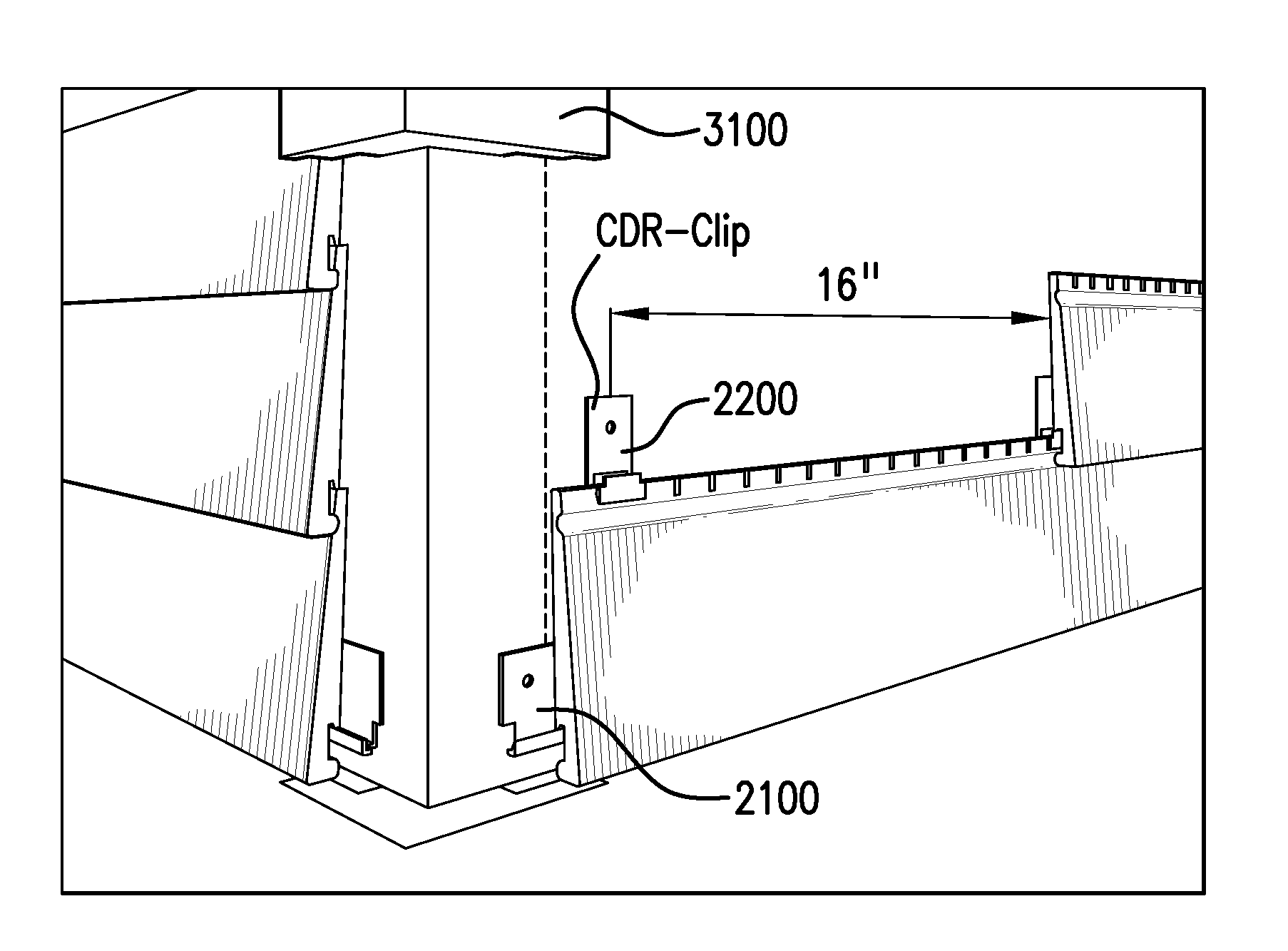
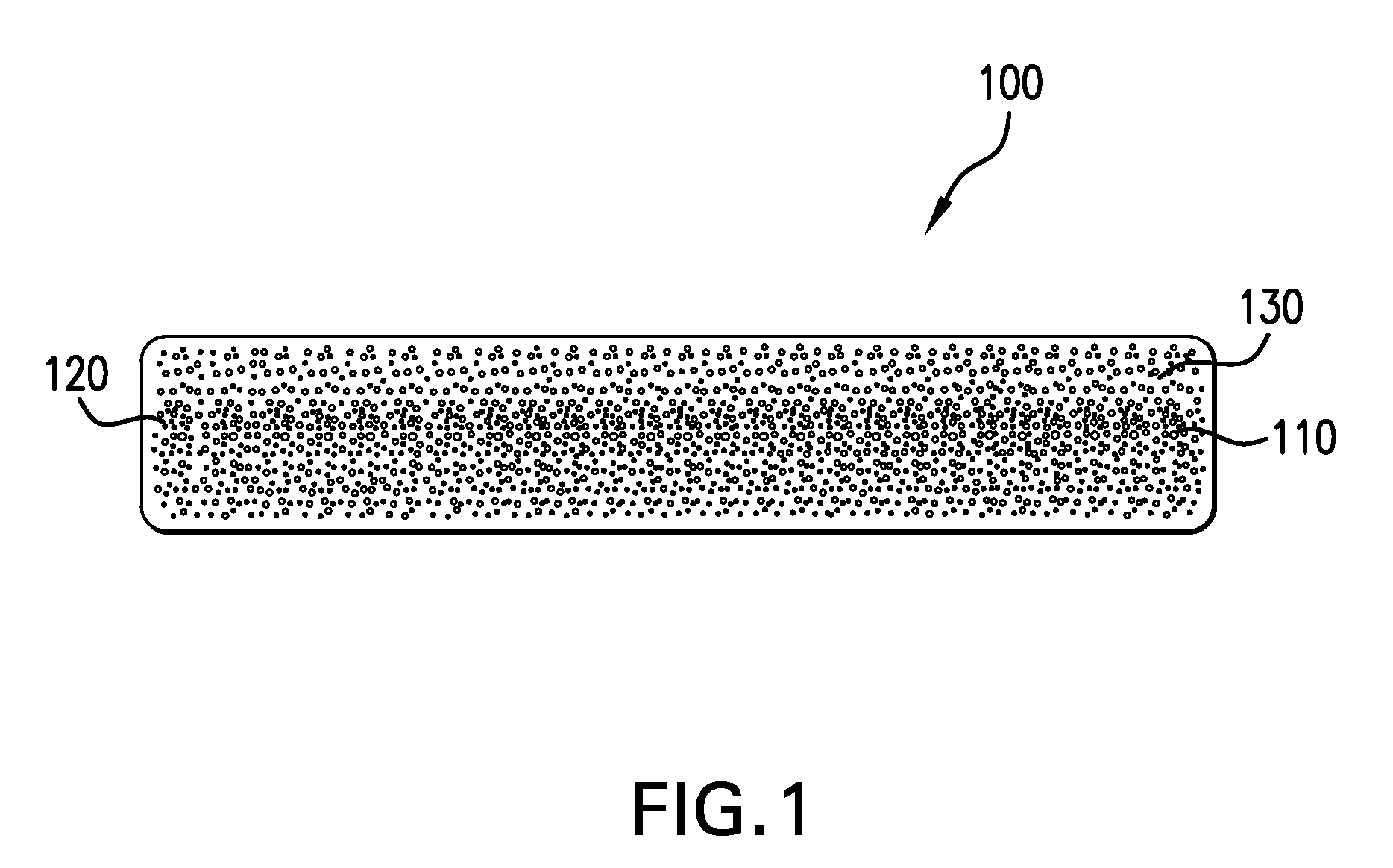
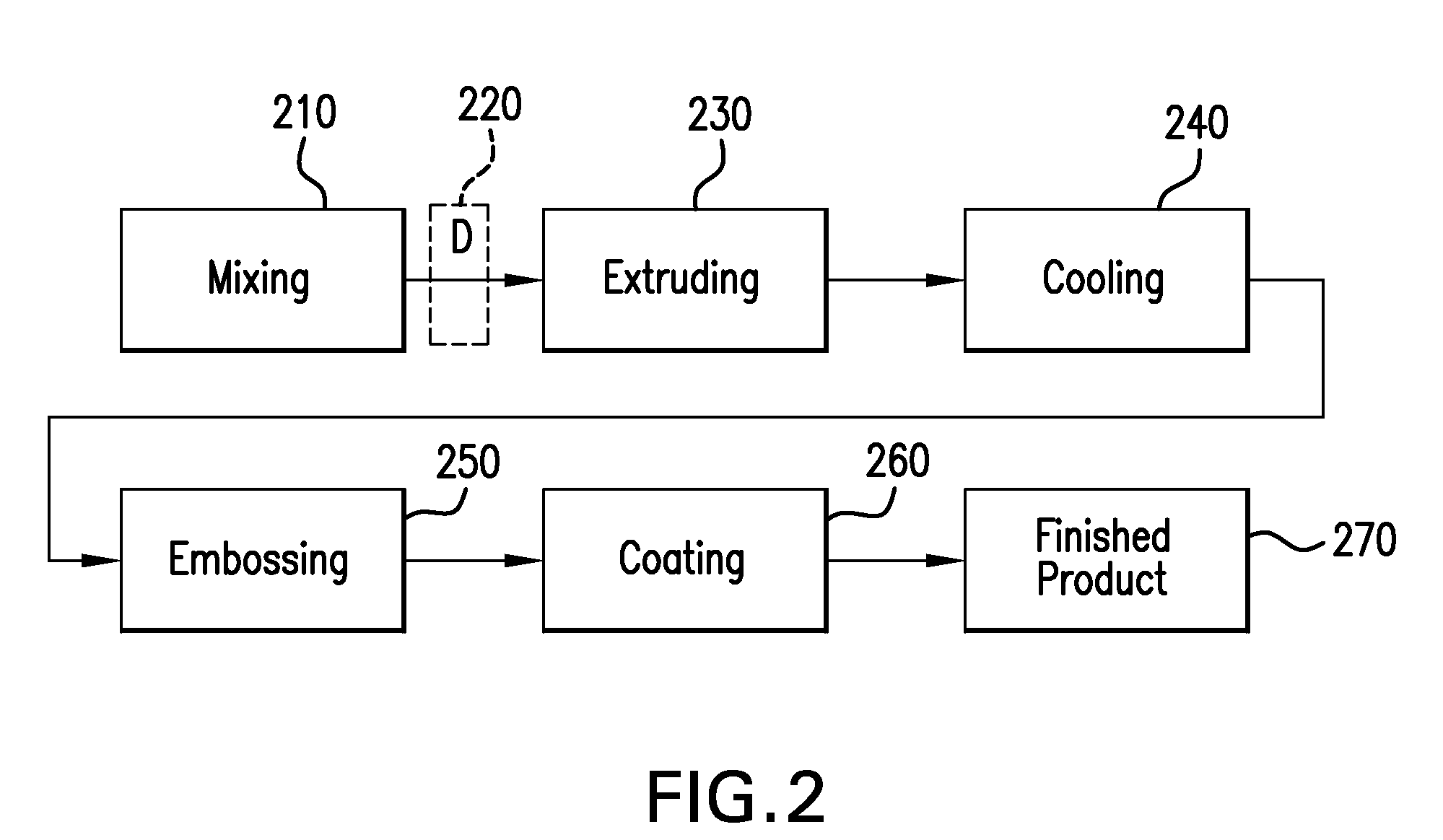
Siding containing composite building material and siding clip
a technology of composite building materials and siding clips, which is applied in the direction of roofs, walls, constructions, etc., can solve the problems of reducing affecting the quality of available natural wood, so as to reduce the absorption rate and reduce the cost. , the effect of reducing the absorption ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0187]A siding panel according to the present invention is prepared having the composition set forth in Table 2.
TABLE 2Substrate CompositionMaterialPPHPVC Resin (FPC 616)100Stabilizer (TM-181)0.8Lubricant (Paraffin 165)0.8Lubricant (PE AC 629A)0.15Lubricant (calcium strearate)0.6Reinforcing Filler18(calcium carbonate, 0.7micron, treated, Omya UFT)Processing Aid6.0(K-400) or (SureCell)Processing Aid (K-175)1.5Titanium Dioxide0.5Blowing Agent0.8(Forte-Cell 247 Azo)
[0188]The ingredients from Table 2 are loaded into its on-line feeders which is calibrated for each individual material dose rate. The raw material feeder systems used to make may be volumetric or gravimetric, or combinations of each. These feeder systems deliver the pre-calibrated volume or weight of each material to a central neck piece which is attached to the feed port of the extruder. Materials are delivered in a “Starve feed” mode which allows the extruder screws to be covered approximately 90% of total depth.
[0189]The...
example 2
[0197]A siding panel having the same substrate composition as in example 1 is prepared and used in the UV coating process.
[0198]The UV-curable urethane / acrylic coating used to coat the panel has the composition set forth below:
MaterialWeight %urethane acrylic:90.7% 10% Alkoxylated Acrylic Monomer10% Acrylate Monomer5% Highly Functional Monomer38.5% Aliphatic Urethane AcrylateEsacure KTO46 photoinitiator 3%30% Ferro Geode Pigments in PMDA10-20% (basedon solids)Nano Byk 3601 40 nm aluminum oxide in3.6%TPGDAAcematt TS1001.4%
[0199]The urethane / acrylic monomer / oligomer composition is transferred to an appropriate vessel. The photo initiator is in liquid form and is mechanically stirred into the batch. Once the photoinitiator is added, the material must be kept away from any UV light sources and the material will have at least a two year shelf life when drummed and sealed.
[0200]The pigments (Ferro Geode) are dispersed in a reactive Sartomer oligomer (PDMA) and are supplied in liquid form...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com