Plant mangrove-associated fungus Culvularia lunata and a simple and efficient method of obtaining high yield of pure mannitol from the same
a technology of plant mangroves and fungi, applied in the field of plant mangrove-associated fungus cu, can solve the problems of relatively high manufacture cost of mannitol, unsatisfactory prior art biotechnical process for the conversion of sugar to mannitol, and high cost of hydrogenated mixtures, and achieves low cost and easy isolation and culture.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example-1
[0109] The leaves from the mangrove plant, Acanthus illicifolius was collected from Sinquerim, Goa coast, India. This fungal culture inhabit Acanthus illicifolius without causing apparent harm to the host. This fungus was isolated from healthy, young leaves where symptoms of fungal infection could not be detected.
[0110] After collection of fresh young leaves of Acanthus, they were transferred to the laboratory in sterile polyethylene bags. The leaves were rinsed with sterile filtered seawater to remove adhered particles and detritus material. The leaves were next kept in a sterile culture chamber for two weeks. At the end of two weeks, the leaves were cut with the help of a sterile scalpel and the pieces were placed on PDA plates. Individual colony was picked aseptically and transferred repeatedly on PDA plates to obtain a pure culture.
example-2
[0111] The isolated culture was designated as Curvularia lunata, NIO-FM.sub.1E#001. Colonies of NIO-FM.sub.1E #001 are fast growing, brown to blackish brown with a black reverse. Conidia are pale brown with three or more traverse septa and are formed apically through a pore (poroconidia) in a sympodially elongated geniculate conidiophore. Conidia are cylindrical or slightly curved, with one of the central cells being larger and darker.
[0112] The purified culture was grown on PDA slants for 7 days. Plugs of agar supporting mycelial growth were cut and transferred aseptically to a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 25 ml potato dextrose broth (HiMedia Laboratories Ltd.) prepared in seawater:distilled water (1:1). The carbon source in this broth was potato starch 4 g / l and dextrose 20 g / l. Flasks were kept under shaker conditions between 28-30.degree. C. for 4-5 days. Subculture from the above flask was aseptically transferred to 5 litre flasks containing 1 litre of the above-mentioned...
example-3
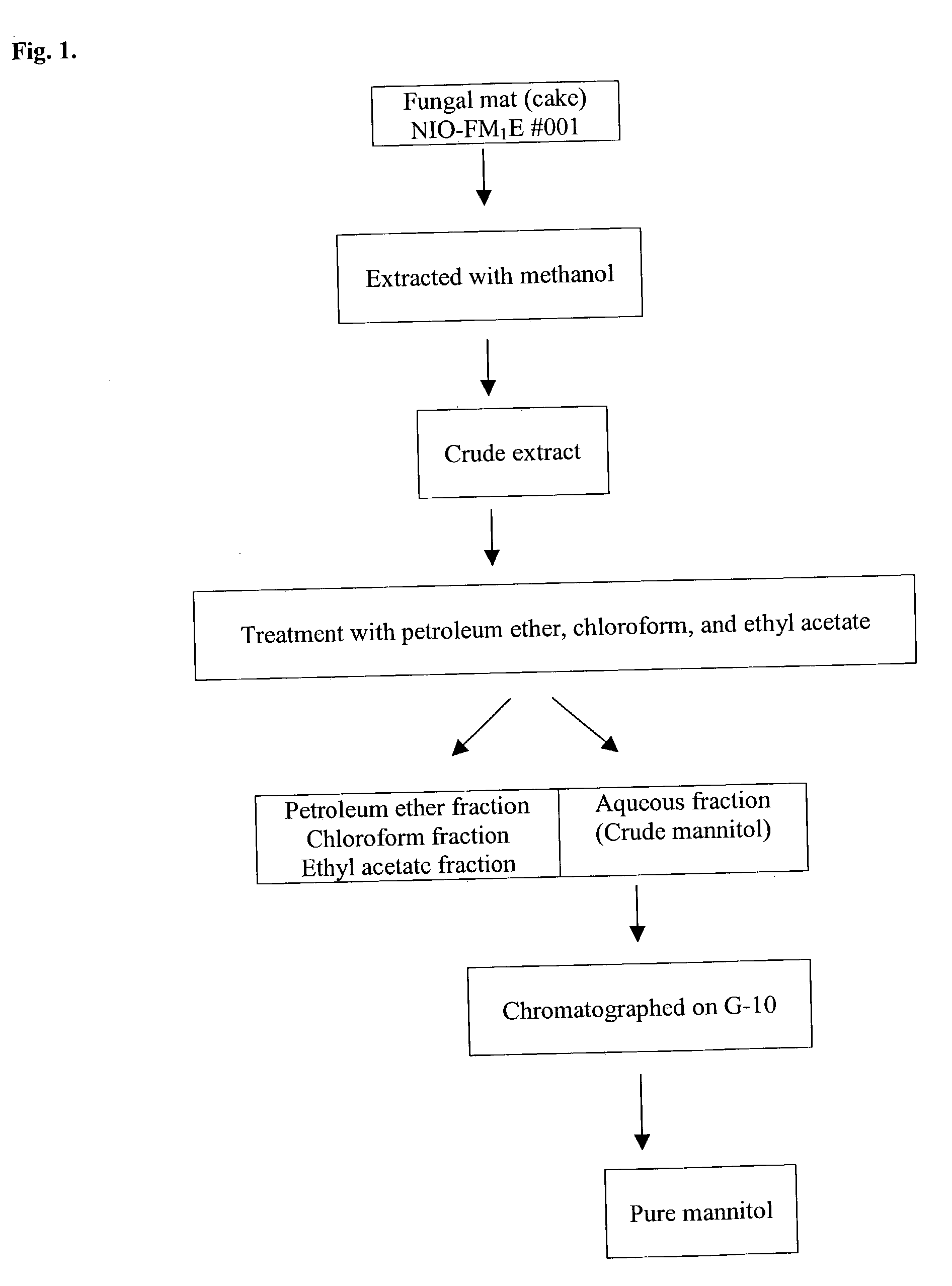
[0113] At the end of the incubation period, mycelia were recovered by filtration and dried in a lyophilizer to determine biomass weight. Dry fungal mat (cake) was extracted with methanol several times with repeated sonication of the cake for cell lysis. The filtrate thus obtained was concentrated to free it from the organic solvent under vacuum evaporation. This resulted in the crude extract of the sample. The crude extract was treated successively with solvents of increasing polarity like petroleum ether, chloroform and ethyl acetate to separate the petroleum ether fraction, chloroform fraction, and ethyl acetate fraction respectively. The last aqueous fraction contained the sugar alcohol as white powder, which constituted about 70% of the total crude extract.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com