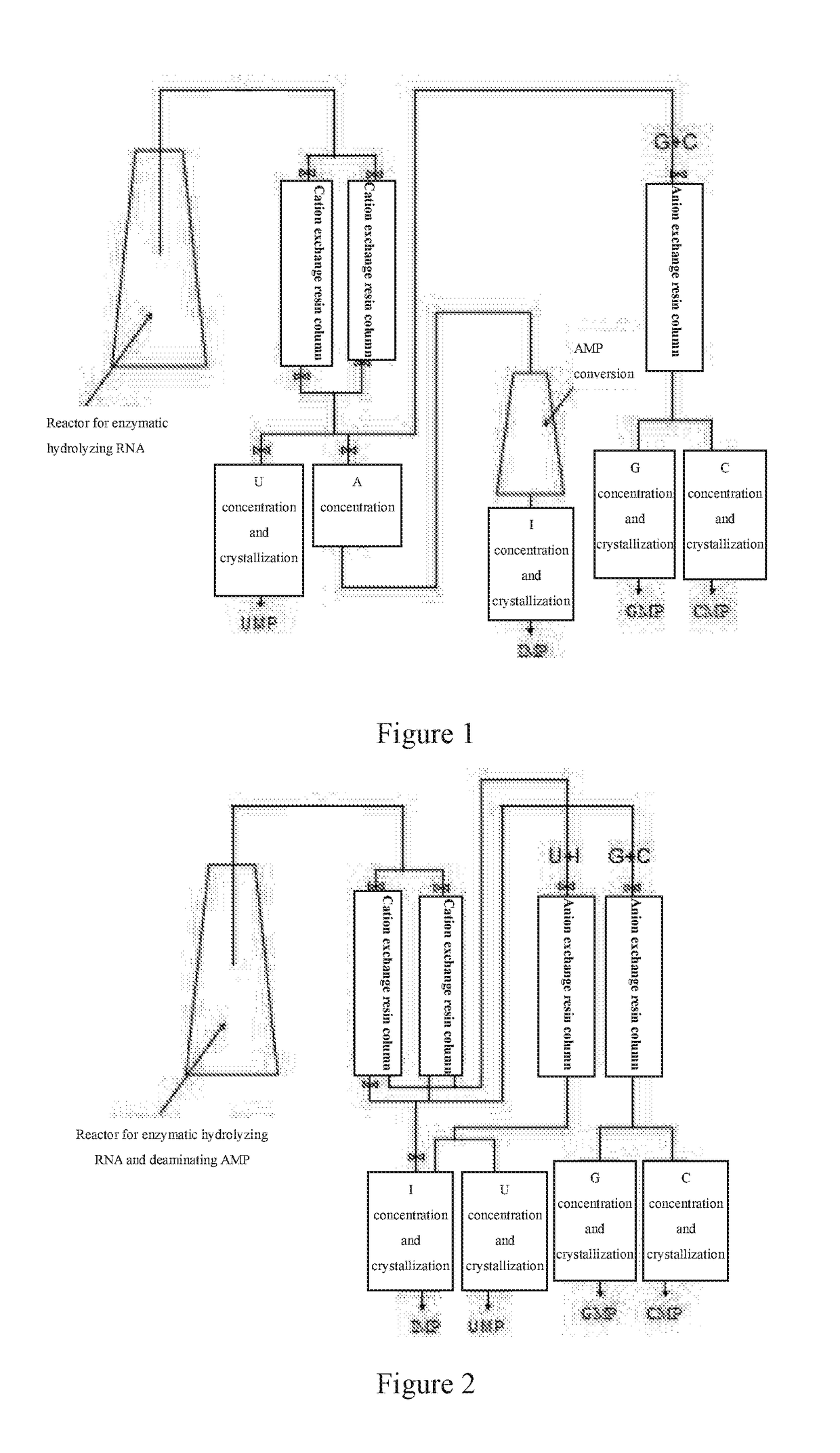
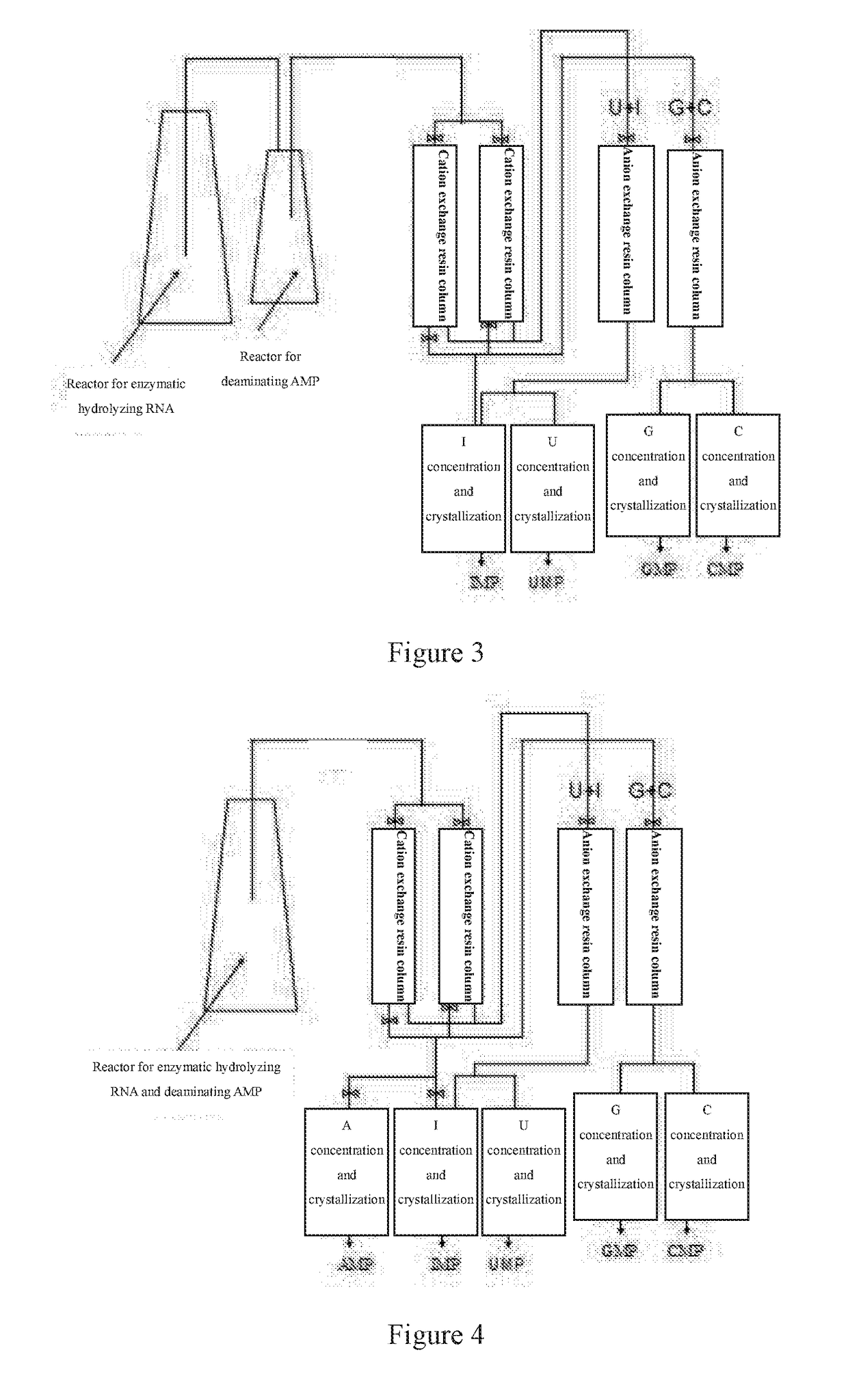
Nucleotide production process
a production process and nucleotide technology, applied in biochemistry apparatus and processes, fermentation, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of difficult separation, difficult crystallisation, and methods for producing nucleotides, and achieve high yield, high purity, and low solubility in water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Nuclease P1
[0075]A seed culture medium and a fermentation medium containing the following ingredients: 50 g / L glucose, 5 g / L peptone, 0.5 g / L KH2PO4, 0.5 g / L K2HPO4.3H2O, 0.4 g / L CaCl2 and 0.4 g / L ZnSO4 were prepared respectively. The pH was adjusted to 6.5 before sterilization.
[0076]Preparation of nuclease P1: Penicillium citrinum N409 was inoculated in the seed culture medium prepared above, cultured at 28° C., 200 rpm for 18 hours, and then inoculated into the fermentation medium with an inoculation quantity of 10% (v / v), cultured at 28° C., 200 rpm for 24 hours, and then the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 8000 rpm, 4° C. for 15 minutes, the supernatant was taken to obtain 420 U / ml of nuclease P1 solution, which was refrigerated at 4° C. until used.
[0077]All nuclease P1 used in the following examples 2-9 was prepared according to the above method.
example 2
Preparation of Nucleotides
[0078]36 g RNA of yeasts was weighed, and formulated into a 6% nucleic acid solution (in which NaOH was added to help dissolving before adjusting the pH to 5.5 with HCl), warmed to 70° C., 21000 U nuclease P1 solution preheated at 45° C. (about 50 ml) was added thereinto, and the reaction is performed for 4.5 hours at 70° C., and then 0.9 g activated carbon was added, the enzymolysis was held for 40 minutes, and then centrifugation, suction filtration and ultra-filtration were performed to obtain 610 ml mixture solution of nucleotides. After detection, the enzymolysis ratio of nucleotides was 85.54%, and the concentration of each nucleotide in the mixture solution of nucleotides was UMP 10.56 g / L, GMP 16.83 g / L, CMP 10.87g / L and AMP 13.5293 g / L.
[0079]50 g pretreated cation exchange resin Amberlite IR-120 and anion exchange resin Amberlite IRA-68 were weighed respectively and packed into columns. The mixture solution of nucleotides obtained above was loaded ...
example 3
Preparation of Nucleotides
[0082]50 g RNA of yeasts was weighed, and formulated into a 5% nucleic acid solution (in which NaOH was added to help dissolving before adjusting the pH to 5.5 with Ha), warmed to 50° C., and then 100000 U nuclease P1 solution preheated at 45° C. (about 240 ml) and 40 U adenosine deaminase powder (about 40 mg) were added thereinto, then the enzymatic hydrolysis-deamination reaction was performed at 50° C., during which 3 mol / L HCl was added to control the pH value at 5.5±0.2, after 5 hours, 2 g activated carbon was added, the enzymolysis was held for 30 minutes, and then centrifugation, suction filtration and ultra-filtration were performed to obtain 1020 ml mixture solution of nucleotides. After detection, the enzymolysis ratio of nucleotides was 88.56%, the converting rate of AMP was 99.9999% and the concentration of each nucleotide in the mixture solution of nucleotides was UMP 8.7692 g / L, GMP 13.9790 g / L, CMP 9.0296 g / L and IMP 11.6635 g / L.
[0083]100 g p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com