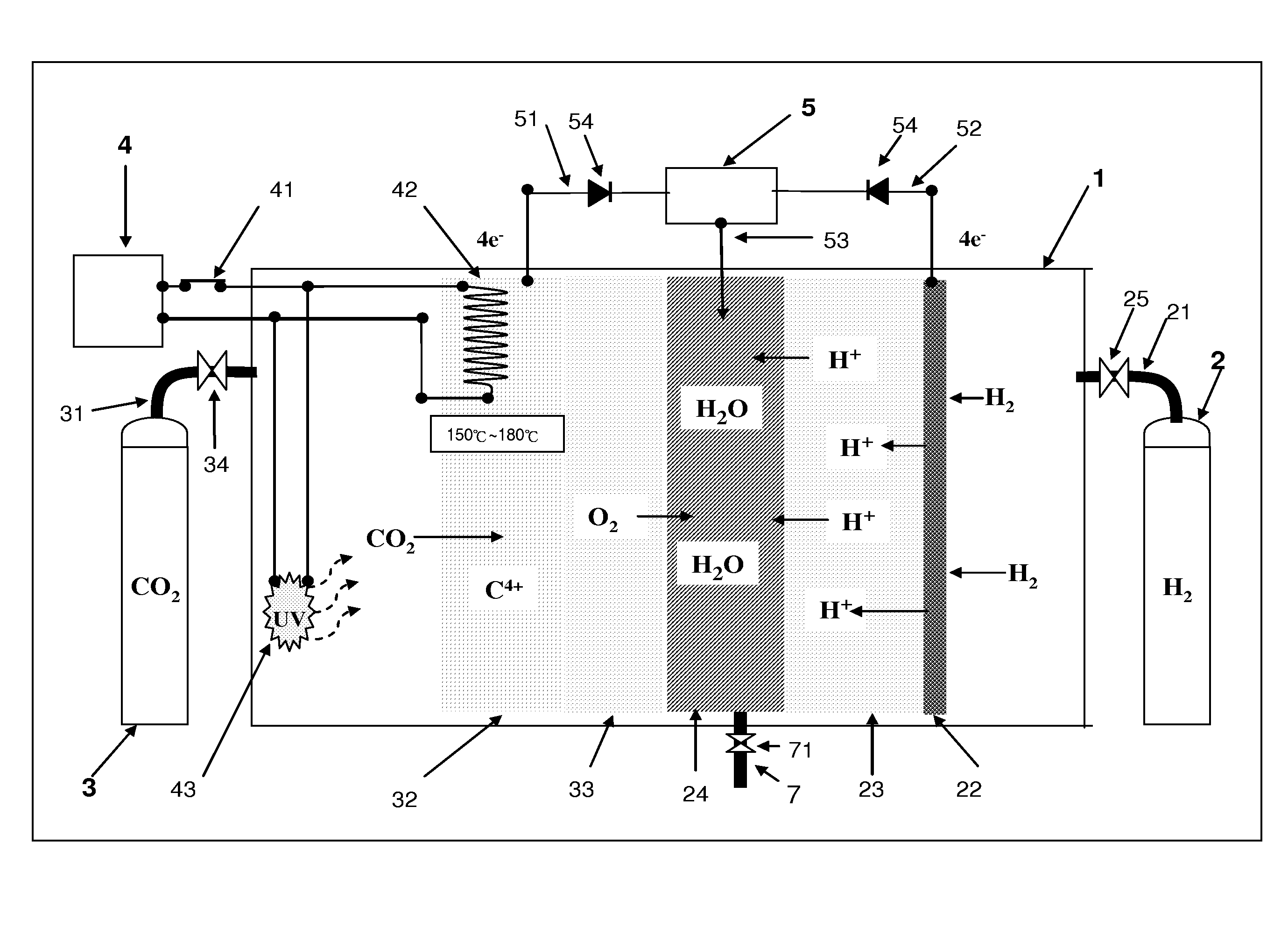
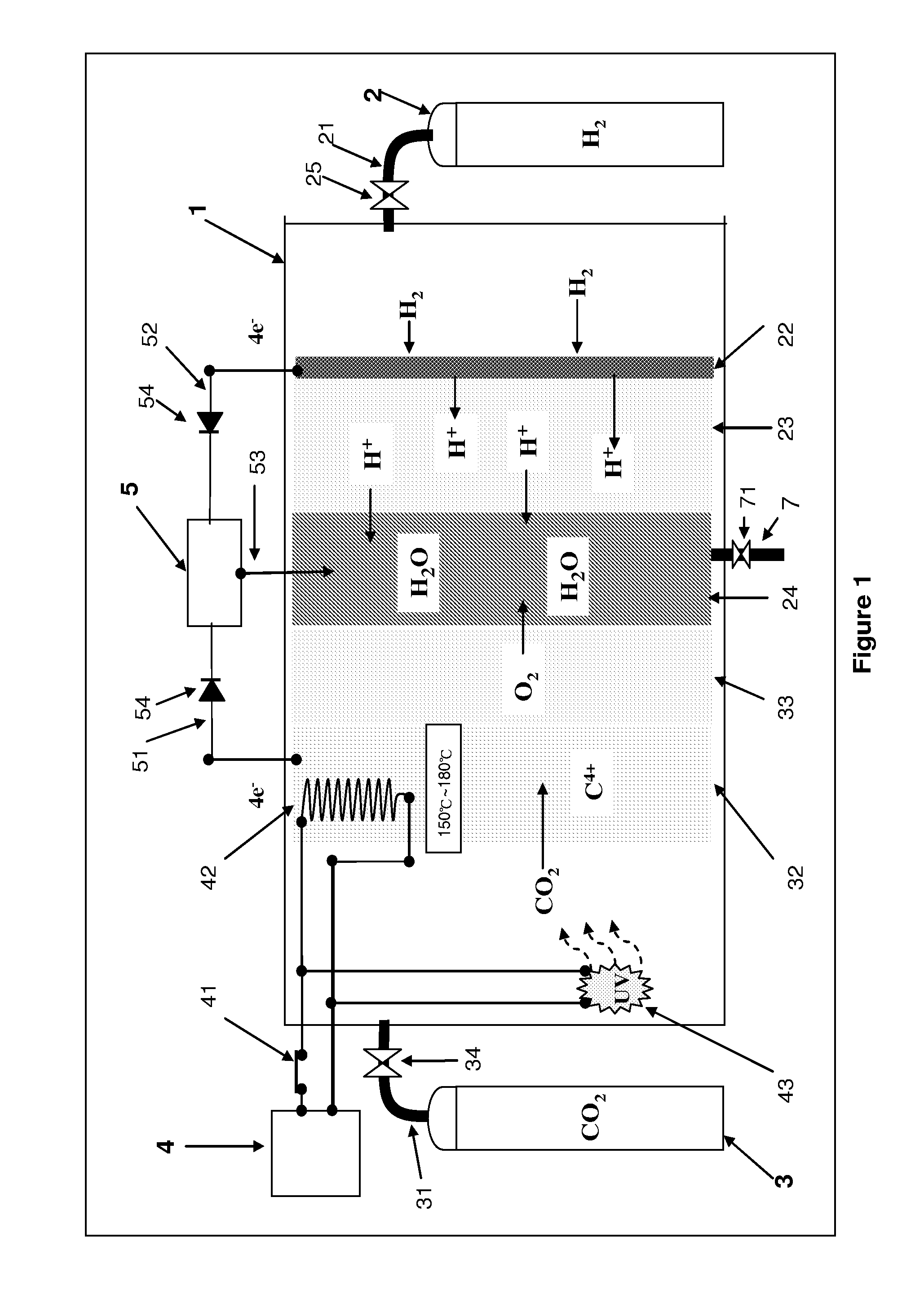
[0011]The continuous supplementary reaction between the
hydrogen fuel
cell and the carbon dioxide pole taken place at the
voltage and the current of the external dual
electron circuit can be recycled and used easily for supporting the consumption for other applications, and the process for four protons (H+) and
oxygen (O2) to be reacted to form water (H2O) will release
heat energy which can be used for different applications through a thermal conducting material, and the
heat energy is recycled and conducted to a carbon dioxide nanometer (nM) reacting pole, and thus greatly reducing the
power consumption required when the temperature of the carbon dioxide nanometer (nM) reacting pole is increased. In other words, if the output capability of a dual-loop fuel
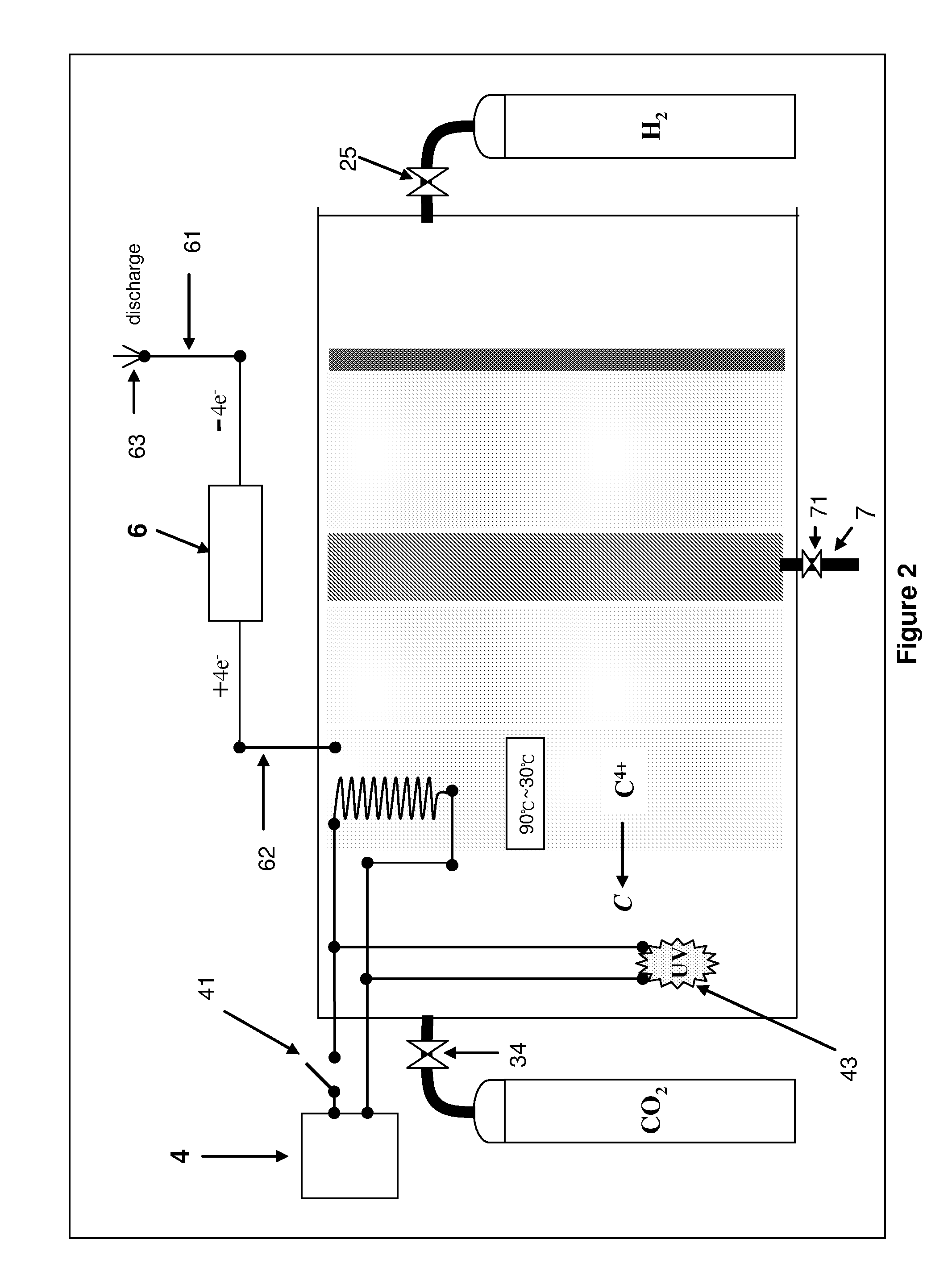
cell drops to a rated 80%, it shows that the performance of the carbon dioxide pole (CO2 pole) drops because the nanopores are filled up with the C4+ nM state carbon. It is necessary to have a second-stage
chemical reaction which is the reduction process of the C4+ nM state carbon, wherein a static charge generator is used for returning the energy of the four electrons (4e−) to the reverse reaction process of the C4+ nM state carbon, and its
chemical reaction equation is given below:C4− nM+4e−↓→C+∇nM.
[0015]Compared with the natural mechanism, the present invention cannot imitate the mechanism of
photosynthesis to achieve the effect of fixing the carbon, but the invention can use the mechanism of photosynthesis to break the
electron bonds of the carbon dioxide (CO2). Therefore, the invention relates to a carbon dioxide (CO2) resolve / decompose method and a reduction method of a non-biological mechanism, and the entire operation process does not involve any
pollution, but gives the beneficial effect of recycled
chemical energy and nanocarbon, which is an excellent solution for the greenhouse gases.
[0016]Since carbon dioxide comes with a strong bond, the methods in the past may be able to
cut off the bonding force of carbon dioxide temporarily, the bond is resumed immediately afterward, and this is a difficult problem and a challenge to all experts in this field. If the materials adopted by these experts only have the characteristic of compensating the electron bond, the carbon dioxide cannot be actually decomposed into carbon and
oxygen, because when the bonding force between carbon and oxygen is weakened, and no other force substitutes the original bonding force between carbon and oxygen, such as providing a new bond between
proton (H+) and oxygen, the extra free electrons will be consumed, and the
quantum state of the C4+ nM state carbon is situated at the base state temporarily, and oxygen will be combined with carbon in the C4+ nM state carbon immediately to form the stable carbon dioxide. With the compensation characteristic of the electron bond of the nanometer structure, the temperature
change control characteristic and the flexibly changing mechanical characteristic in accordance with the present invention, the
decomposition and recycle of carbon dioxide can be achieved. The
photon resolve / decompose mechanism of the invention with non-biological features for industrial
mass production is definitely a feasible solution for greenhouse gases. We can change the temperature of the nanometer structure easily to spread open the nano tangle tentacles filled with C4+ nM state carbon to successfully release carbon from the C4+ nM state carbon to for particulate carbon, so that the carbon dioxide pole (CO2 pole) of the nanometer structure resumes its original shape to facilitate a reuse. The key point is to develop a carbon dioxide
decomposition and recycle device in an industrial
mass production scale without the limitations of volume and capacity. Any close space can be used for an installation, and the installed product can be as large as a football field or as small as a toaster.
[0018](1) A plurality of large carbon dioxide
decomposition and recycle devices installed according to the present invention should be multi-linked devices and operating parallel in alternately. The devices can be installed at an exhaust outlet of a thermal power
plant, a steel
plant or a
cement plant for removing electric charges and dusts, and rinsing the exhaust of high-concentration carbon dioxide, and effectively decomposing and recycling carbon dioxide into carbon and pure water. The invention provides a tool for protecting the environment and attempting to minimize carbon to zero. The key point of this application of the carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device resides on the decomposition and recycle of carbon dioxide into carbon and pure water, and it becomes a beneficial tool for a certain company for protecting environment and reducing carbon. The buying party of carbon becomes a selling party who sells the reduced carbon quota to the industries such as airline, transportation, gas, and oil extraction industries that cannot reduce carbon technically. In addition to making additional profits, these companies also protect the environment. Of course, we cannot reduce carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere to 280 ppm. of 1800 immediately, but we can effectively control carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases from rising. At present, our earth already has excessive carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases. Although the forests and
coral in seas on earth can
clean up the greenhouse gases, it may take a couple of centuries before a healthy earth is recovered. Without the assistance of the carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device in accordance with the present invention, the construction and mission of reducing carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases on earth will be more difficult and time-consuming or require tens or hundreds of times of costs.
[0019](2) A small carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device in accordance with the present invention is installed in a manned spaceship, and uses the high-energy photons of the
sunlight for electrolyzing water into
hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) as a fuel source of a CO2 fuel
cell. The invention carries on a constant filter cycle in a spaceship cabin for producing water used for the
electrolysis by the optoelectric effect of the
sunlight in order to prepare
hydrogen and oxygen, wherein oxygen is provided for the
respiration of astronauts, and hydrogen is provided for the use as a fuel for a hydrogen pole of the carbon dioxide decompose device (CO2 fuel cell), and the concentration of carbon dioxide in the spaceship cabin will remain low due to the
continuous operation of the carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device. The carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device of the present invention is primarily used for generating and supplying
electric power to the spaceship cabin, and controlling the concentration of carbon dioxide, and both are equally important. Although the concentration of carbon dioxide in the spaceship cabin may not be too high, the device of the invention relates to operations of a constant cycle, thus, controlling the concentration of carbon dioxide in the spaceship cabin within a normal standard value effectively and naturally avoid accidents and risks during
outer space missions. In other words, the carbon dioxide absorbing device in the Apollo 13 spaceship cabin prevents the recurrence of having a carbon dioxide concentration approaching a critical limit encountered by the astronauts, and also gives the additional benefit of a fuel cell.
[0021](4) The carbon (C) recycled by the carbon dioxide decomposition and recycle device is nano-scale pure particulate carbon without any
impurity, and the scope of its application is extensive, particularly used as a
raw material for man-made diamonds. This application can greatly enhance the
hit rate of the
crystallization of man-made diamonds, lower the manufacturing cost, and improve the quality. The recycled nanocarbon can be used for manufacturing high-end
carbon fibers as a premium material for manufacturing aircrafts or nanocarbon tubes or nanocarbon meshes used for fuel cell poles. The nanocarbon recycled by this device overcomes the
yield rate issue of the carbon
wafer fabrication process to expedite the development of the next-generation carbon
wafer products and substitutes the current
silicon wafer process that almost approaches the upper limit of Moore's Law and allows future information products produced by the carbon manufacturing process to have the light, handy, power-saving and quick functions.
 Login to View More
Login to View More