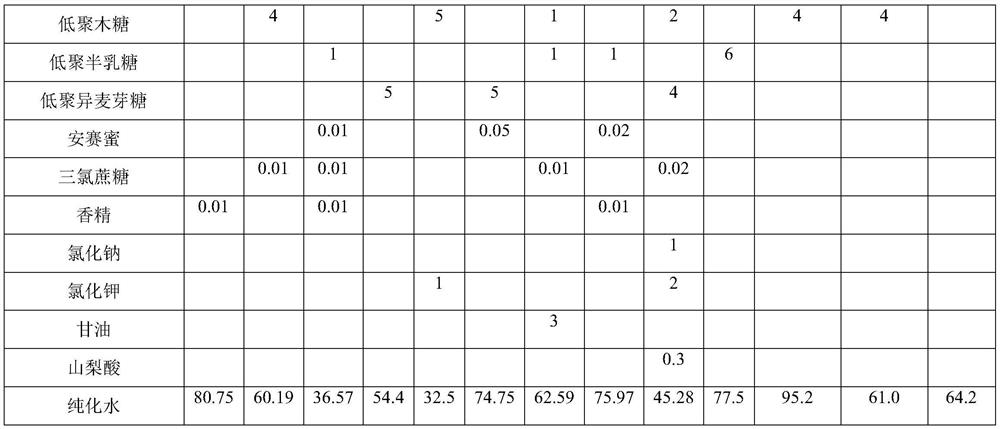
[0033] Table 1 Experimental example and prescription of comparative example
[0034]
[0035]
Embodiment 2
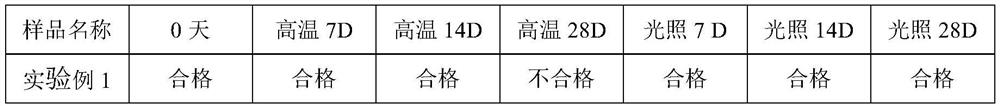
[0036] Example 2. Stability test
[0037] The ascorbic acid component is easily oxidized. In order to verify and test the stability of the oral liquid of the present invention and the ascorbic acid component, the following experiments were carried out.
[0038] 1. Detection method
[0039] Test samples: Experimental Examples 1-10, Comparative Examples 1 and 3.
[0040] Test conditions: high temperature (60℃), light (4500±500Lux).
[0041] Sampling time: 0 days, 7 days, 14 days, 28 days
[0042] Detection indicators / standards:
[0043] Solution color: Compared with the same volume of yellow No. 4 standard colorimetric solution, it should not be darker.
[0044] Determination method of ascorbic acid component content (in L-ascorbic acid): refer to the content detection method of vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) contained in the 2020 edition of the "Chinese Pharmacopoeia", and use the iodine titration method to determine.
[0045]Ascorbic acid content standard: 90.0-110.0%.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3, antibacterial efficacy test
[0055] In order to detect and verify the antiseptic and bacteriostatic efficacy of the oral liquid of the present invention, the following experiments were carried out.
[0056] 1. Detection method
[0057] Test samples: Experimental Examples 1-10.
[0058] Test strains: Candida albicans, Aspergillus niger, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli.
[0059] The detection standard is detected according to the standards and methods of the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia: bacteria: 14 days, the reduced lg value is >3, and the reduced lg value of 28 days is ≤0.5 compared with 14 days. Fungi: 14 days, the reduced lg value > 1, 28 days compared with 14 days, the reduced lg value ≤ 0.5.
[0060] 2. Experimental results
[0061] The antibacterial efficacy test results of the laxative oral liquids of Experimental Examples 1-10 are shown in Table 4-8. ①, ②, and ③ in the table represent the lg value ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com