Patents
Literature
64 results about "Deterministic function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deterministic Functions. The functions which always return same output when they called with a particular set of input values in the same state of the database are known as deterministic functions.
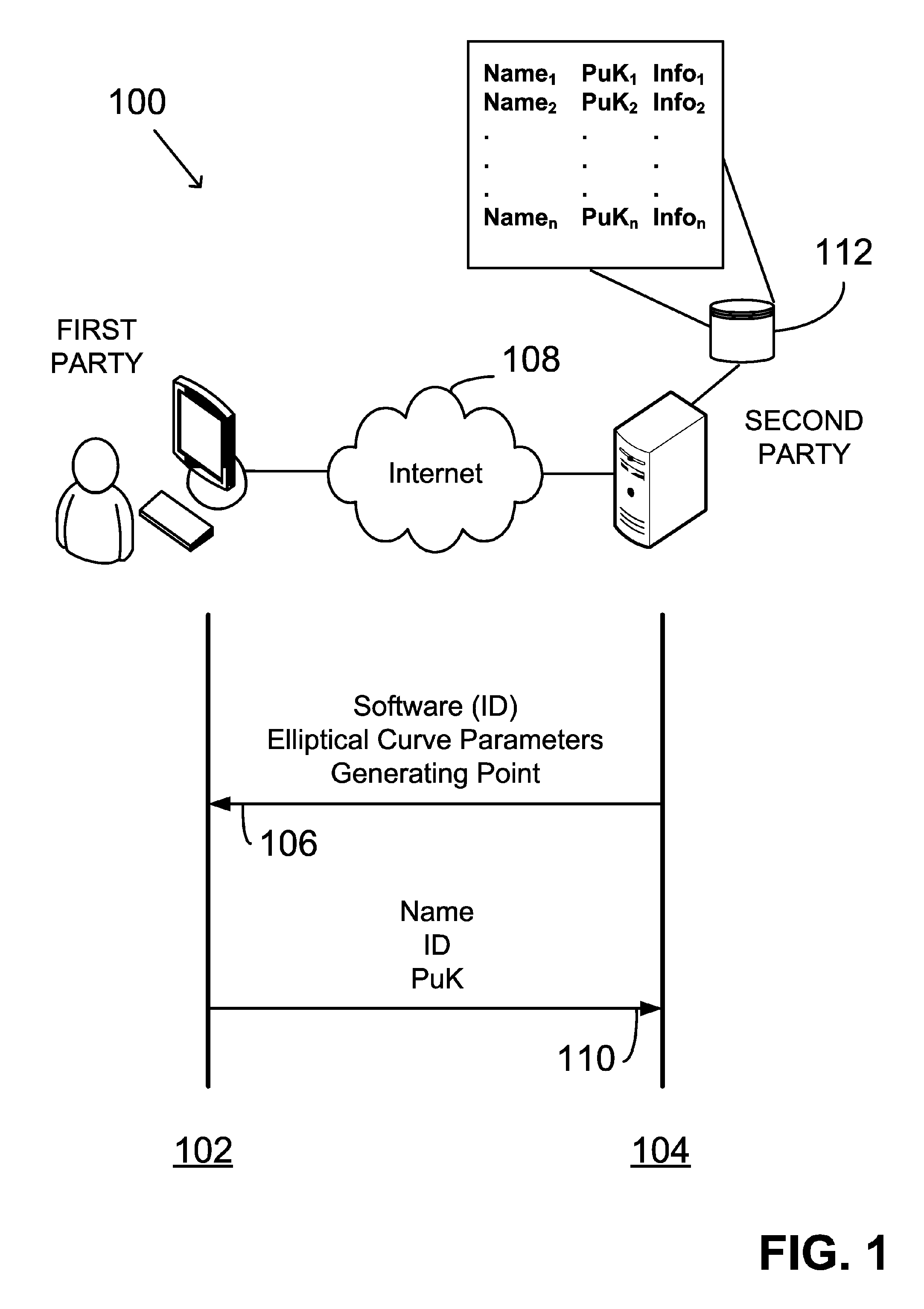
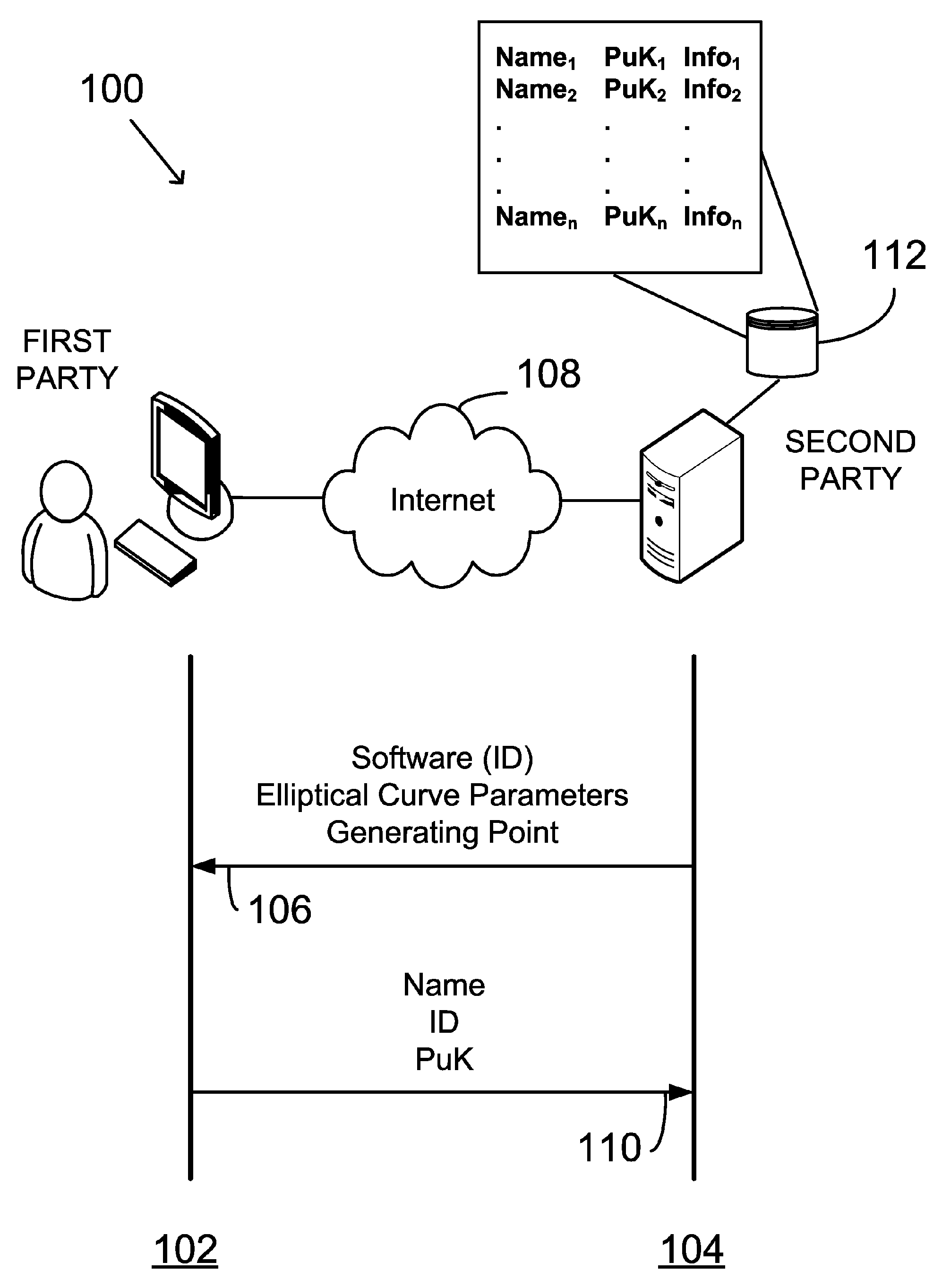
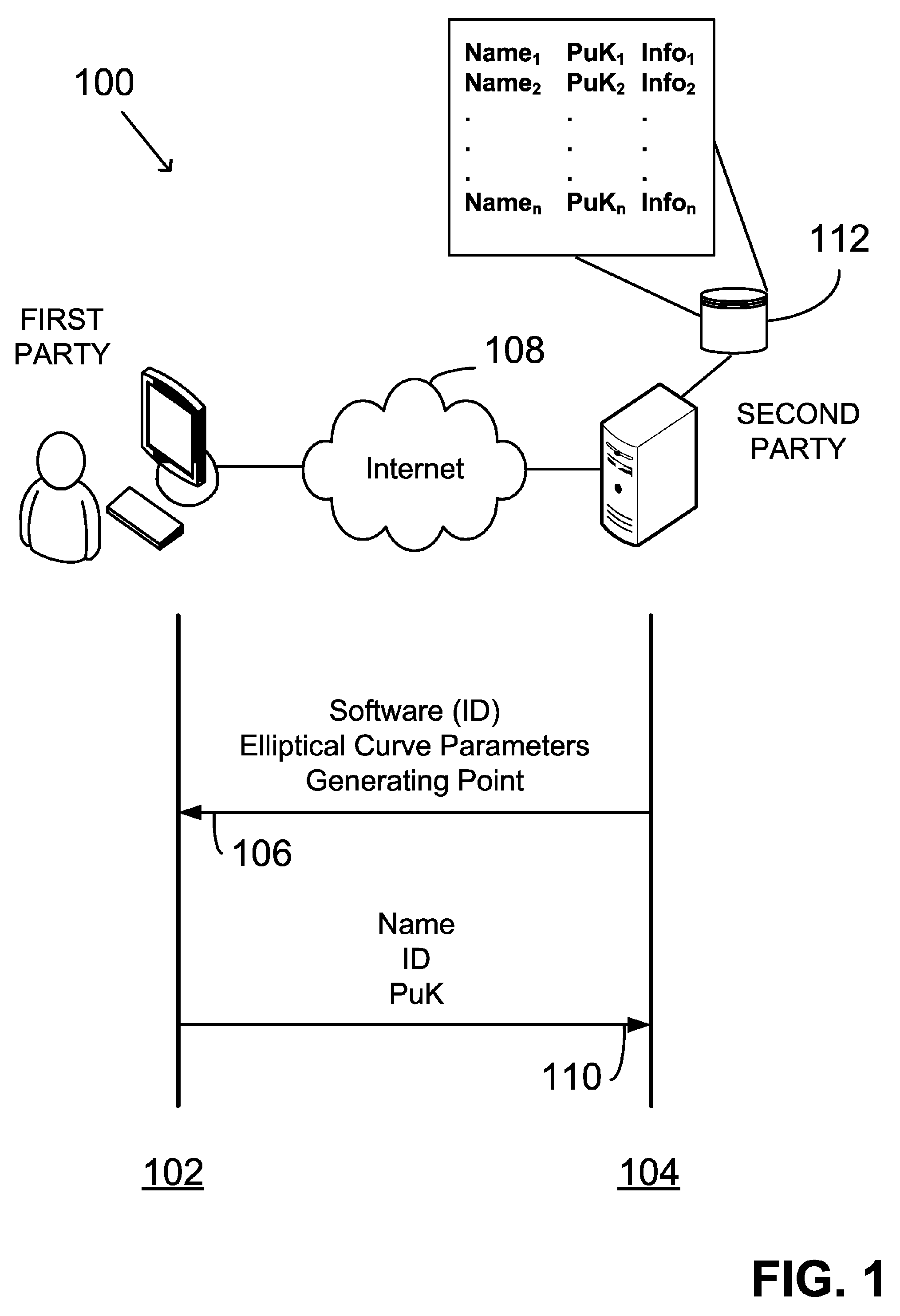
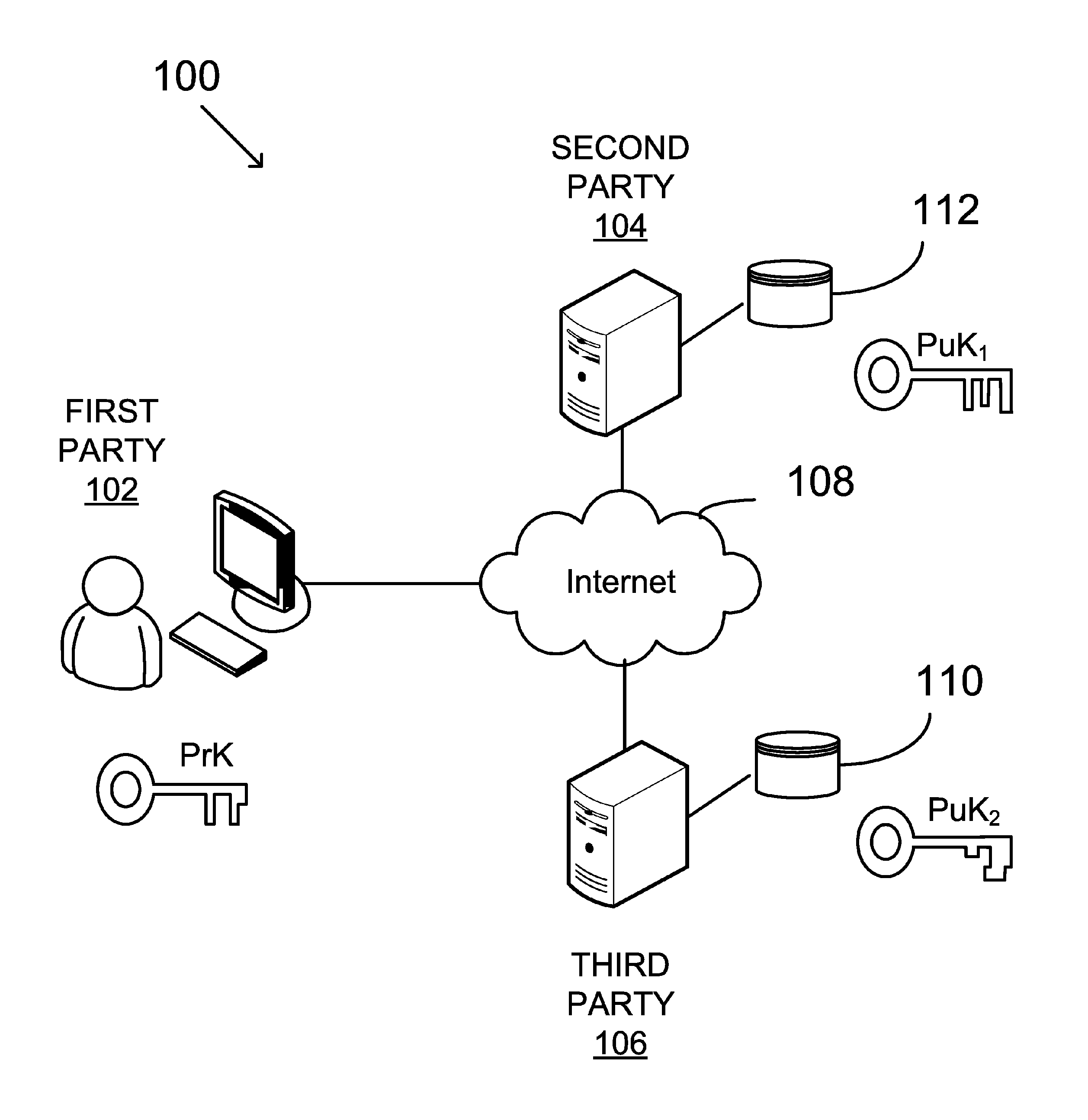
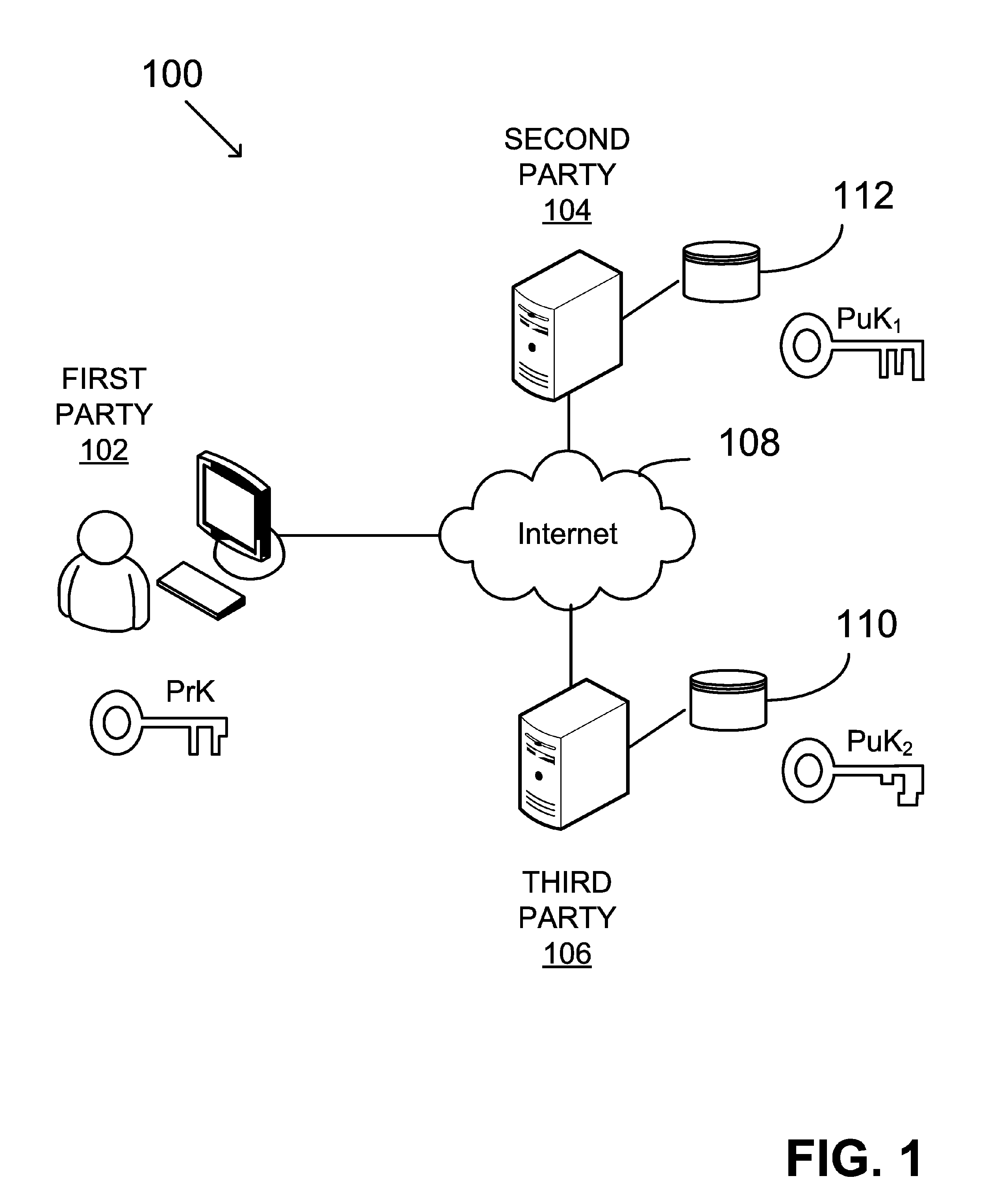
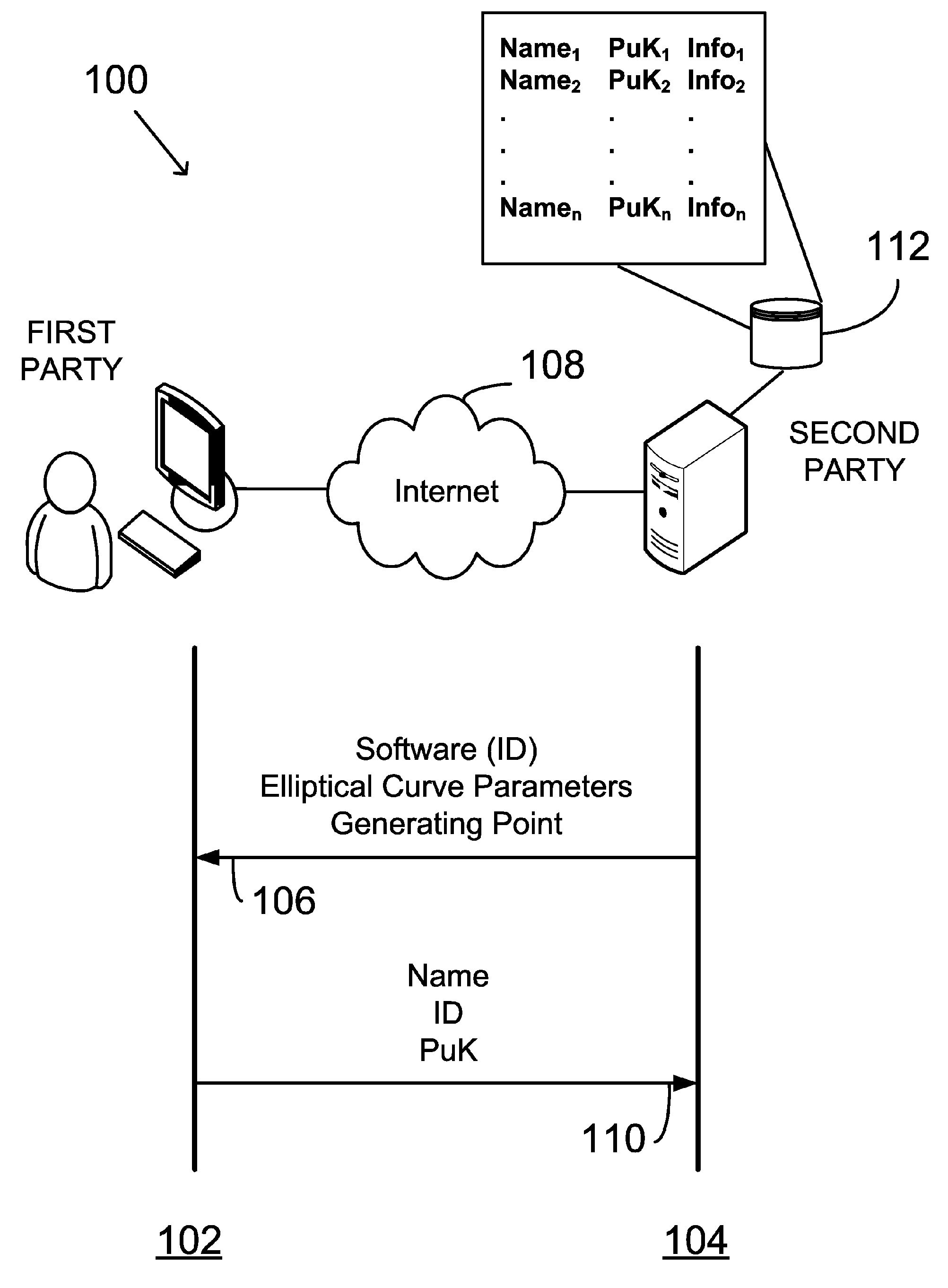
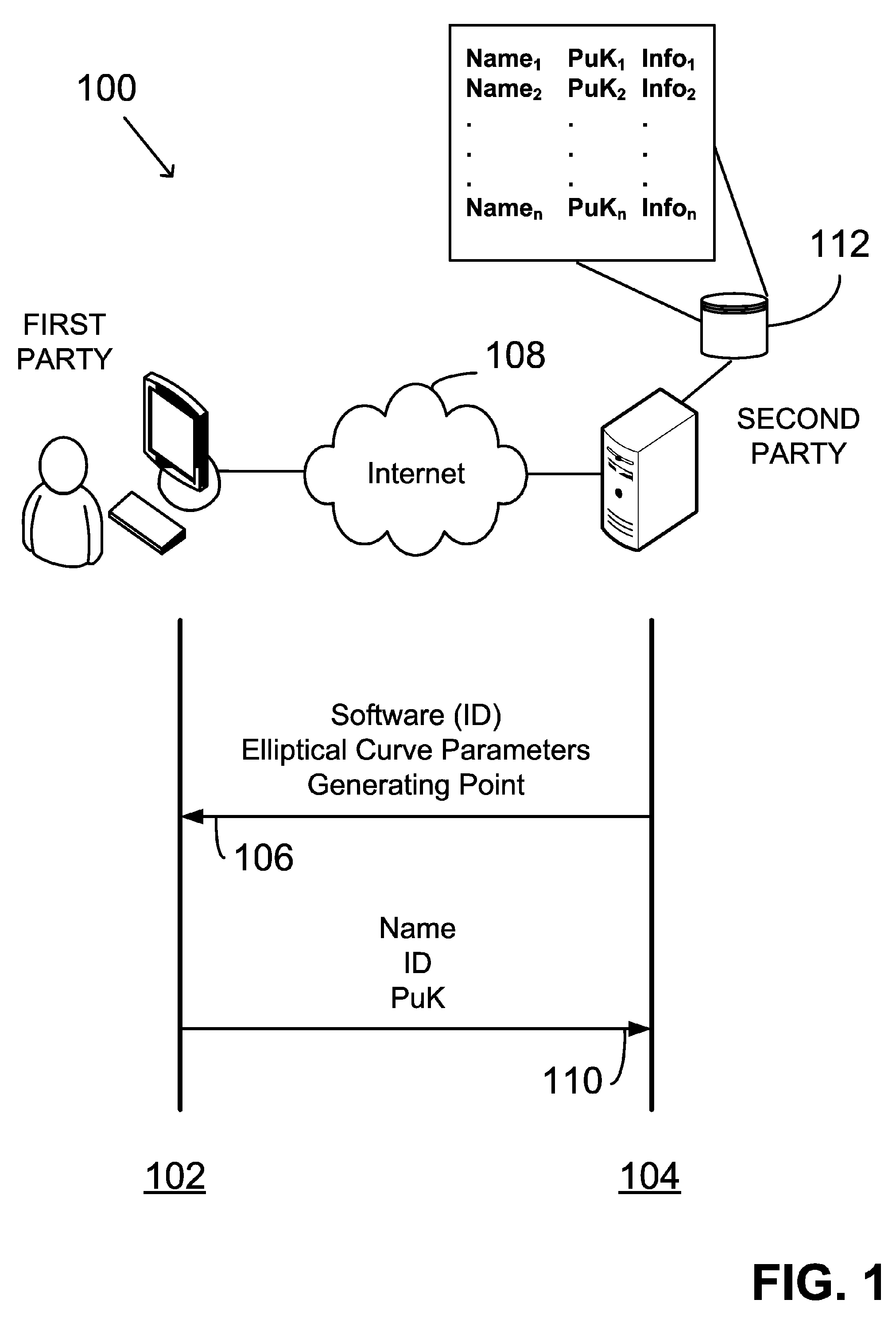
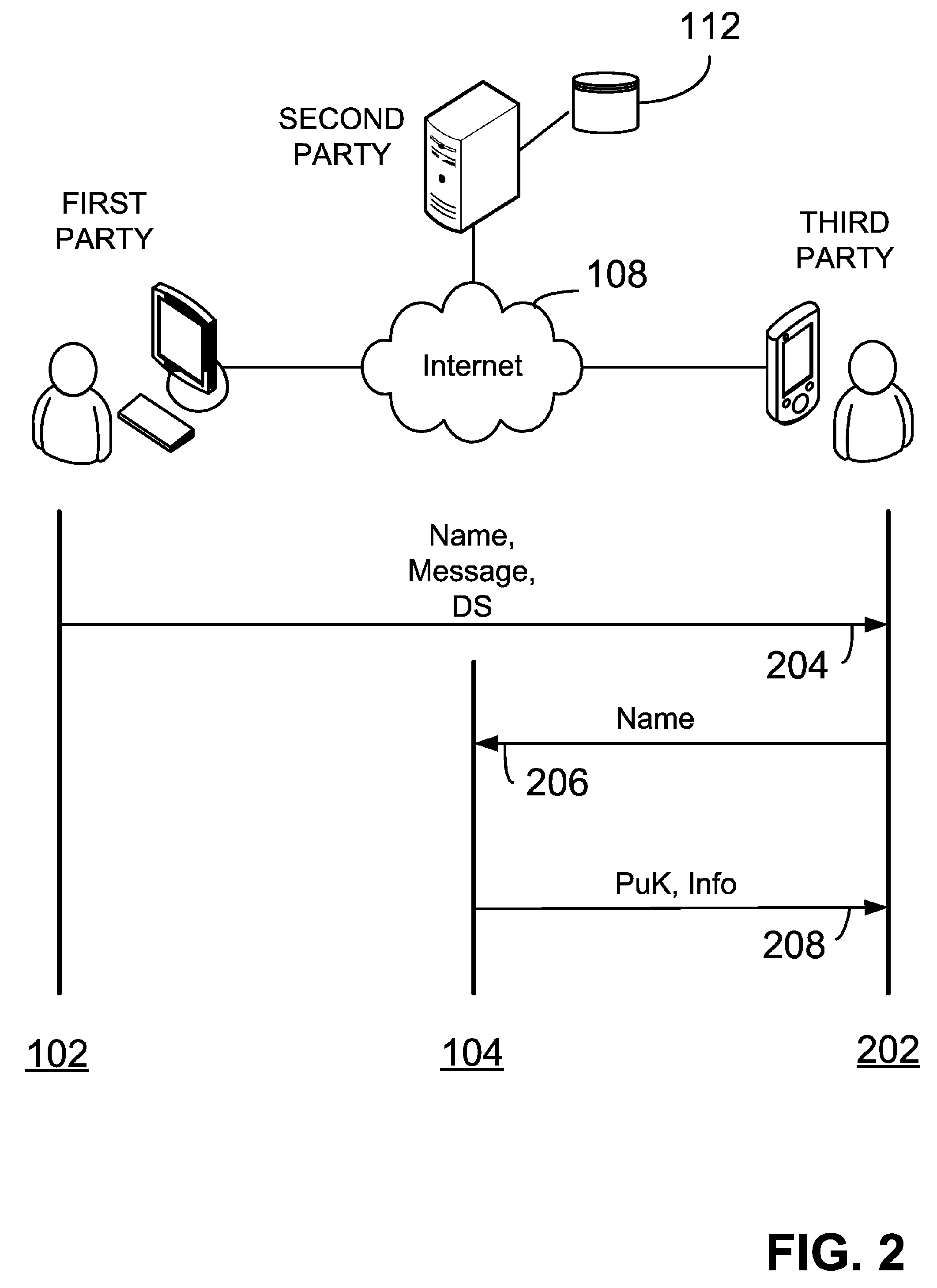
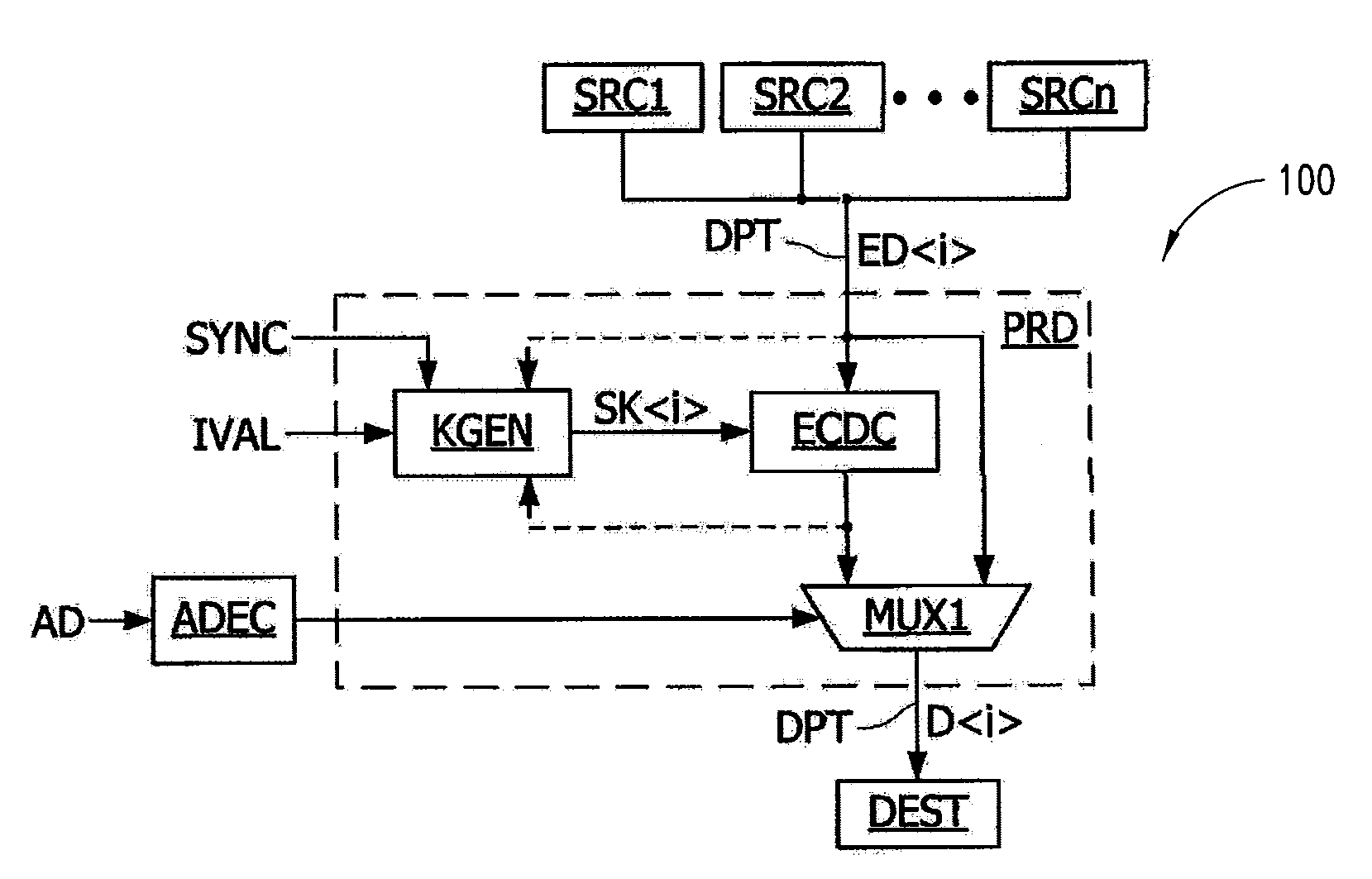
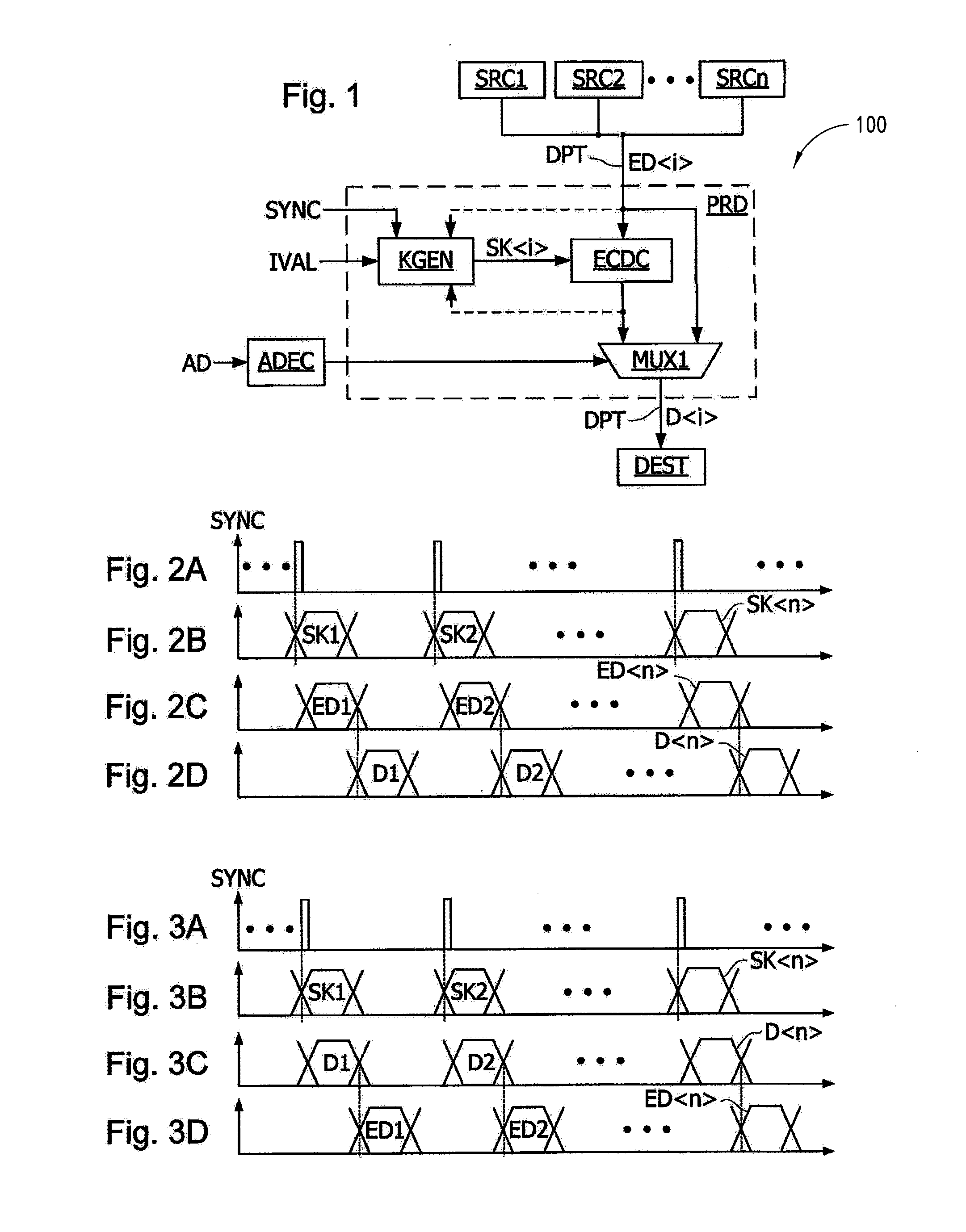
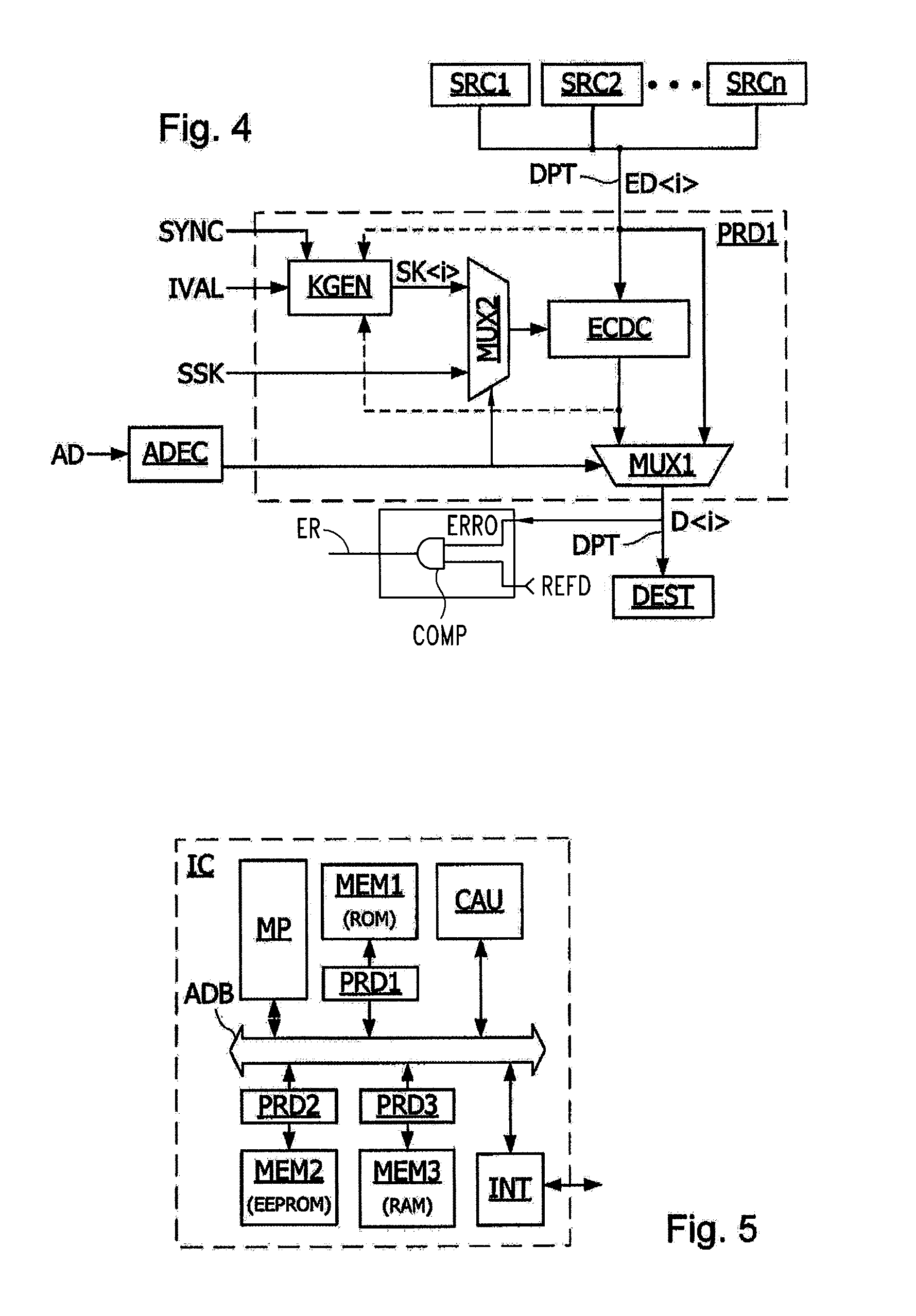
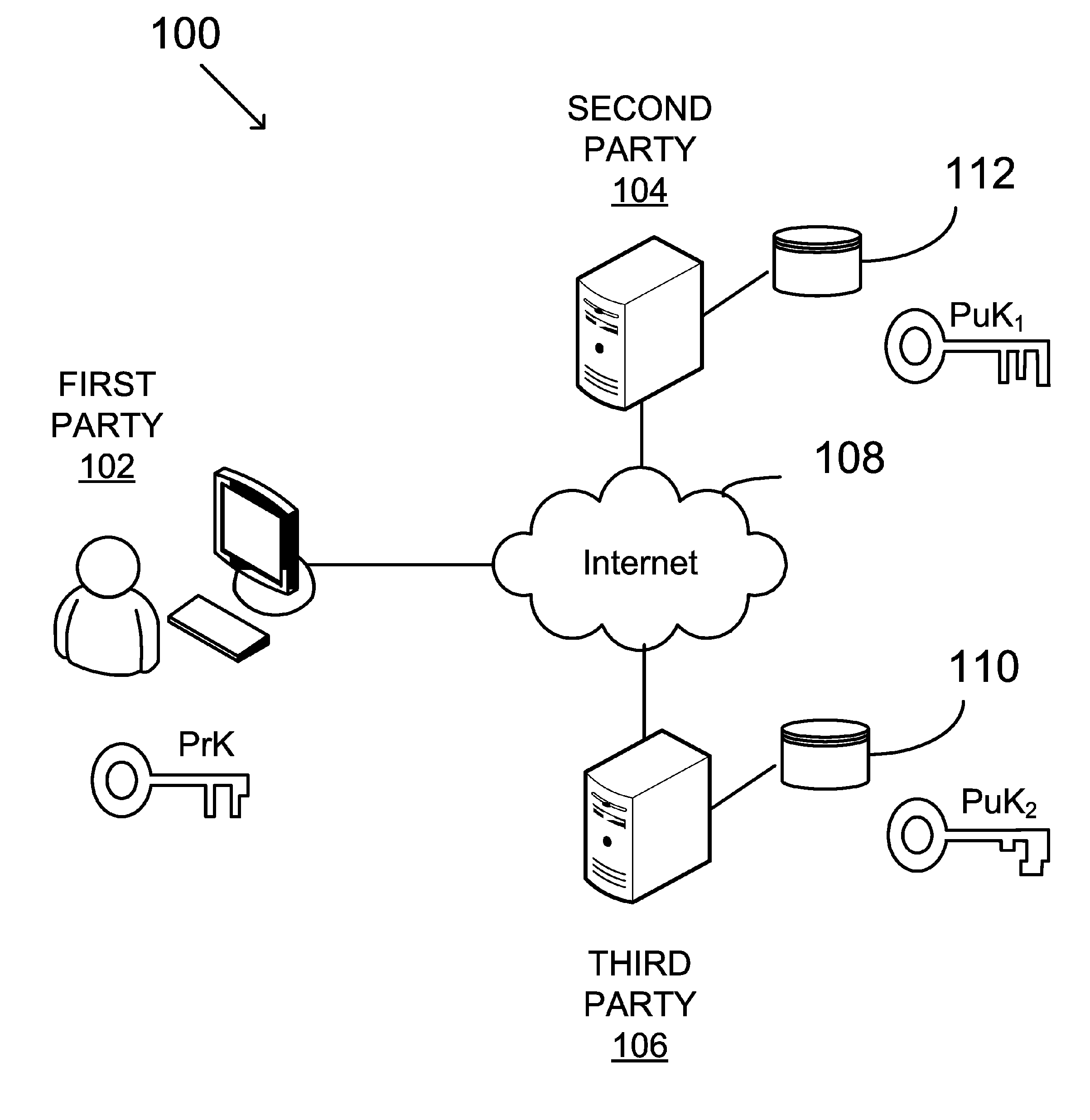
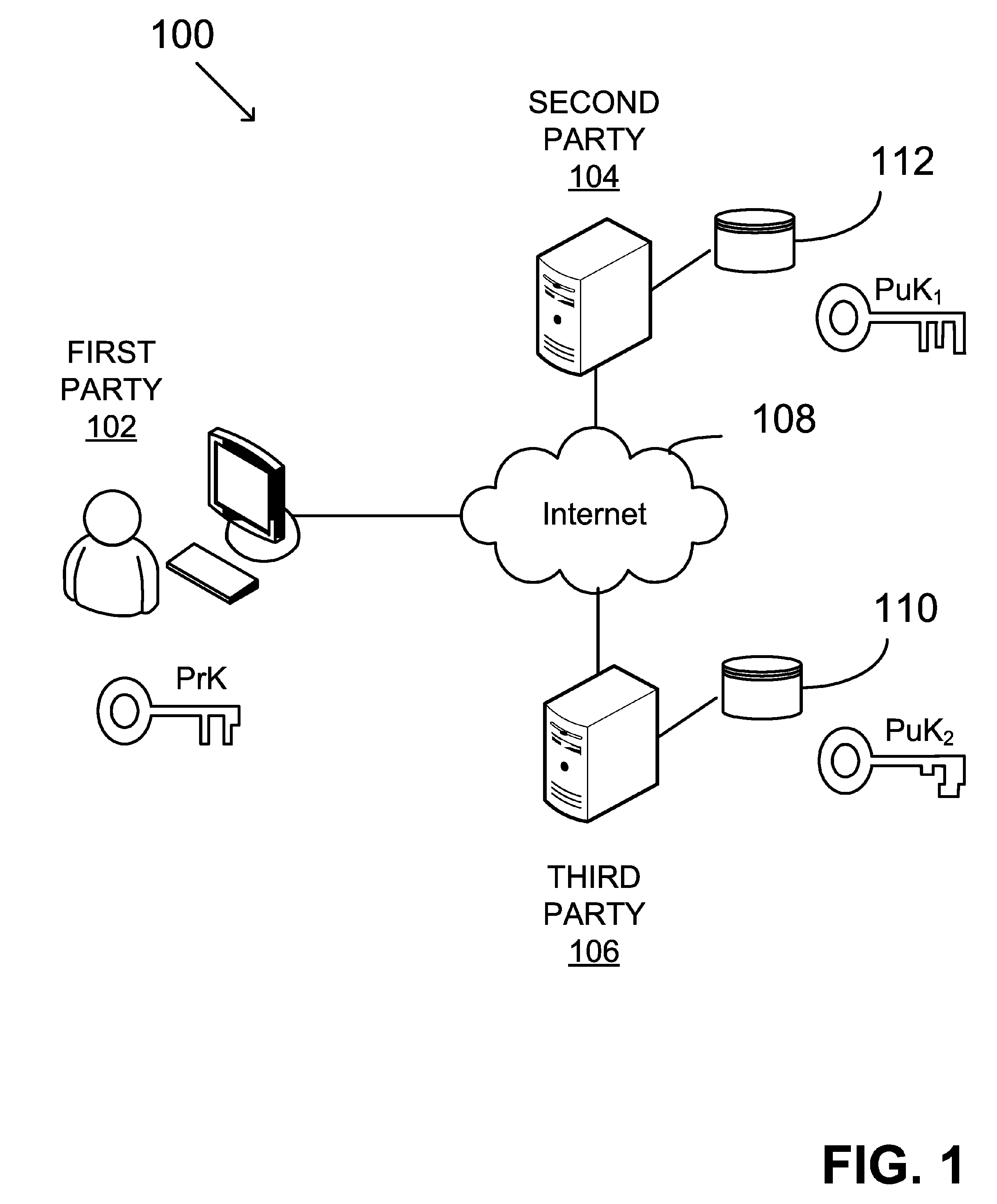
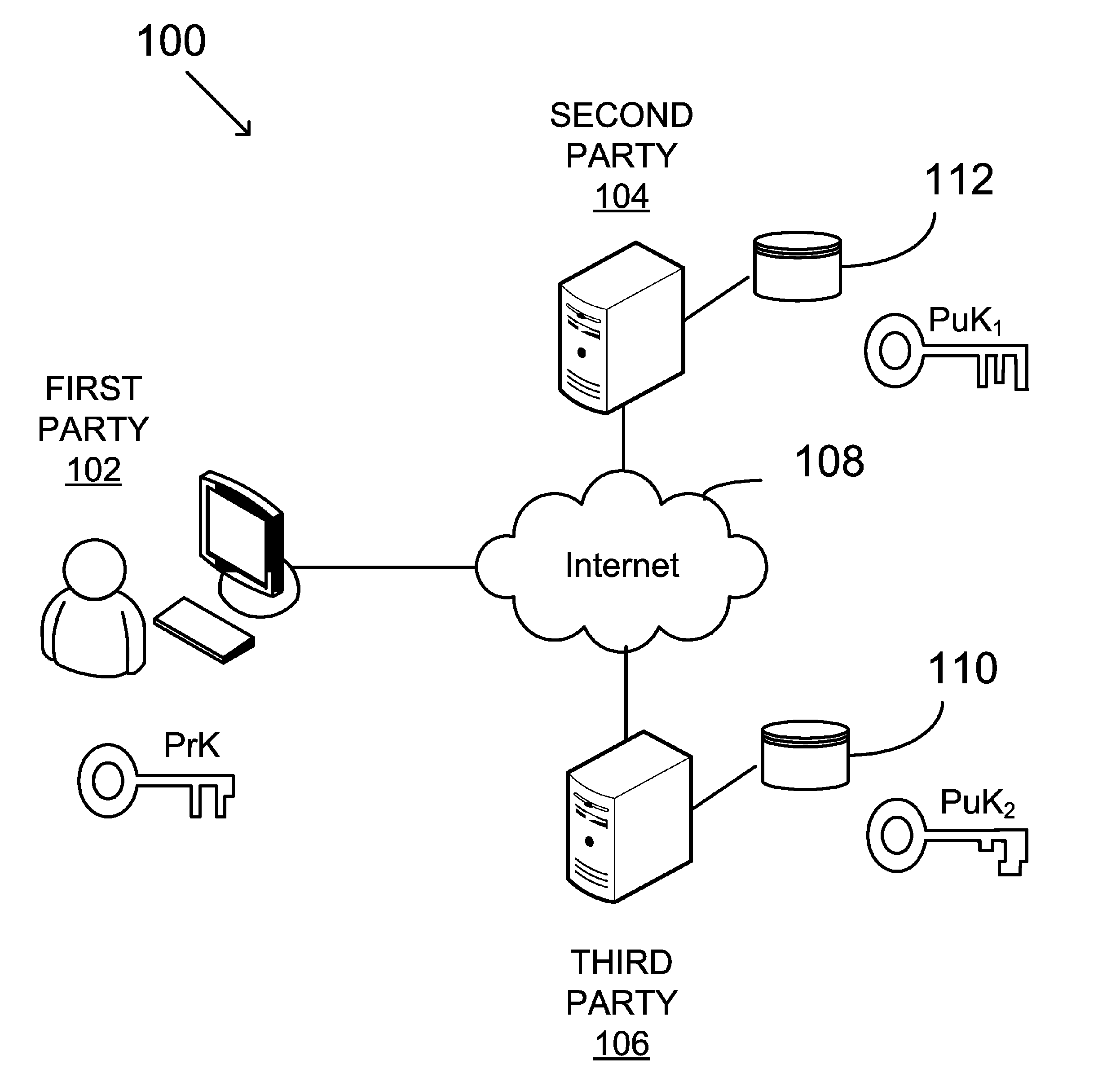
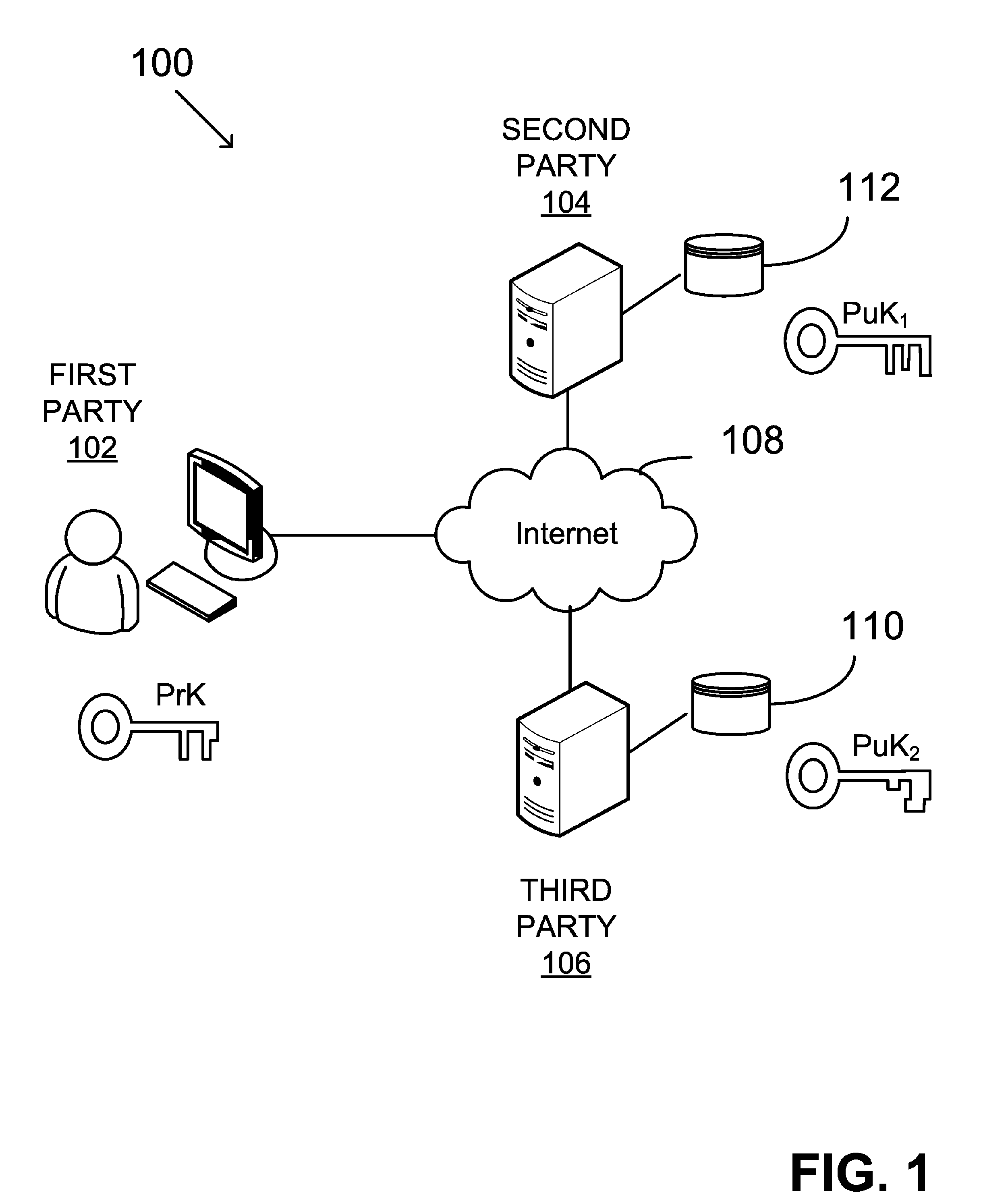
System and method for generating a digital certificate
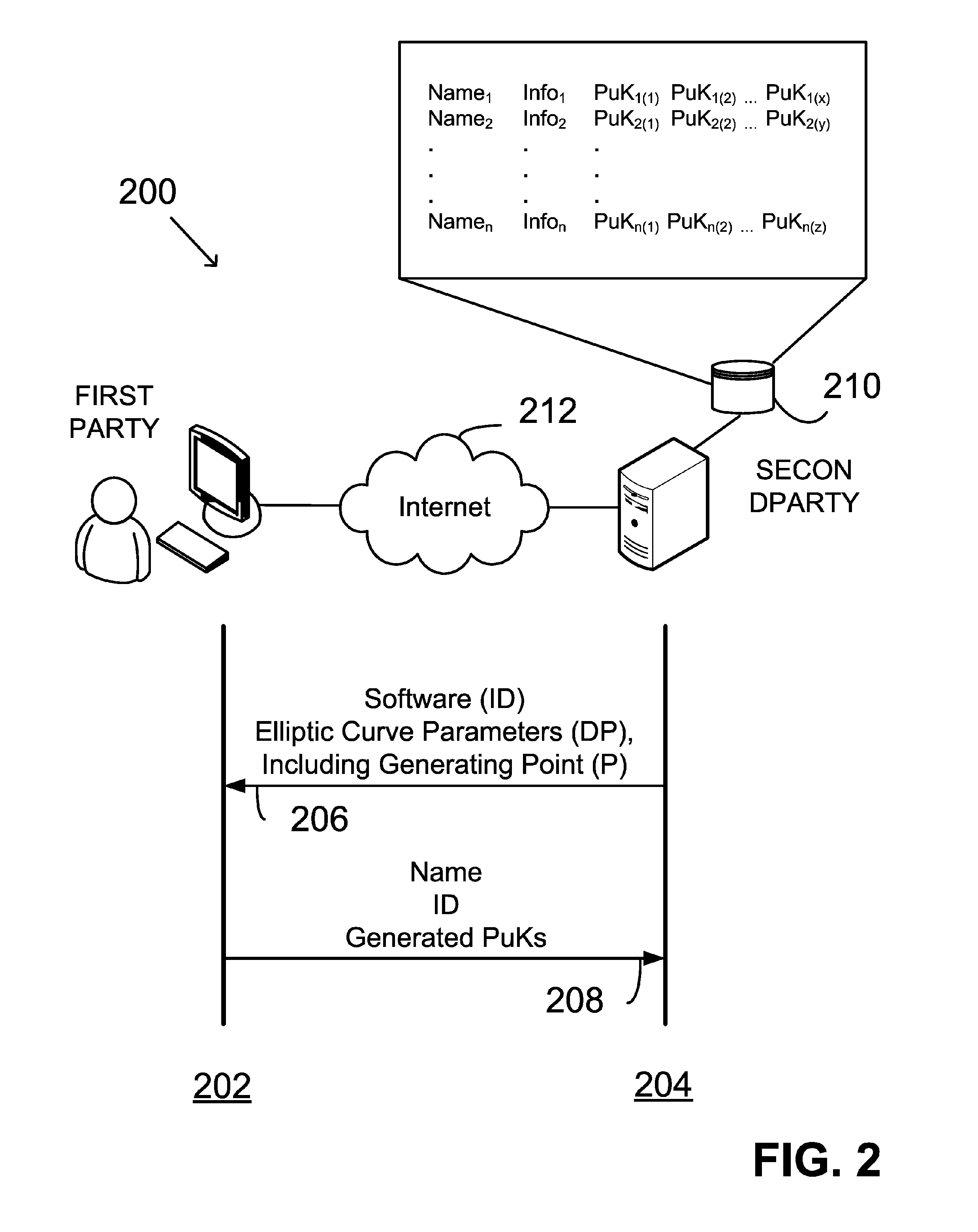
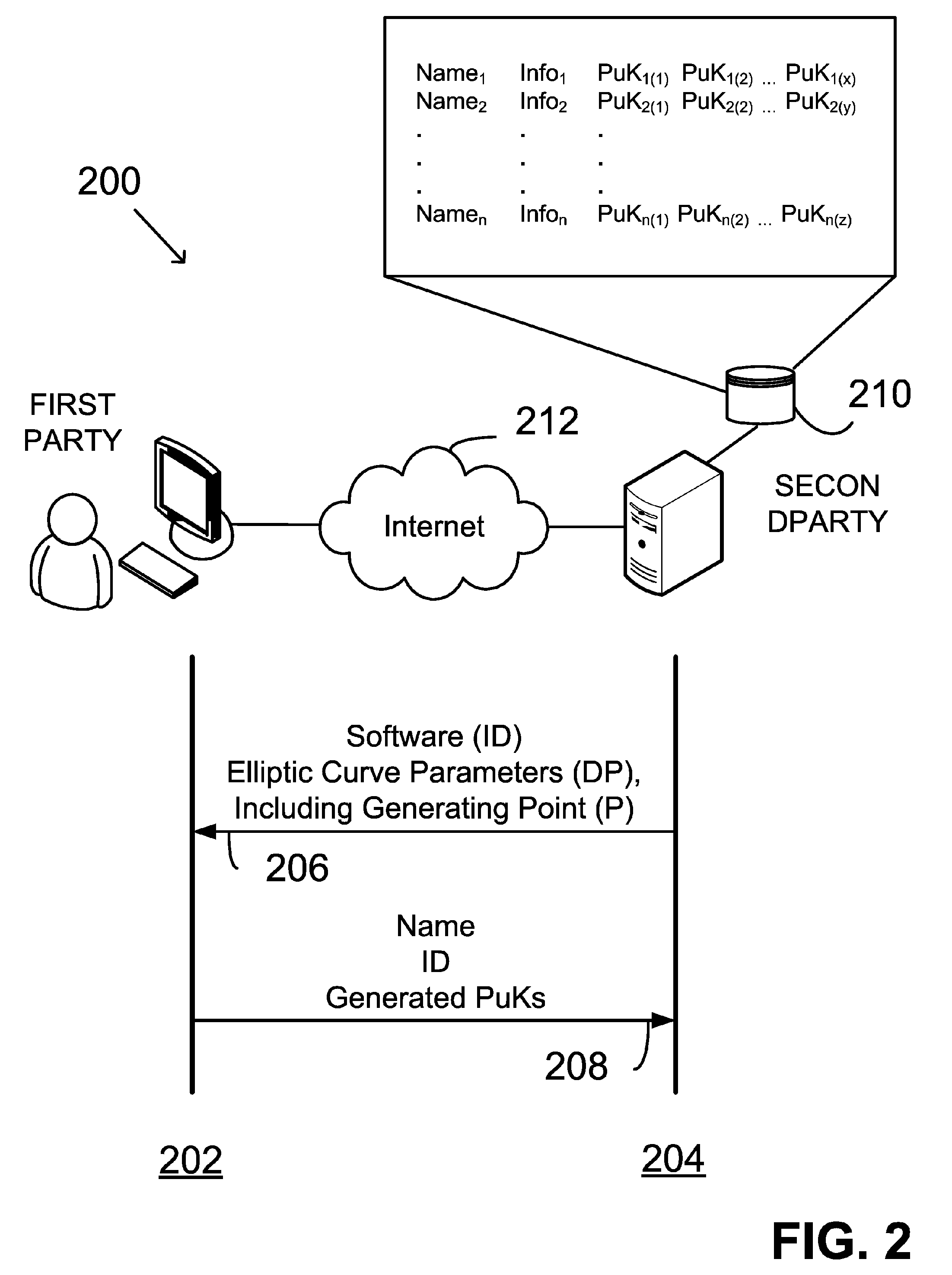
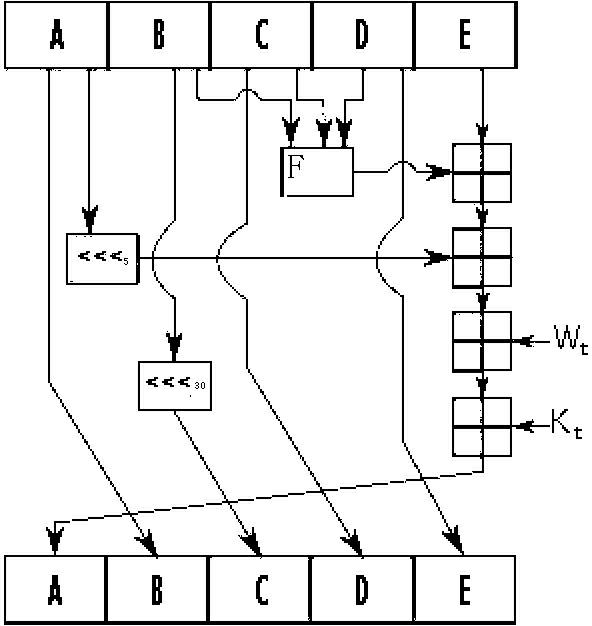
ActiveUS20050138361A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer graphics (images)Deterministic function
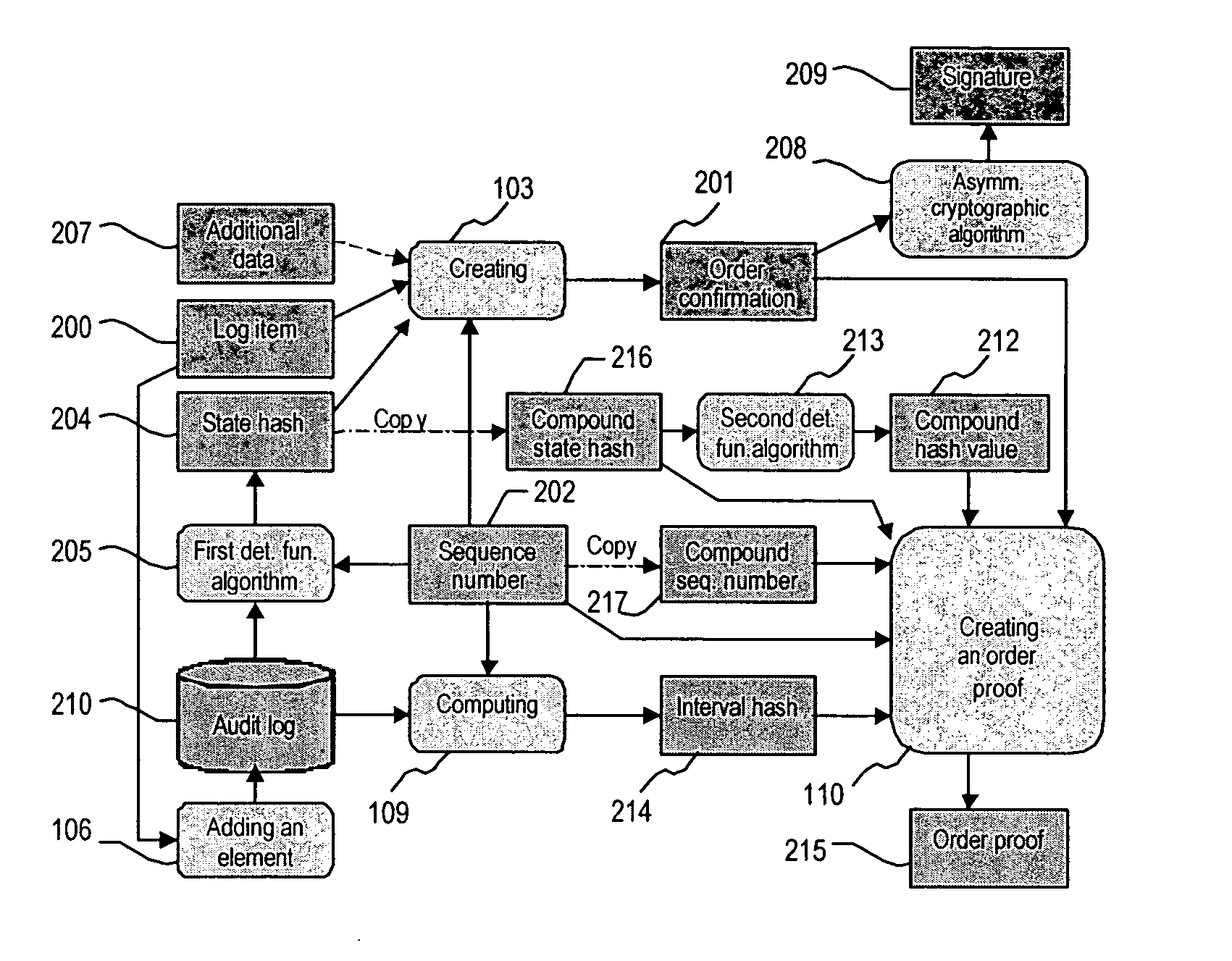
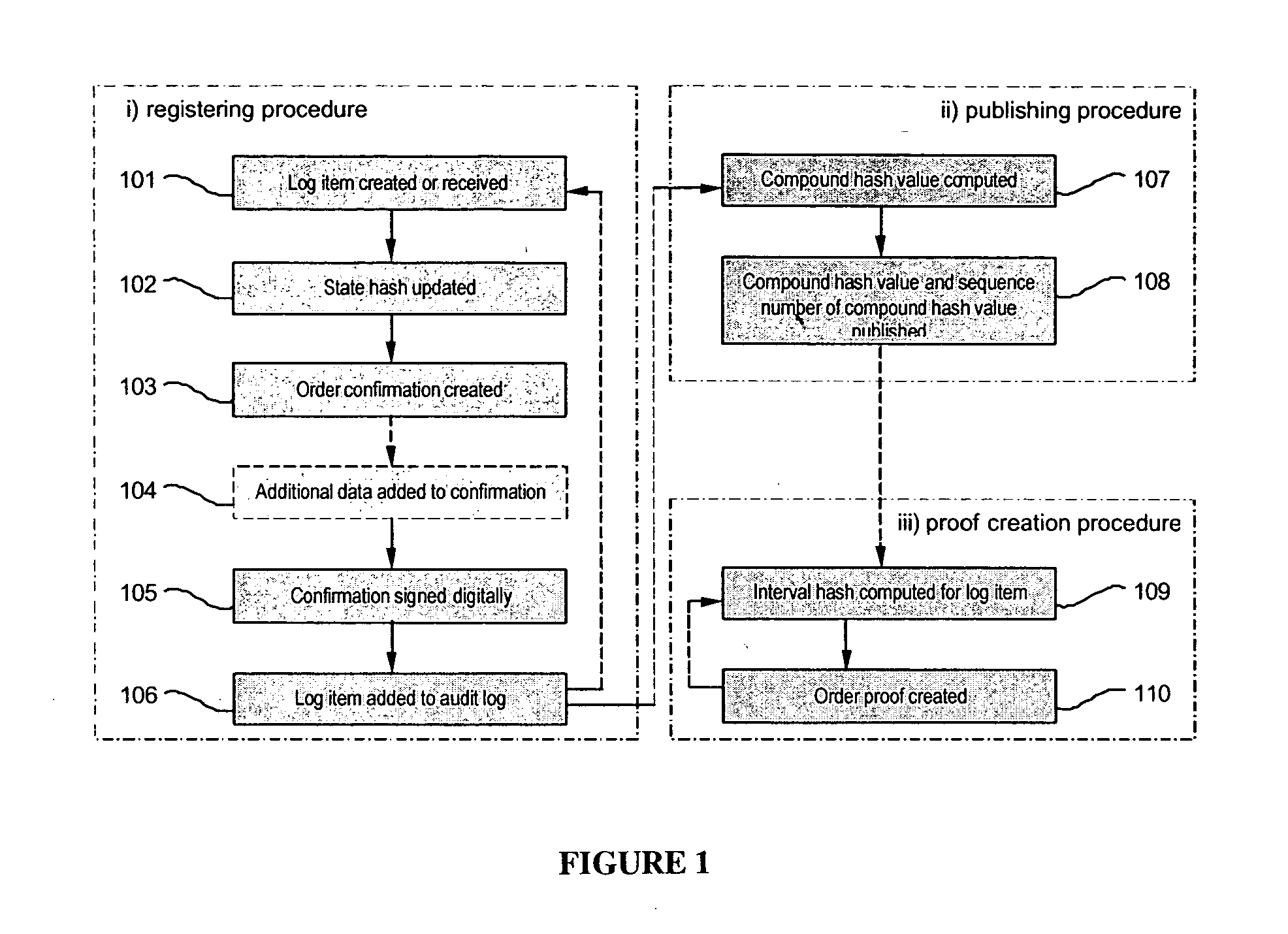
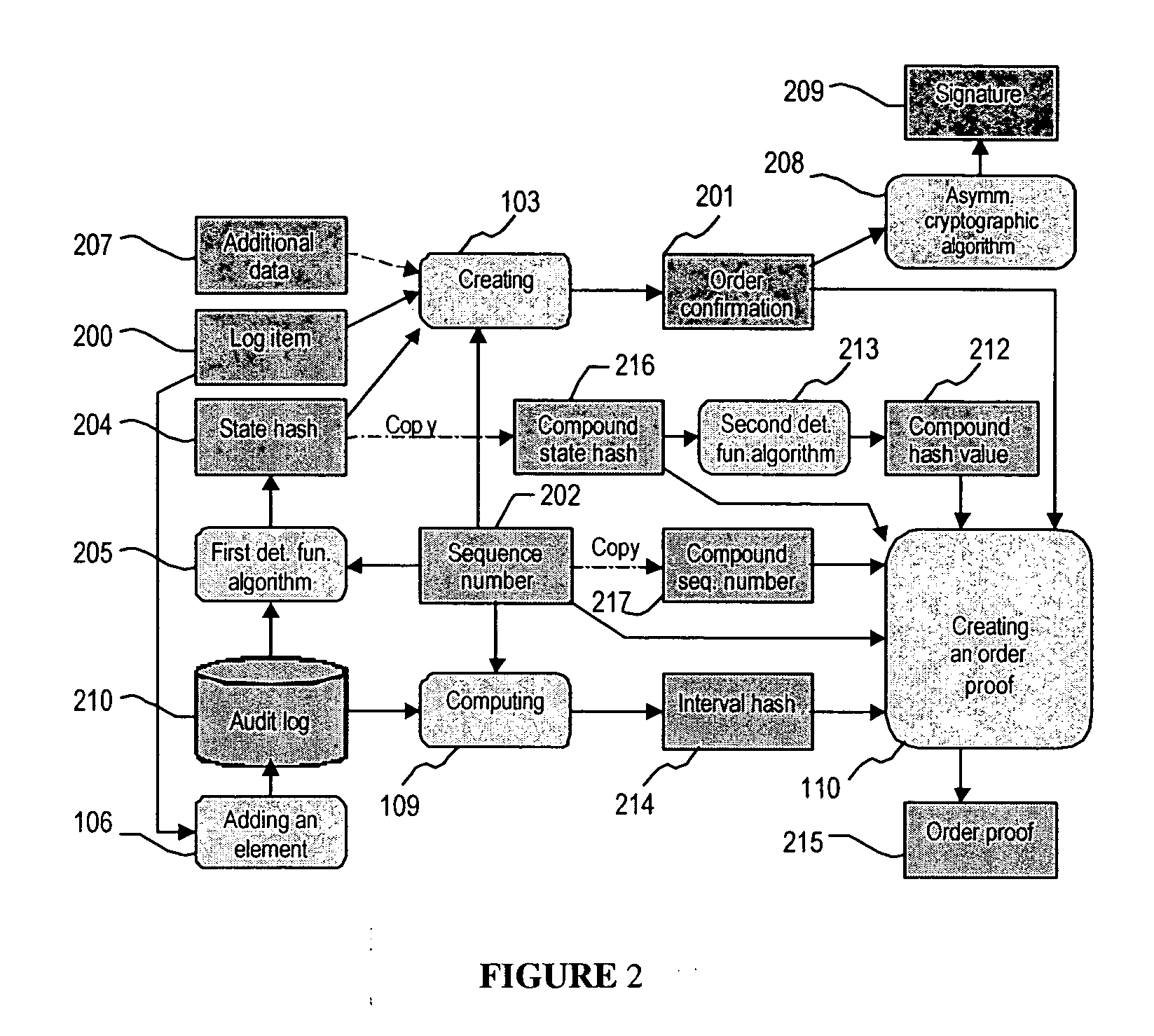
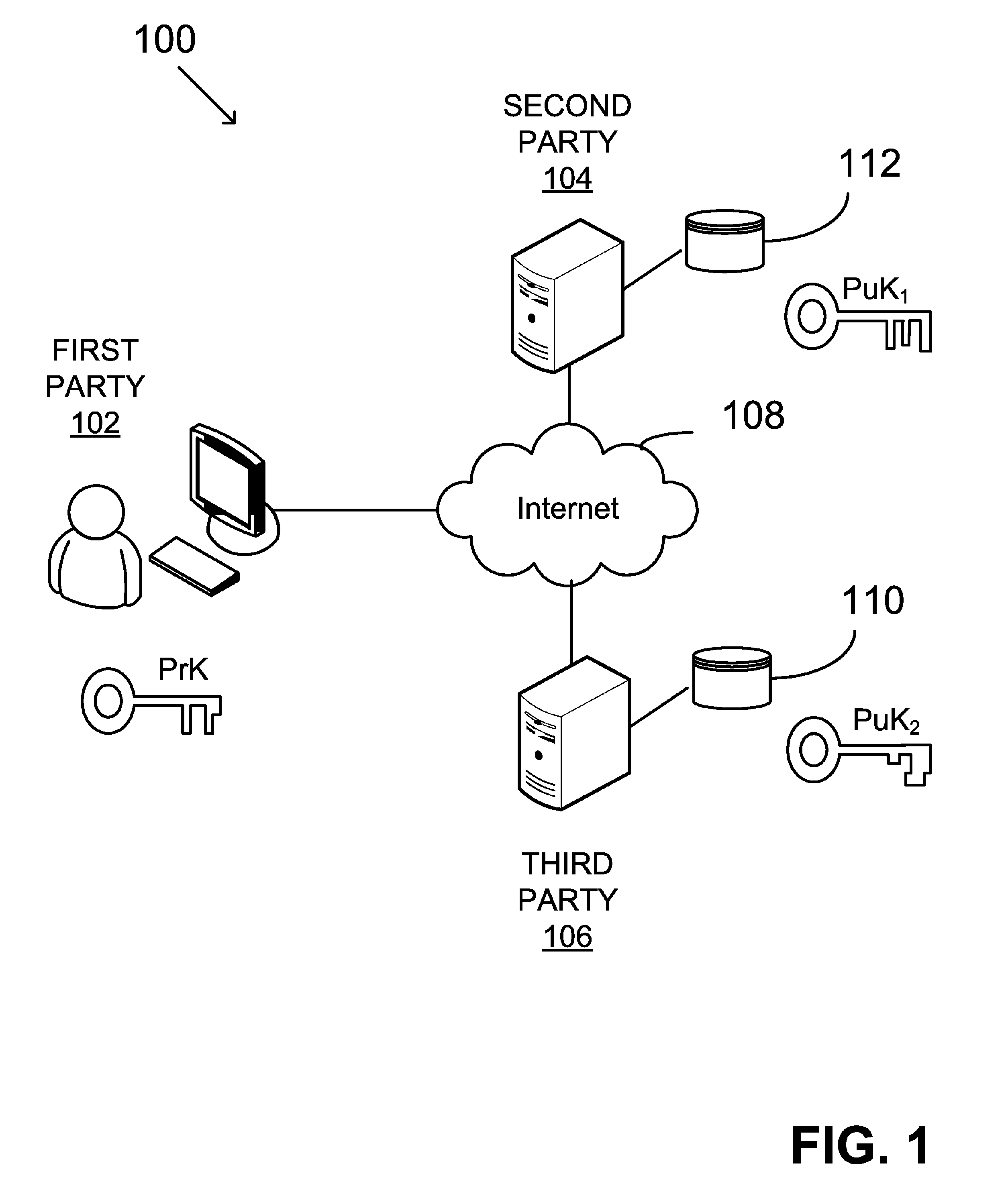
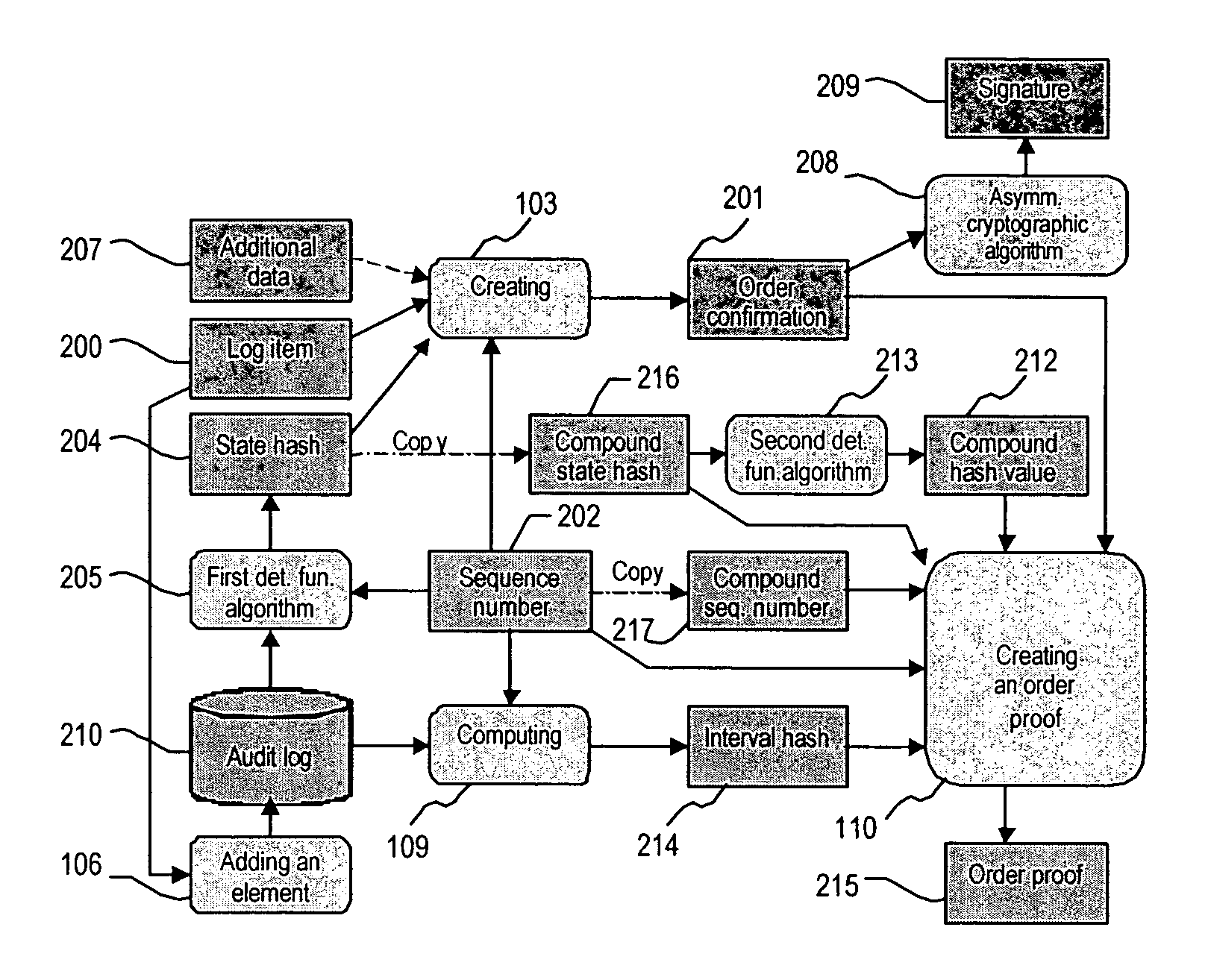
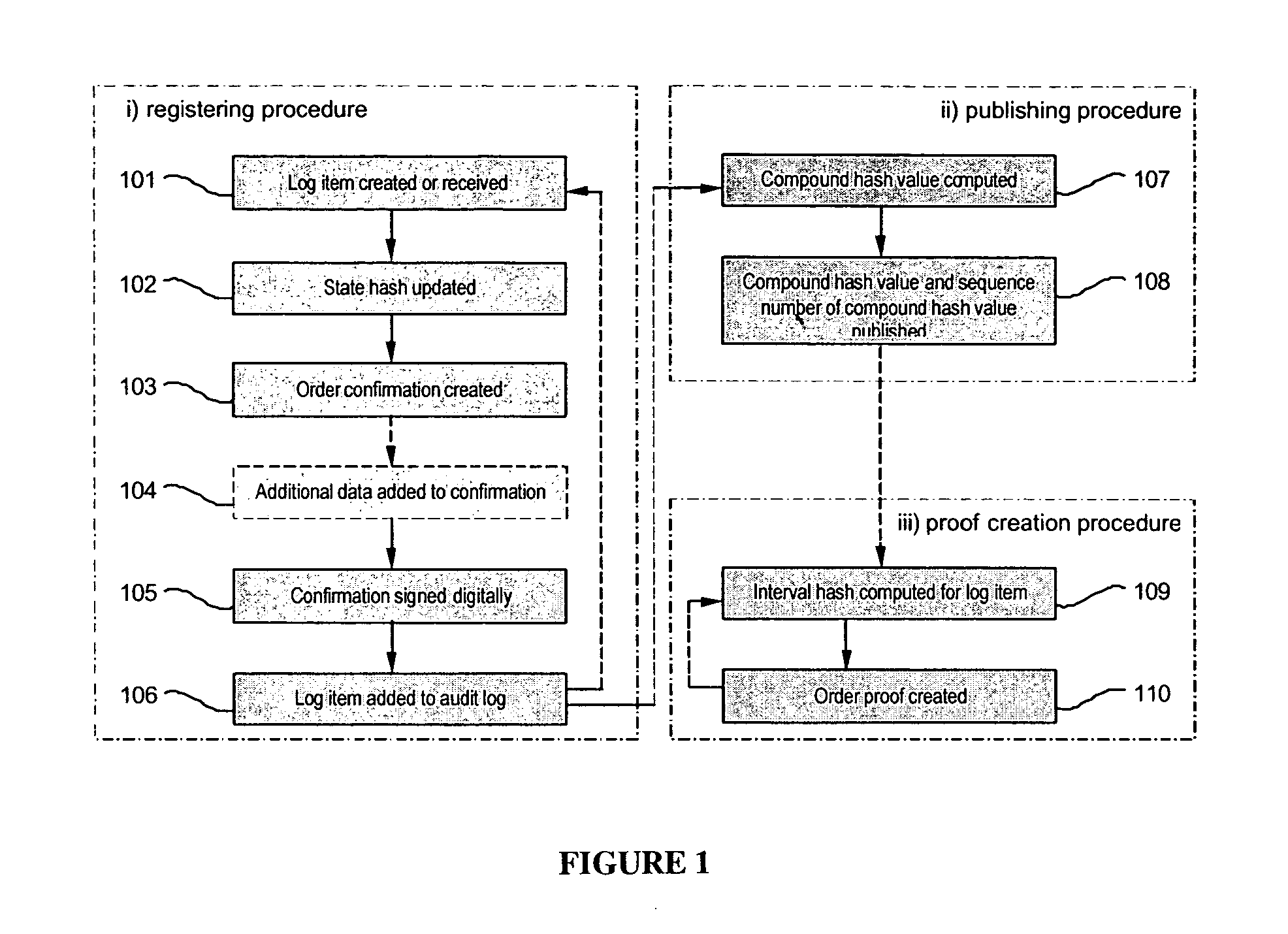
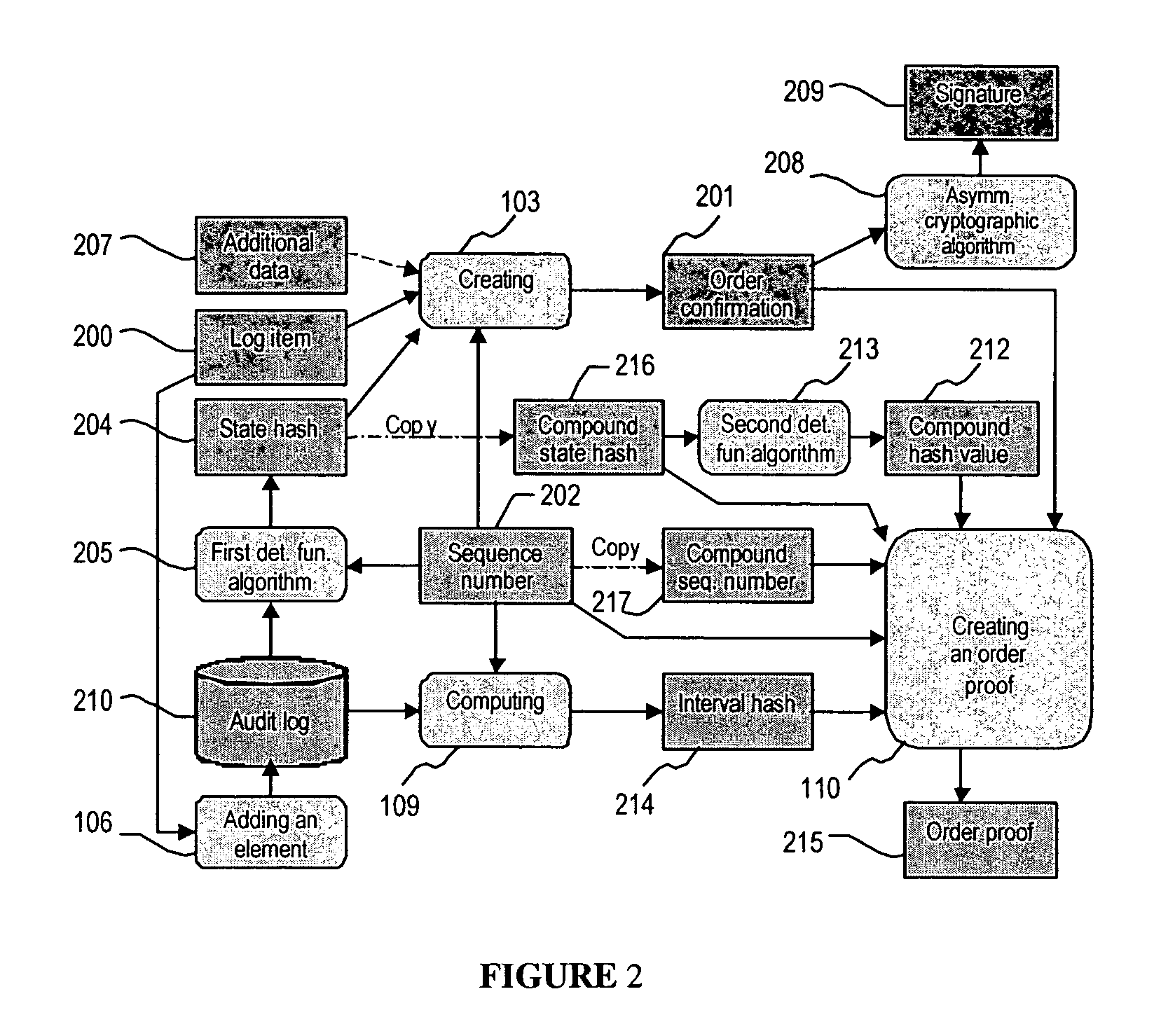
A system and method for generating a digital certificate is provided wherein a new digital record is received and is assigned a sequence value. A first composite digital value is generated by applying a first deterministic function to the digital records stored in a repository. The sequence value and first composite digital value are included in a first certificate. After the digital record is added to the repository, a second composite digital value is generated by applying a second deterministic function to the digital records in the repository. This second composite digital value, and a composite sequence value, are published. An interval digital value which is based upon the first and second composite digital values, and the sequence value, are included in a second certificate which thus verifies the authenticity and sequence value of the digital record.
Owner:GUARDTIME SA
Facilitating digital signature based on ephemeral private key
InactiveUS20060156012A1Facilitating adoption and useUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionUser inputDigital signature
Facilitating communication using a digital signature includes: receiving user input data (UID); generating a first key as a deterministic function of the UID; clearing the UID; generating a second key as a deterministic function of the first key; clearing the first key following generation of the second key; and exporting the second key. Neither the UID nor the first key is exported. Thereafter, a digital signature is generated by again receiving the UID; regenerating the first key using the deterministic function and the UID; clearing the UID; generating a digital signature as a function of the regenerated first key; clearing the regenerated first key following generation of the digital signature; and exporting the generated digital signature.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Asymmetric key cryptosystem based on shared knowledge
InactiveUS20060153364A1Facilitating adoption and usePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationDigital signatureTheoretical computer science
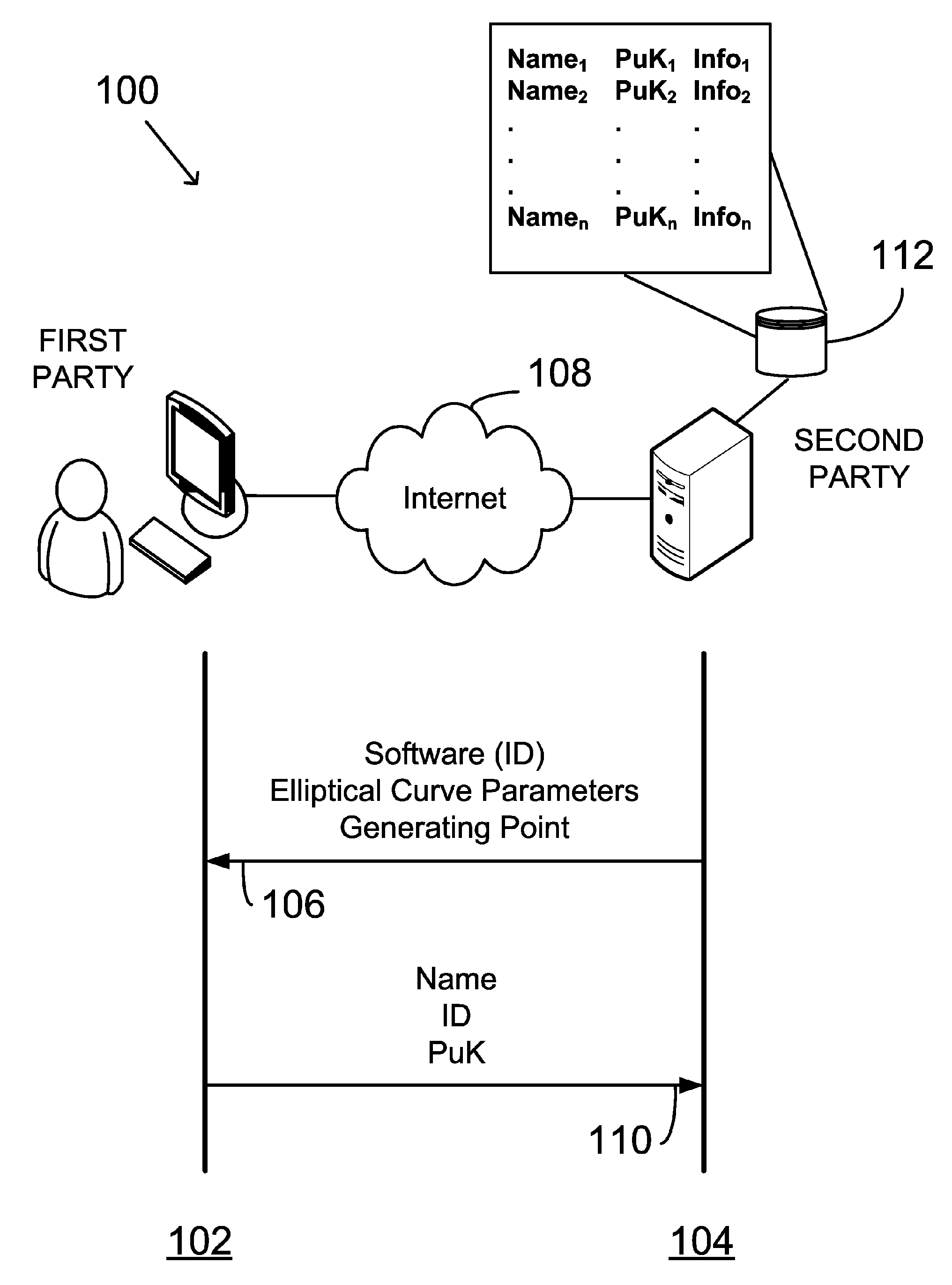
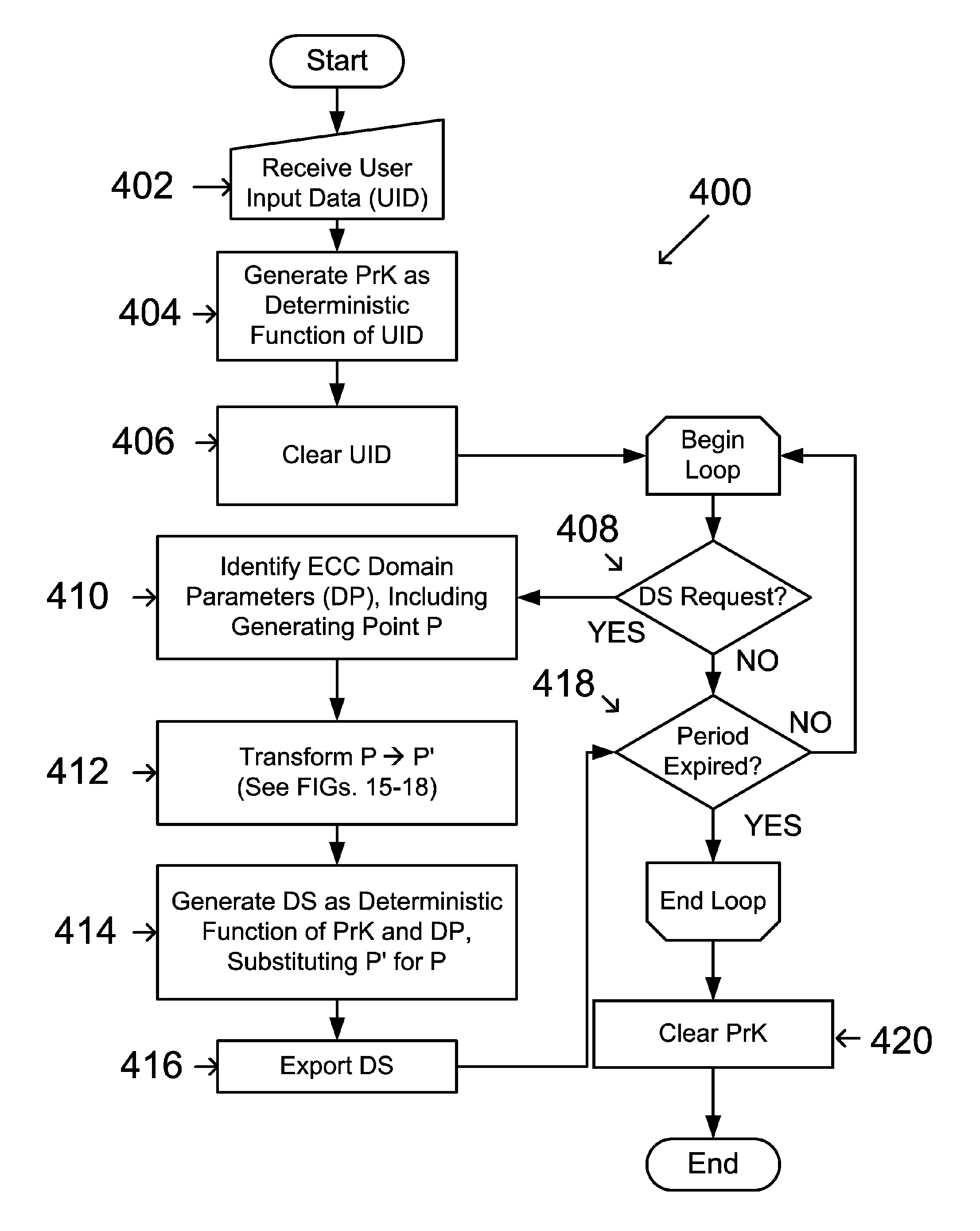
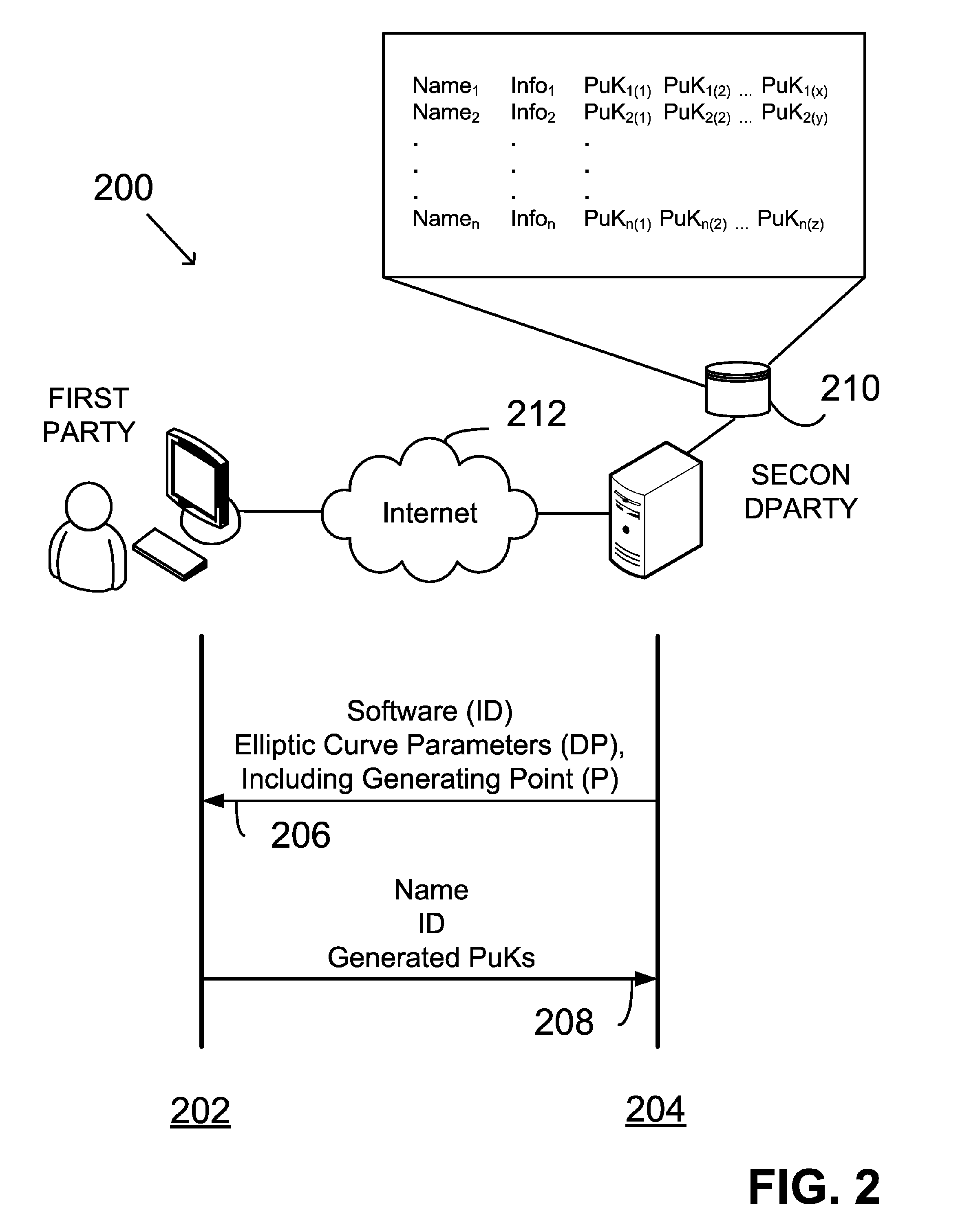
An asymmetric key cryptosystem is provided using a private key of a public-private key pair by: identifying domain parameters of a finite cyclic group, the domain parameters including an initial generating point; transforming the initial generating point into a new generating point as a deterministic function; generating the public key as a deterministic function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point; and generating the digital signature as a deterministic function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point.
Owner:FIRST DATA
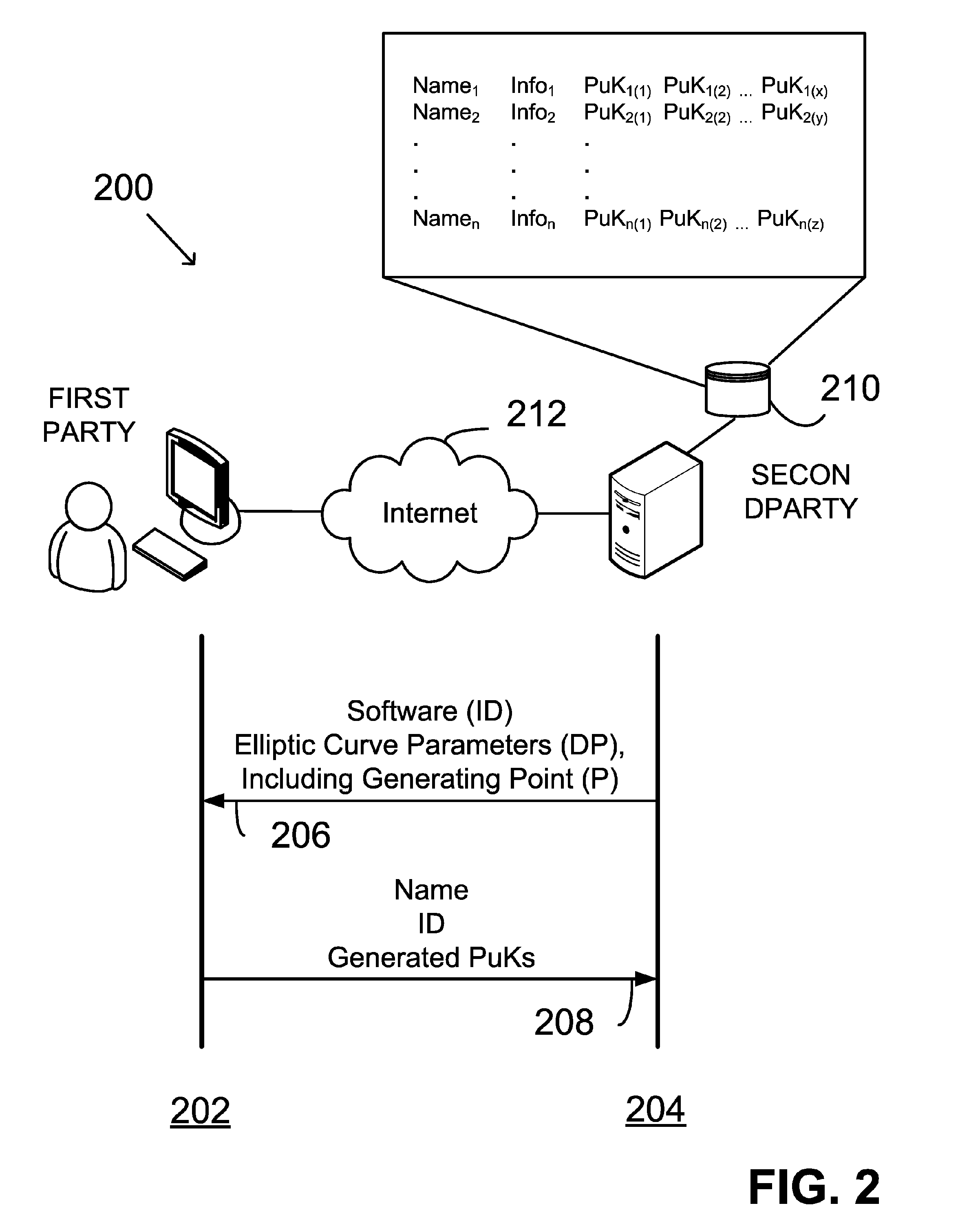
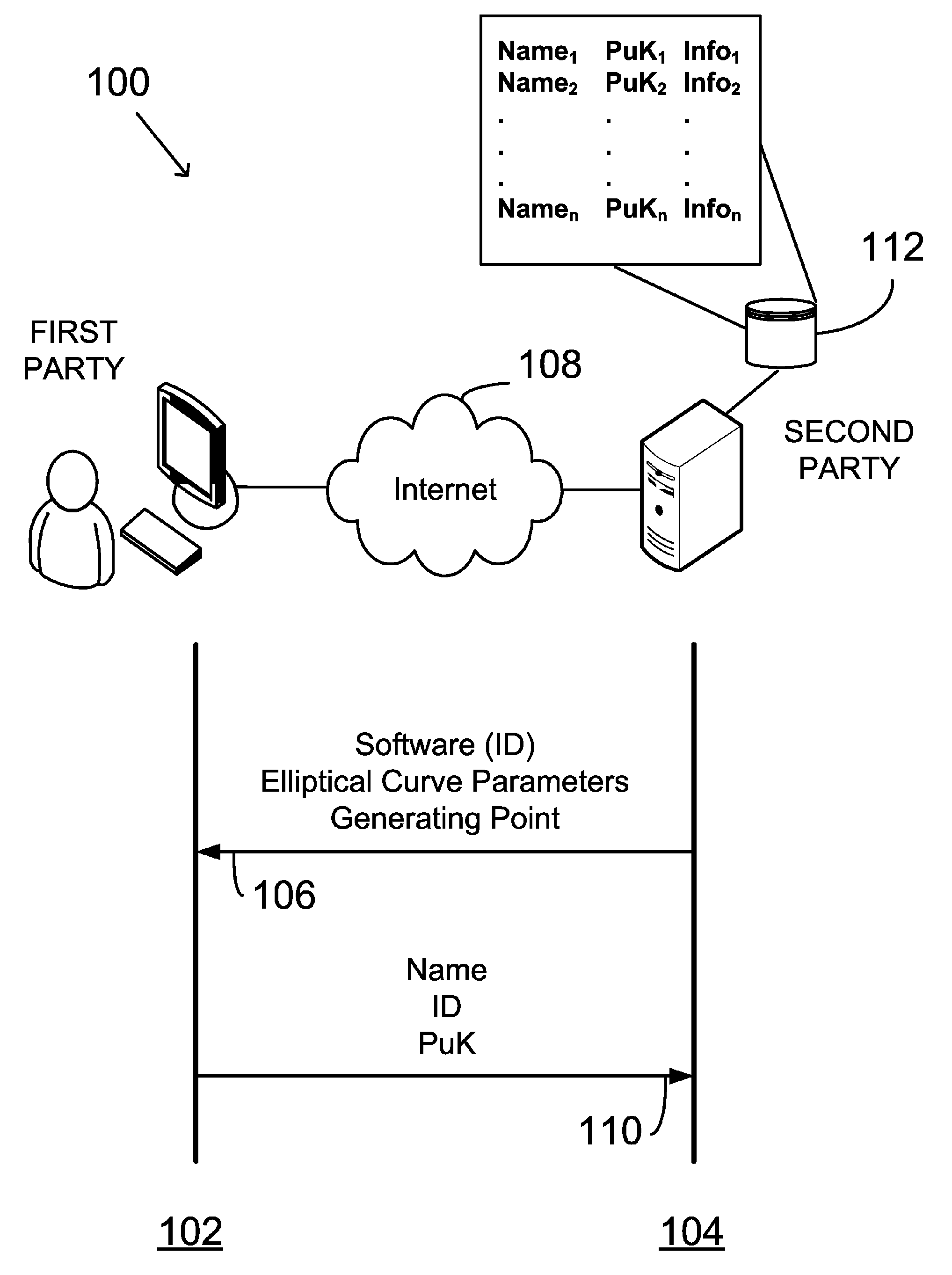
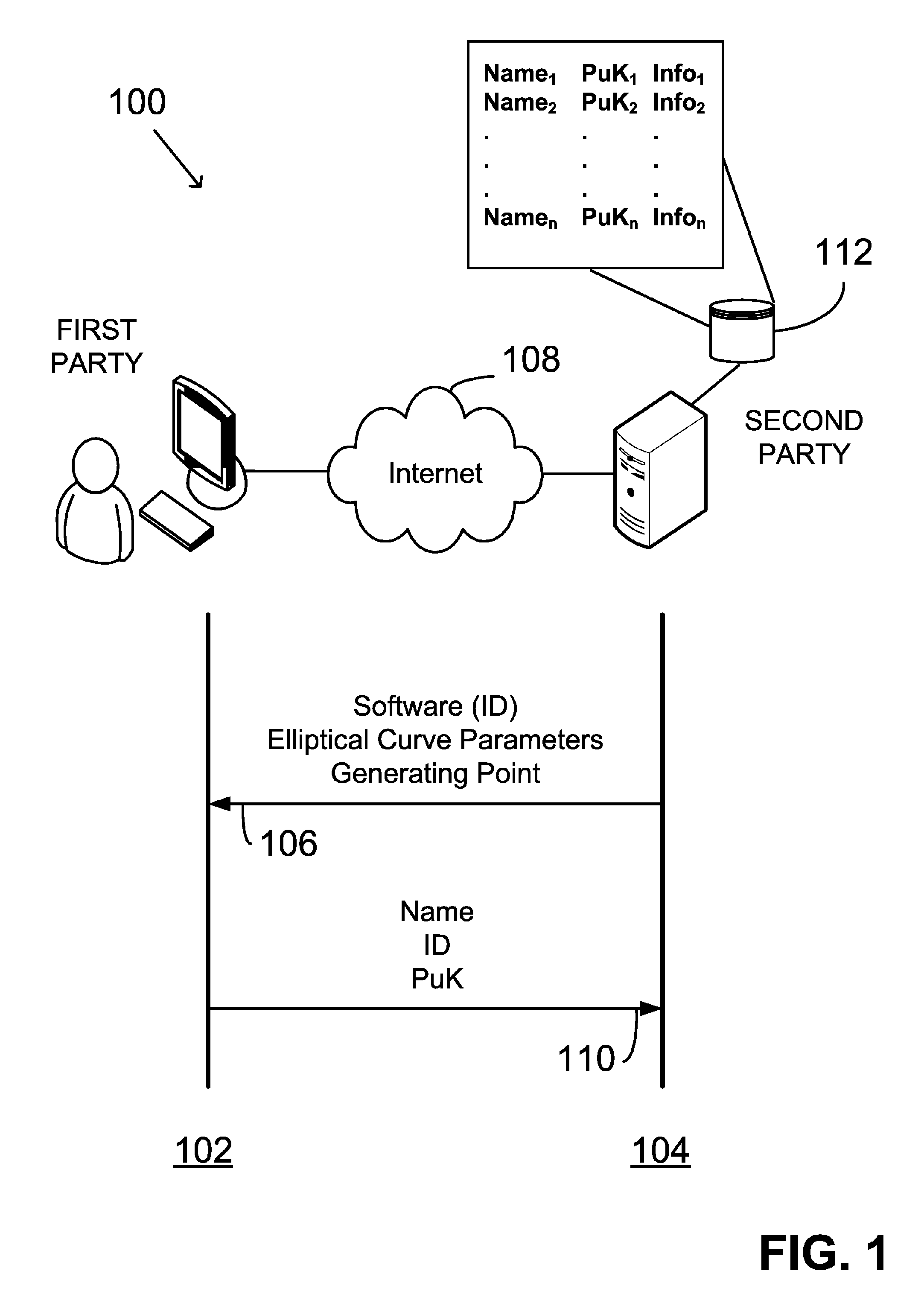
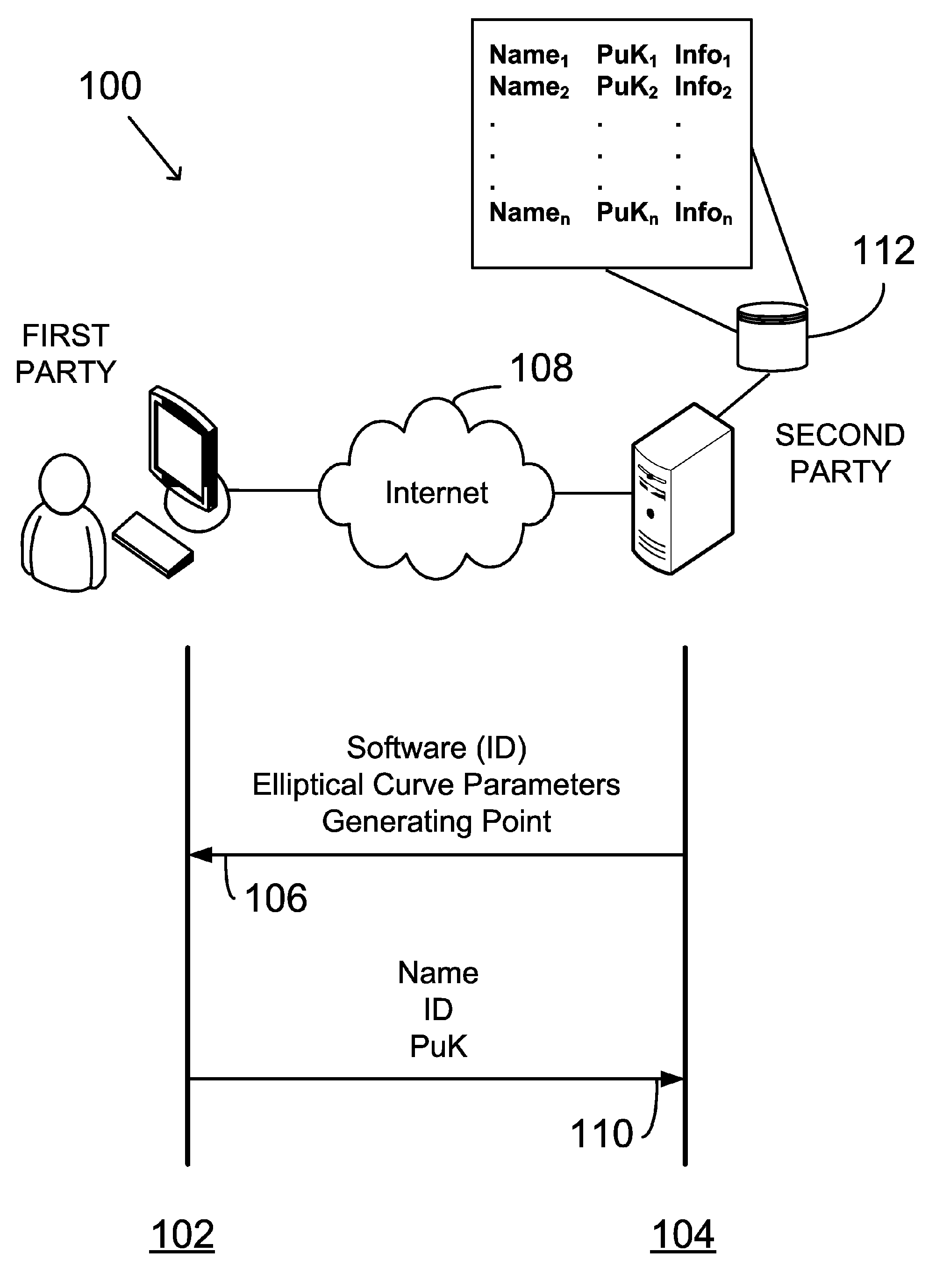
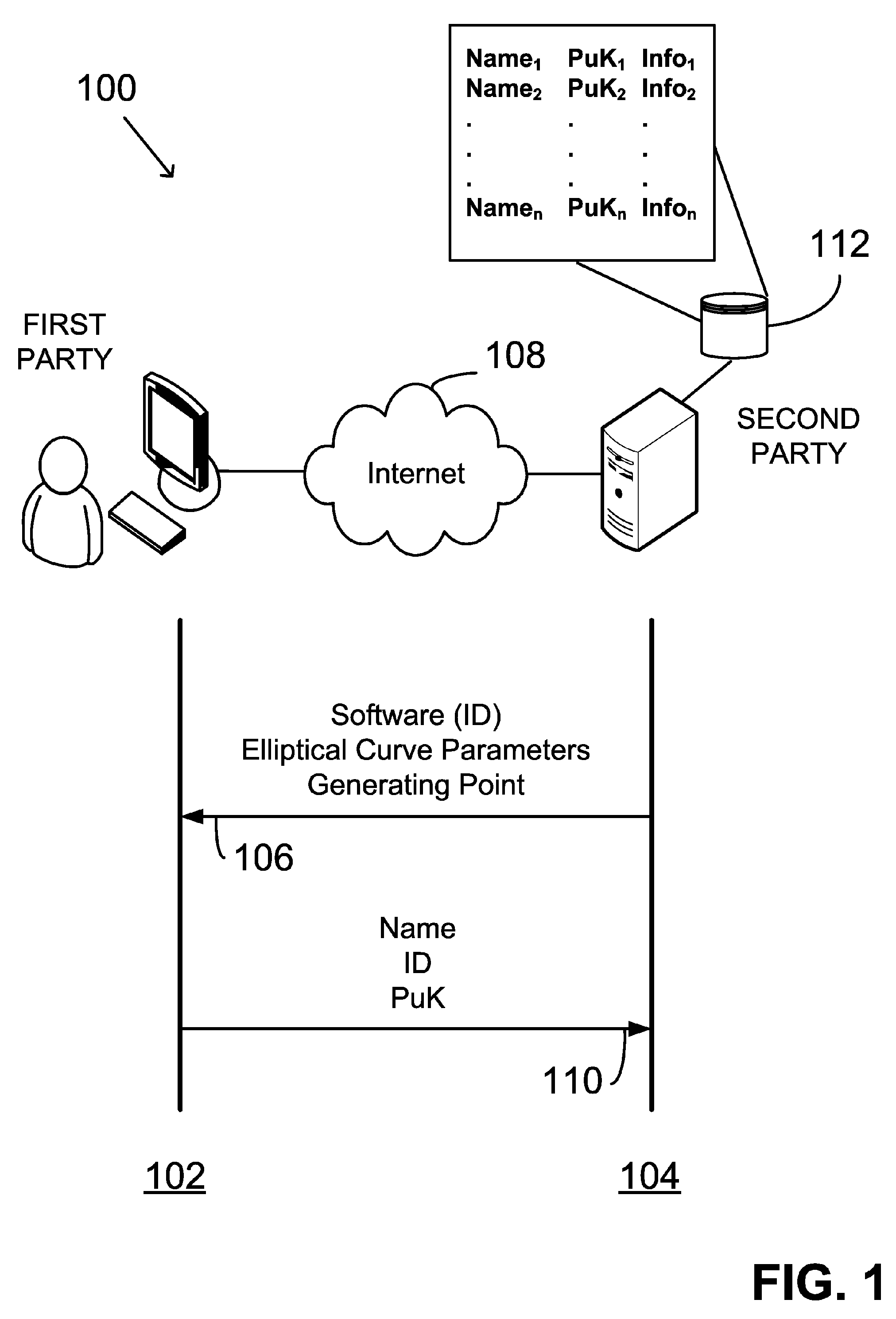
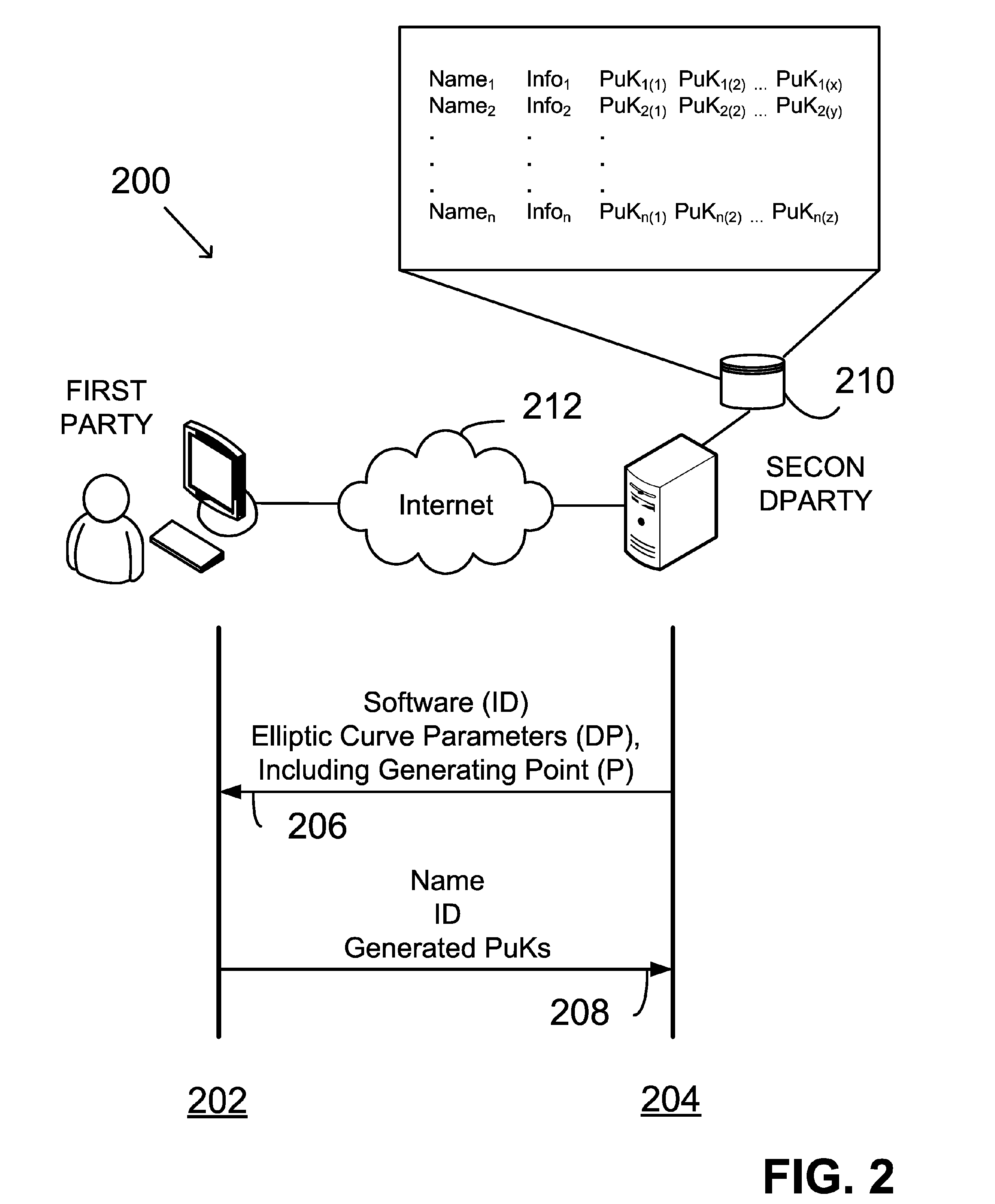
Generating public-private key pair based on user input data
InactiveUS20060153370A1Facilitating adoptionEasy to usePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareUser input
Keys of a public-private key pair are provided by: receiving into a computer system input data from a user (UID); generating within the computer system a first key as a deterministic function of the UID; and generating within the computer system a second key as a deterministic function of the first key. The first key is the private key and the second key is the public key. The first key is cleared from the computer system following generation of the second key. Neither the UID nor the first key is exported from the computer system. The second key may be exported from the computer system.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Electronic transformer error prediction method
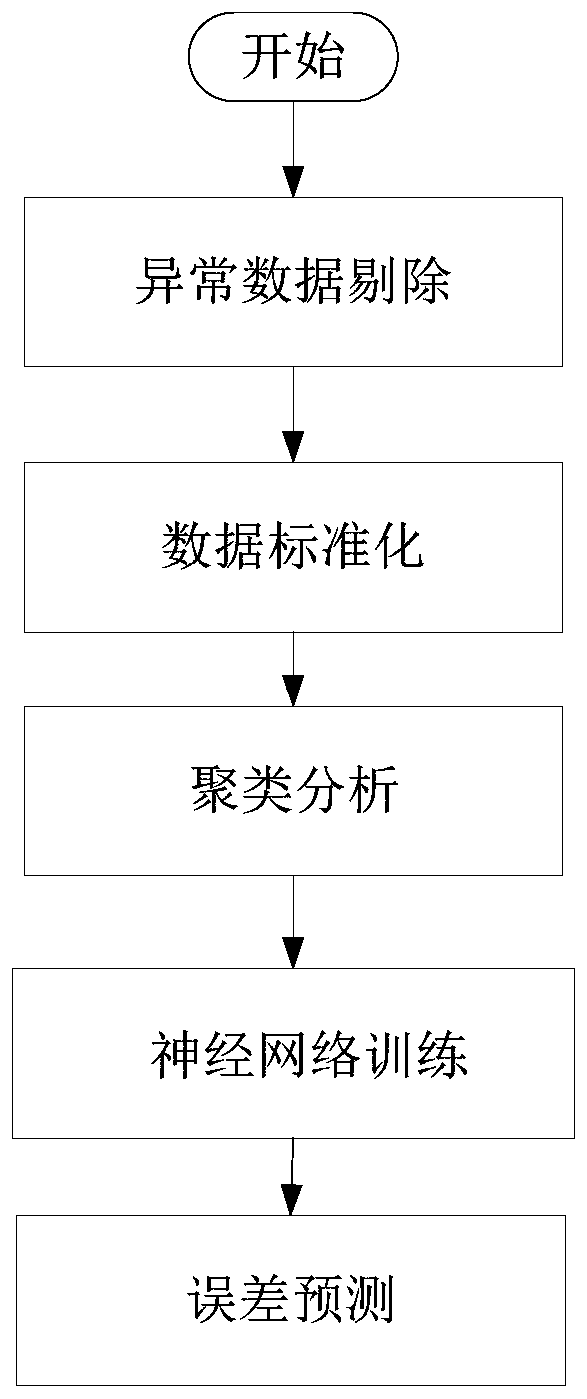
ActiveCN110095744ASolve the problem that there is no definite functional relationshipRealize online estimationElectrical measurementsTransformerDeterministic function
The invention discloses an electronic transformer error prediction method. The method comprises: collecting error data and environmental parameter data of an electronic transformer to generate sampledata and rejecting abnormal data among the collected data; on the basis of a Z-score standardization method, carrying out standardization processing on the sample data; carrying out clustering processing on historical data of environmental parameters and establishing an electronic transformer error prediction model by training and learning; and according to the environmental parameter values, predicting a ratio error and an angular difference of the electronic transformer based on a prediction model. The method has the following advantages: no physical model needs to be established; on the basis of the multi-dimensional data driving method, the online estimation of the electronic transformer error can be realized according to the error data and environmental parameter data of the electronic transformer, so that a problem that no deterministic function relation exists between the error and the environmental parameter of the electronic transformer is solved and the accuracy of electronictransformer error prediction is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +5
System and method for compiling temporal expressions
InactiveUS6920583B1Avoid difficult choicesFunctional testingComputer aided designTheoretical computer scienceDeterministic function
A system and method for enabling the behavior of temporal expressions to be analyzed for the evaluation of such expressions. The process of evaluating such expressions ultimately results in the construction of a finite state machine, such that the set of non-deterministic functions for describing the behavior of dynamic and relativistic systems is reduced to such a system. The behavior of the finite state machine can then be examined and analyzed. The present invention is useful for such applications as the examination of the temporal behavior of a DUT (device under test), as well as for examining the behavior of dynamic systems.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN ISRAEL II
Digital signature software using ephemeral private key and system
InactiveUS20060156013A1Facilitating adoption and useUser identity/authority verificationComputer networkDigital signature
Facilitating communication using a digital signature includes: communicating software to a first party; receiving from the first party a public key of a public-private key pair generated using the software; and recording in a database the public key in association with information pertaining to the software. The key pair is generated by: receiving input data from a user (UID); generating the private key as a deterministic function of the UID; clearing the UID from the computer system; generating the public key as a deterministic function of the private key; clearing the private key from the computer system; and exporting the public key. The software generates a digital signature by again receiving the UID and regenerating the private key using the deterministic function and UID, after which, the private key and UID again are cleared.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Systems, Methods, and Computer Program Products for Secure Optimistic Mechanisms for Constrained Devices
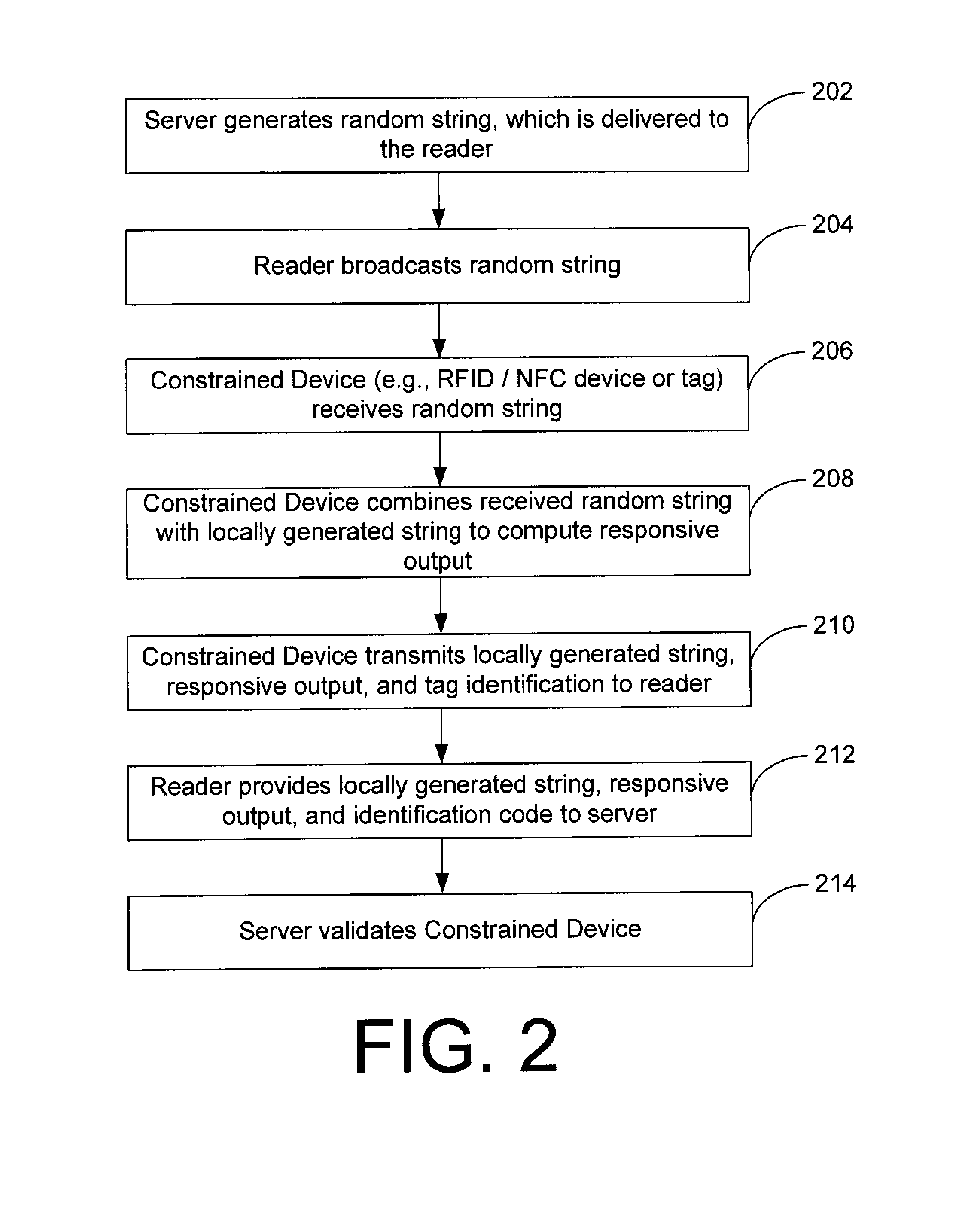
InactiveUS20140019759A1User identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementDeterministic functionRandom string
Embodiments of the invention may provide for systems and methods for secure authentication. The systems and methods may include receiving, by a constrained device, a random string transmitted from a server; determining, by the constrained device, a responsive output by evaluating a first deterministic function based upon the received random string, a locally generated string and a first private key stored on the constrained device; and transmitting at least one portion of the responsive output and the locally generated string from the constrained device to a server. The systems and methods may also include determining, by the server, a validation output by evaluating a second deterministic function based upon the random string, the locally generated string, and a second private key of a plurality of private keys stored on the server; and authenticating the constrained device based upon the server matching the transmitted at least one portion of the responsive output to at least a portion of the validation output.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
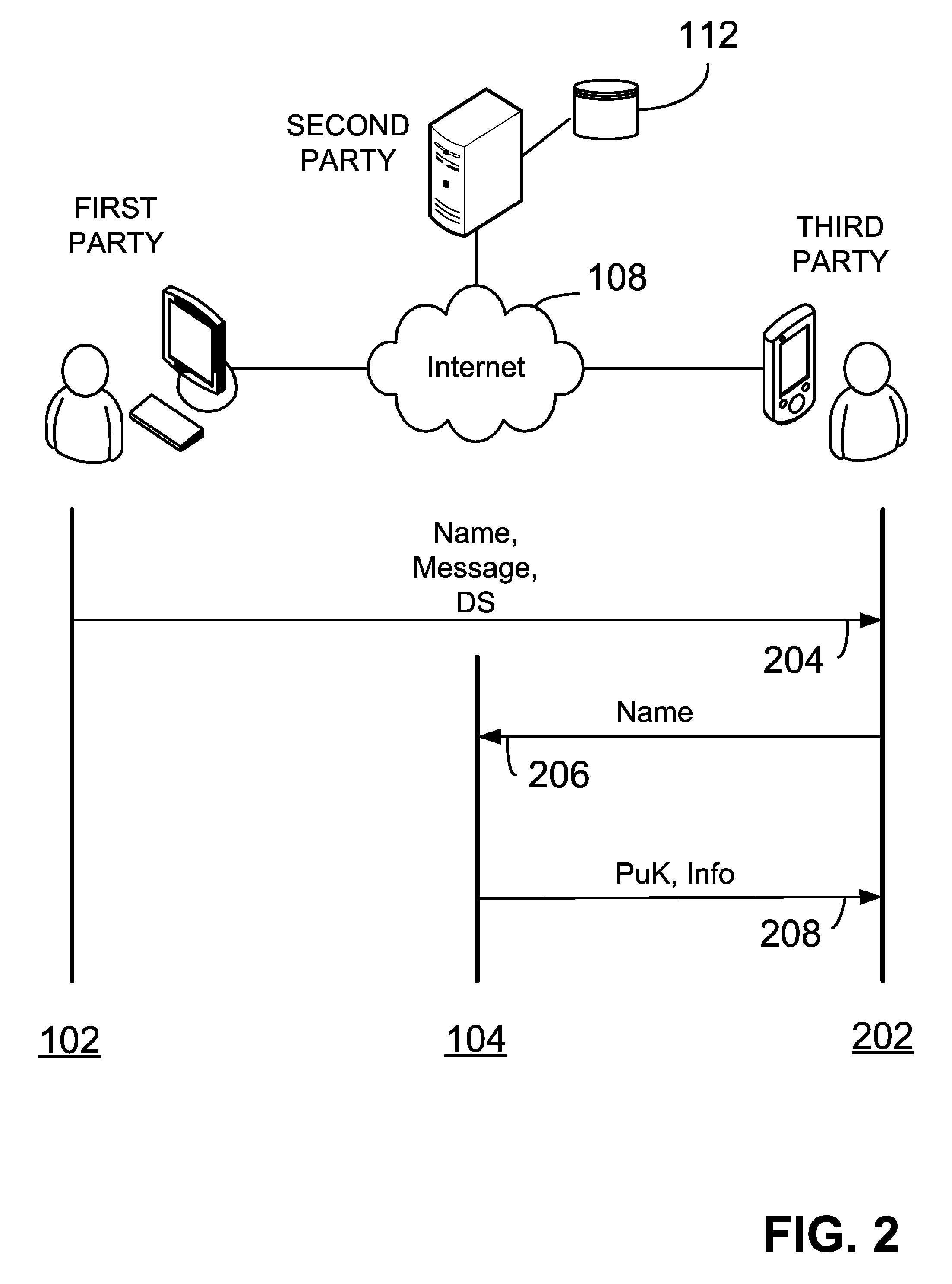
Providing digital signature and public key based on shared knowledge
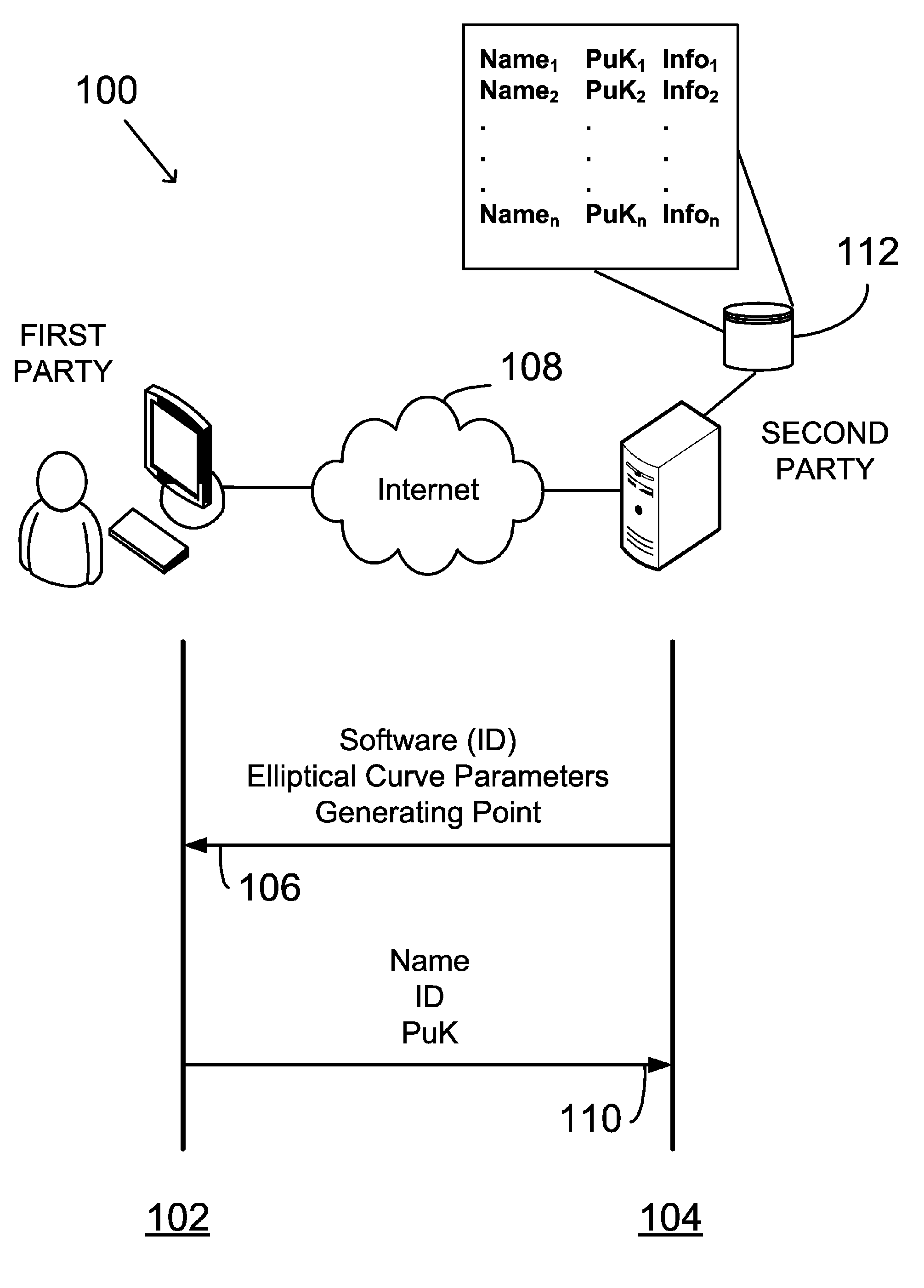
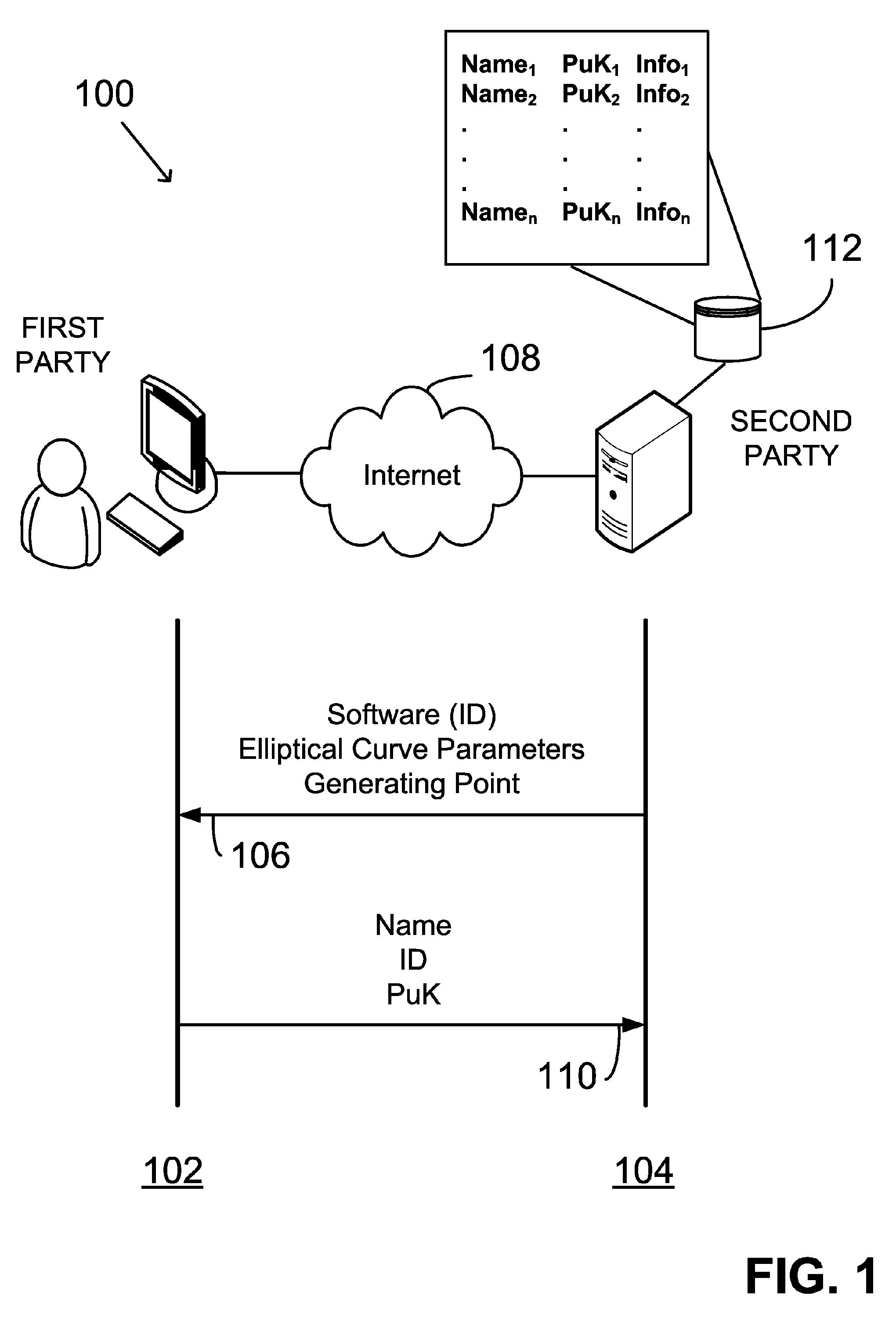
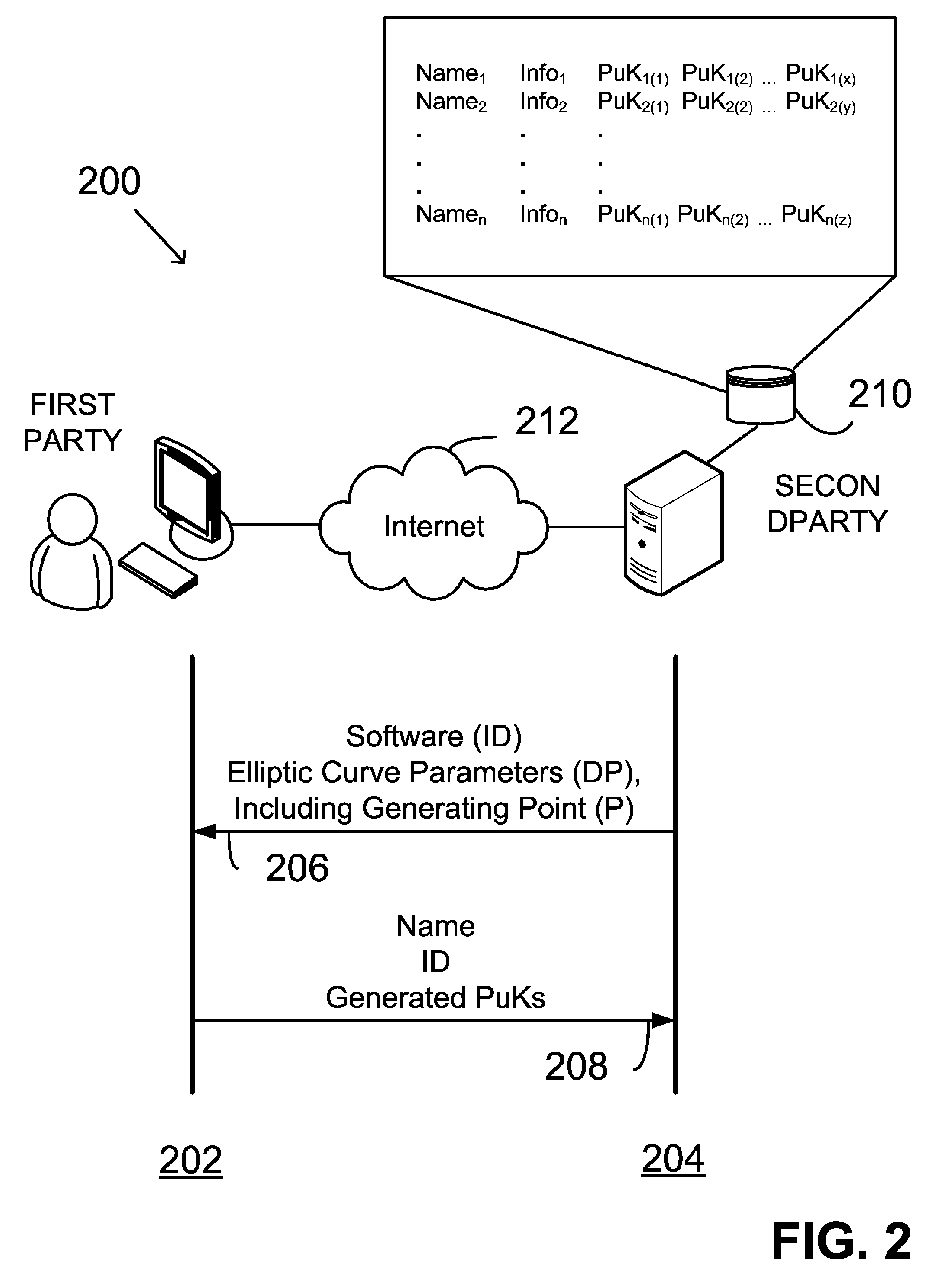
ActiveUS7593527B2Facilitating adoption and usePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureDeterministic function
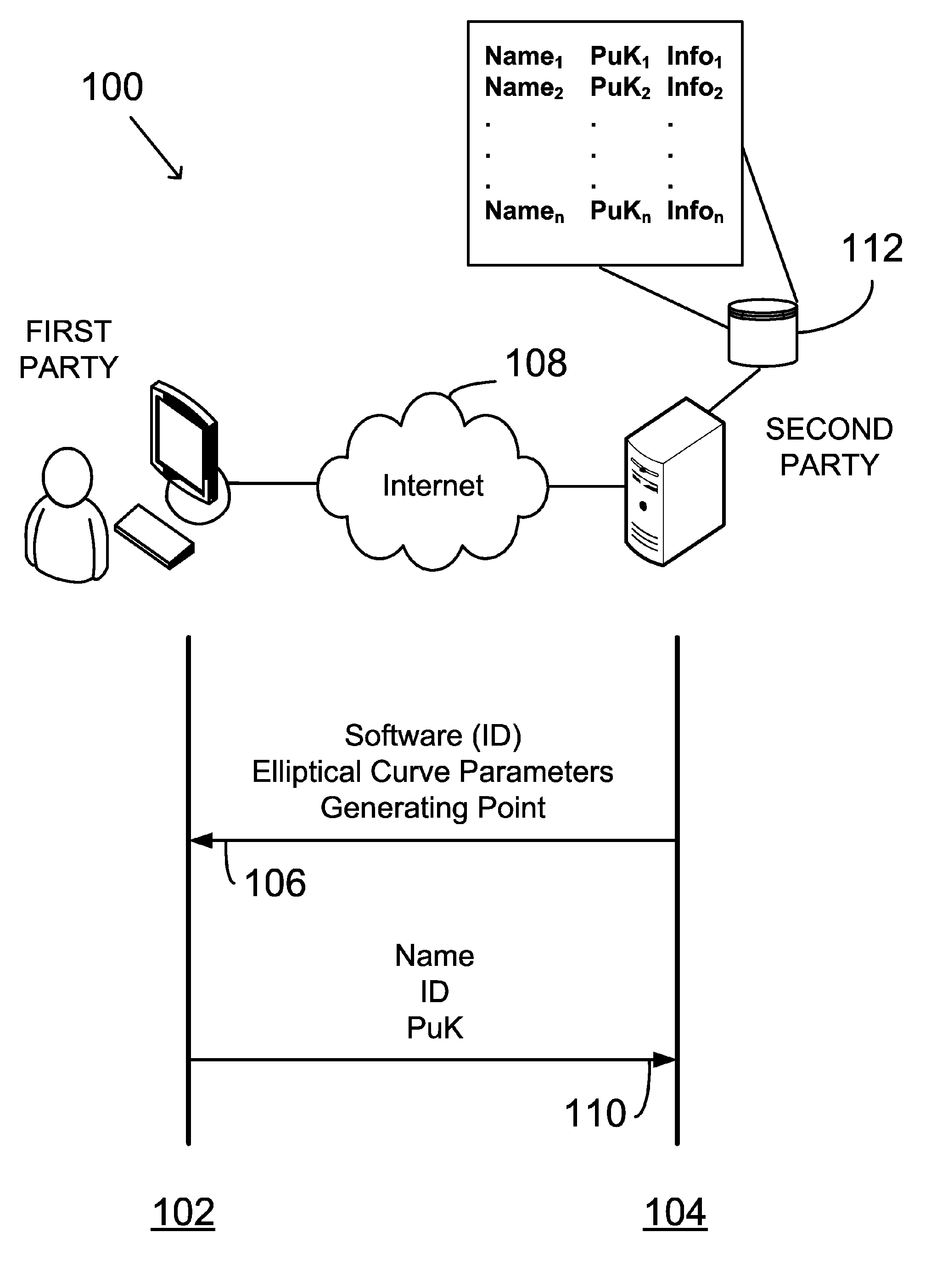
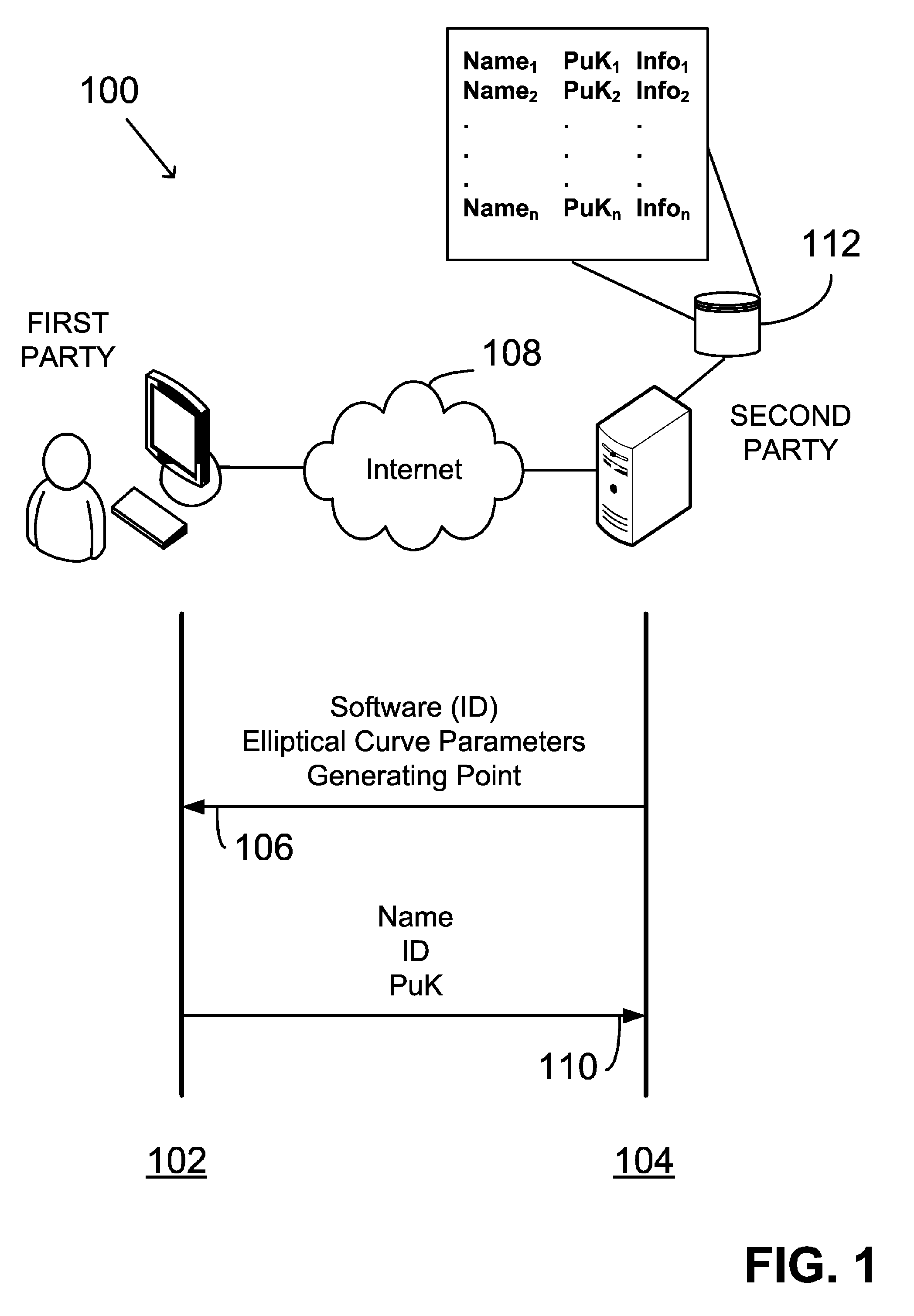
A public key and digital signature is provided using a private key of a public-private key pair in an elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) by: identifying domain parameters of an elliptic curve for use in elliptic curve cryptography, the domain parameters including an initial generating point; transforming the generating point into a new generating point as a deterministic function; generating the public key as a deterministic function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point; and generating the digital signature as a function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point.
Owner:FIRST DATA
System and method for generating a digital certificate
ActiveUS7698557B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer graphics (images)Digital recording
A system and method for generating a digital certificate is provided wherein a new digital record is received and is assigned a sequence value. A first composite digital value is generated by applying a first deterministic function to the digital records stored in a repository. The sequence value and first composite digital value are included in a first certificate. After the digital record is added to the repository, a second composite digital value is generated by applying a second deterministic function to the digital records in the repository. This second composite digital value, and a composite sequence value, are published. An interval digital value which is based upon the first and second composite digital values, and the sequence value, are included in a second certificate which thus verifies the authenticity and sequence value of the digital record.
Owner:GUARDTIME SA
Providing cryptographic key based on user input data
InactiveUS20060153369A1Facilitating adoption and usePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationUser inputComputerized system
A cryptographic key is provided based on user input data (UID) by: receiving into a computer system the UID; generating within the computer system the cryptographic key as a deterministic function of the UID; and clearing from the computer system the UID following the generation of the cryptographic key. The UID is not exported from the computer system. The cryptographic key may be a public key or private key. If the cryptographic key is a public key, then the cryptographic key is exported from the computer system. If the cryptographic key is a private key, then the cryptographic key is not exported from the computer system, and is cleared from the computer system within a single day of the generation of the cryptographic key.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Providing digital signature and public key based on shared knowledge
ActiveUS20060153365A1Facilitating adoptionEasy to usePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureDeterministic function
A public key and digital signature is provided using a private key of a public-private key pair in an elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) by: identifying domain parameters of an elliptic curve for use in elliptic curve cryptography, the domain parameters including an initial generating point; transforming the generating point into a new generating point as a deterministic function; generating the public key as a deterministic function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point; and generating the digital signature as a function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the new generating point is substituted for the initial generating point.
Owner:FIRST DATA
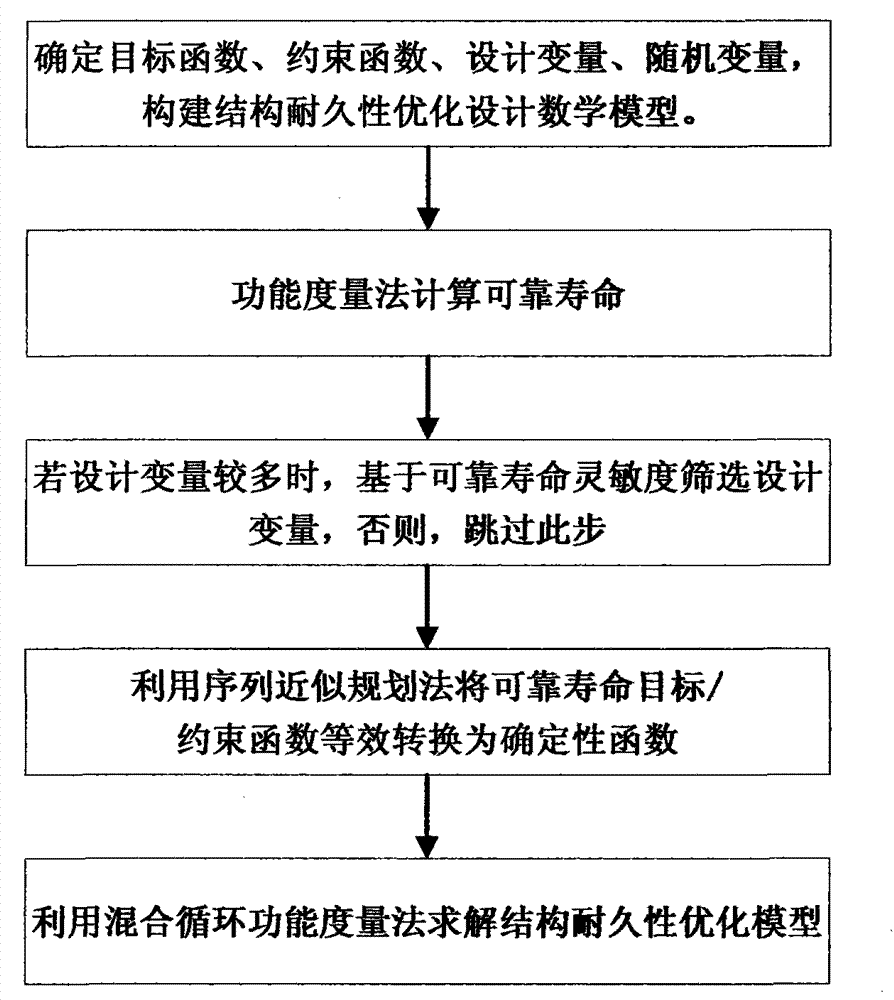
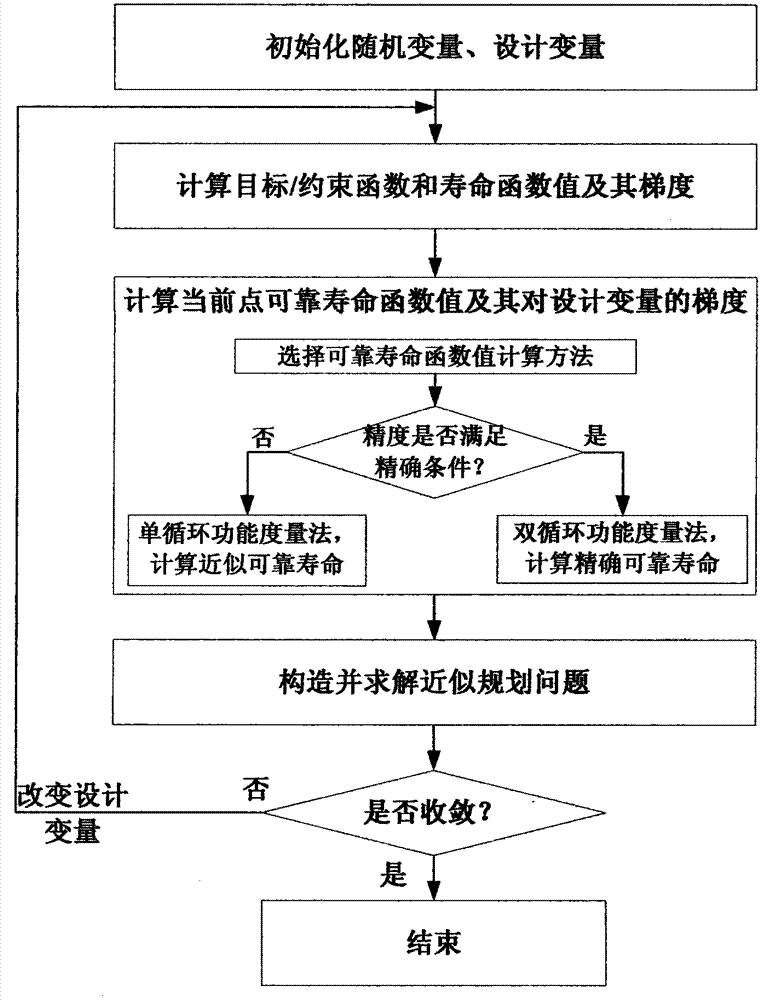
Method for optimally designing durability of structure on basis of reliable service life
InactiveCN103399992AImprove efficiencyFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelDeterministic function
The invention provides a method for optimally designing the durability of a structure. The reliable service life is an object / a constraint in the method. The method mainly includes five steps of determining objective functions, constraint functions, design variables and random variables and constructing a mathematical model for optimally designing the durability of the structure; computing the reliable service life by a function measurement process; screening the design variables on the basis of the sensitivity of the reliable service life; equivalently converting the objective function / the constraint functions of the reliable service life into deterministic functions by a sequential approximation programming process; solving a model for optimizing the durability of the structure by a mixed cycle function measurement process. The method has the advantage that an optimal design scheme which meets the requirement on the longest reliable service life of the structure or the durability of the structure can be determined by means of an optimal design.
Owner:中国兵器科学研究院
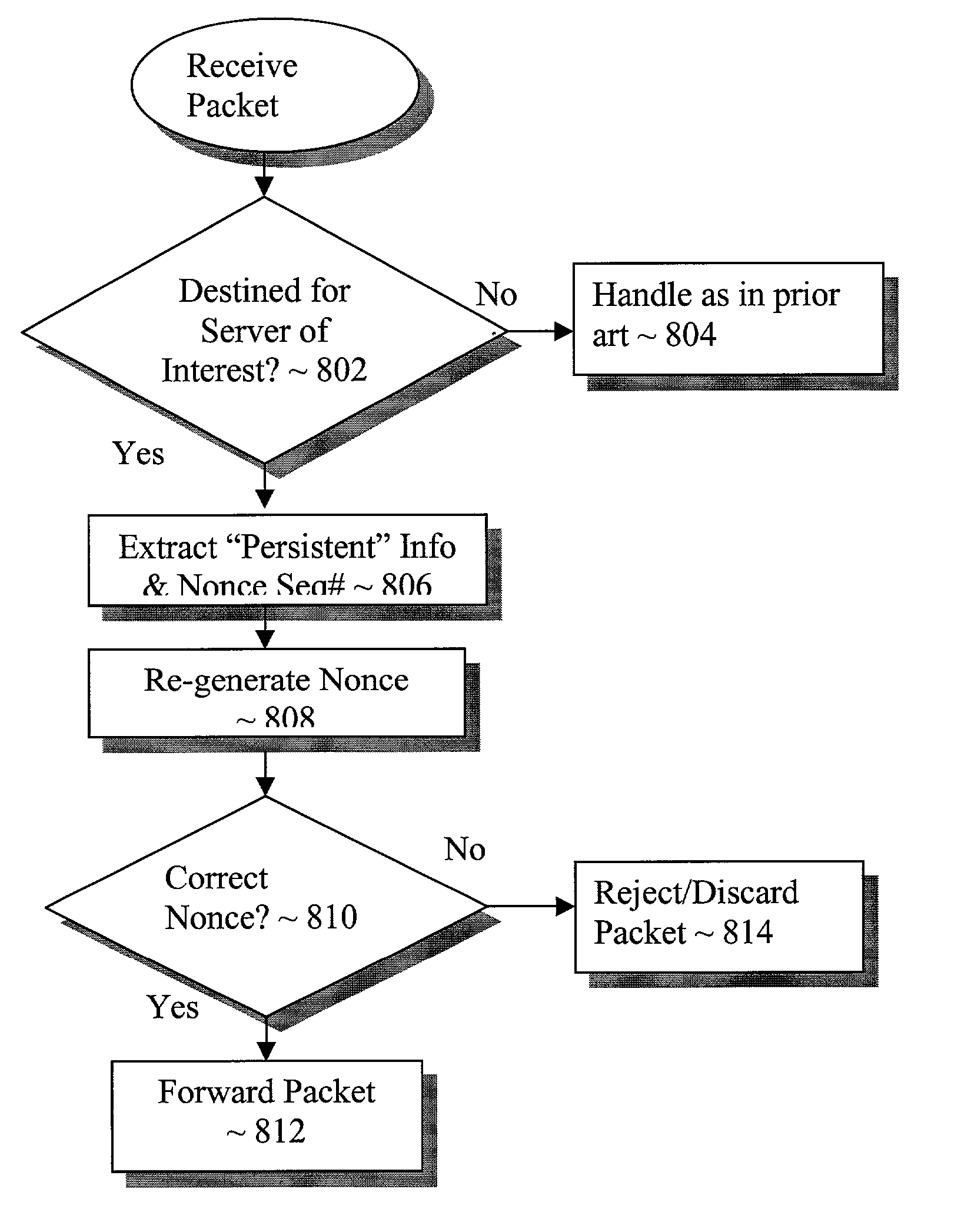
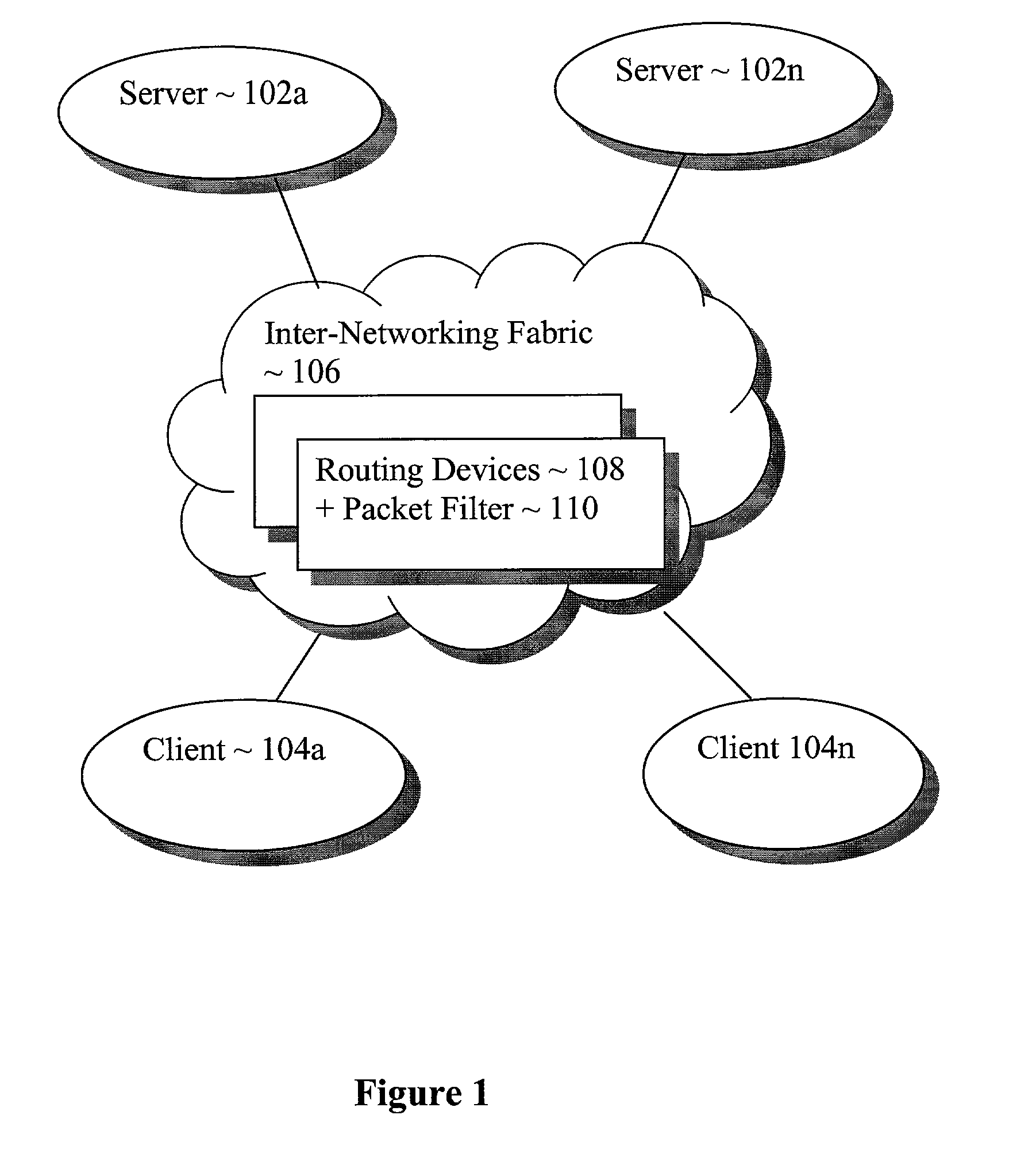
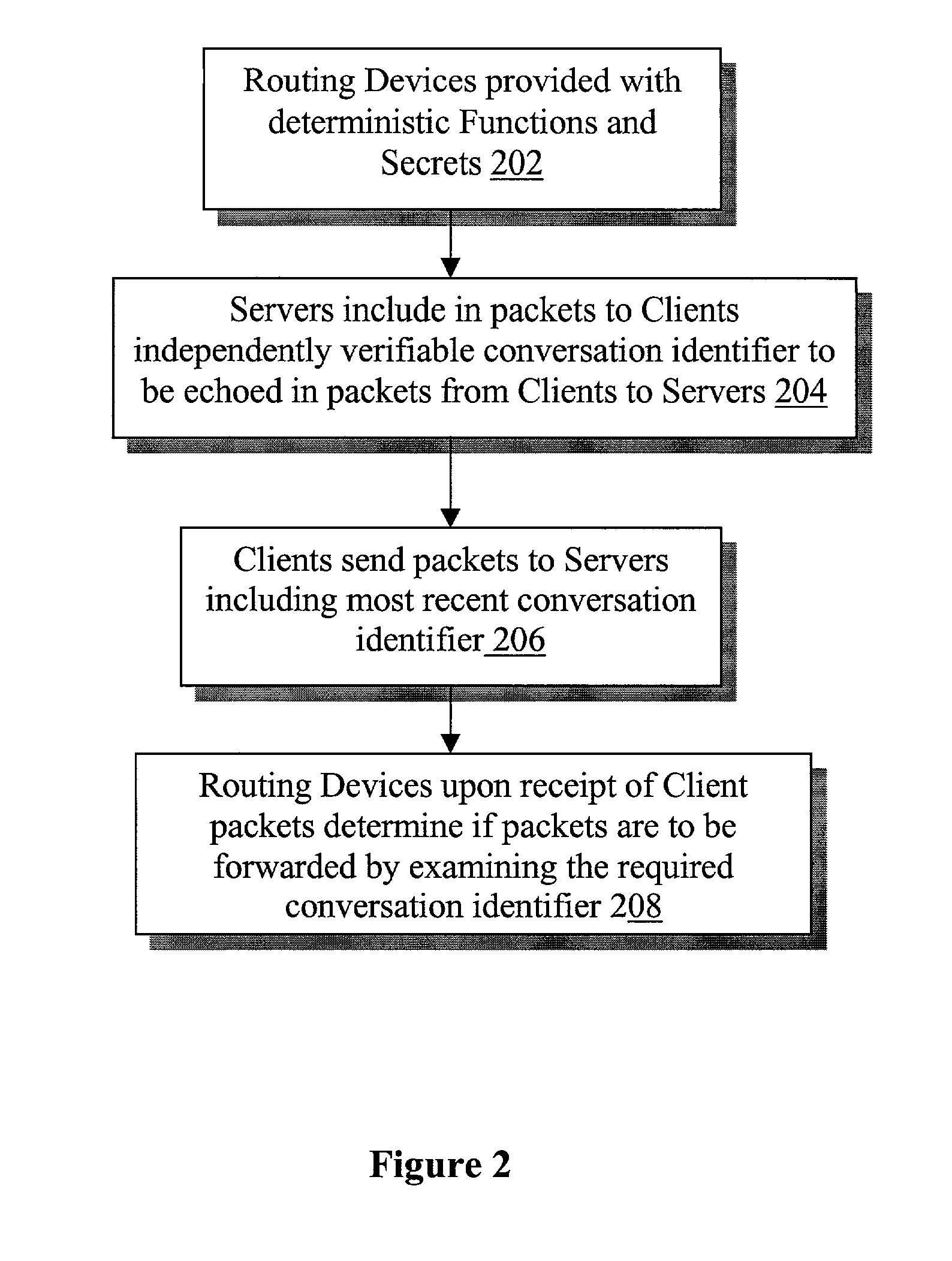
Independent detection and filtering of undesirable packets
ActiveUS8271678B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork packetDeterministic function
A server, using a deterministic function, a secret value and persistent information of a packet, destined for a client device, generates and includes a conversation identifier for inclusion with the packet. The client device in turn includes the conversation identifier in a subsequent packet sent by the client device destined for the server. An intermediate routing device having knowledge of the deterministic function and the secret value, upon receiving the packet en-route from the client device to the server, would independently determine whether the packet is a part of a conversation between the client and the server, by independently verifying the included conversation identifier, and forward or not forward the packet accordingly. As result, undesirable packets may be independently detected and filtered for the server.
Owner:ARBOR NETWORKS
Generating digital signatures using ephemeral cryptographic key
InactiveUS20060153371A1Facilitating adoptionEasy to useKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic key generationDigital signature
Generating a digital signature utilizing a cryptograph key includes: receiving into a computer system input data from a user (UID); generating within the computer system a cryptographic key as a deterministic function of the UID; clearing from the computer system the UID; generating within the computer system a digital signature as a function of the generated cryptographic key; and clearing the generated cryptographic key from the computer system following generation of the digital signature. The digital signature further may be generated as a function of whether a digital signature has yet been generated using the generated cryptographic key following receipt of the UID. Neither the received UID nor the generated cryptographic key is exported from the computer system.
Owner:FIRST DATA
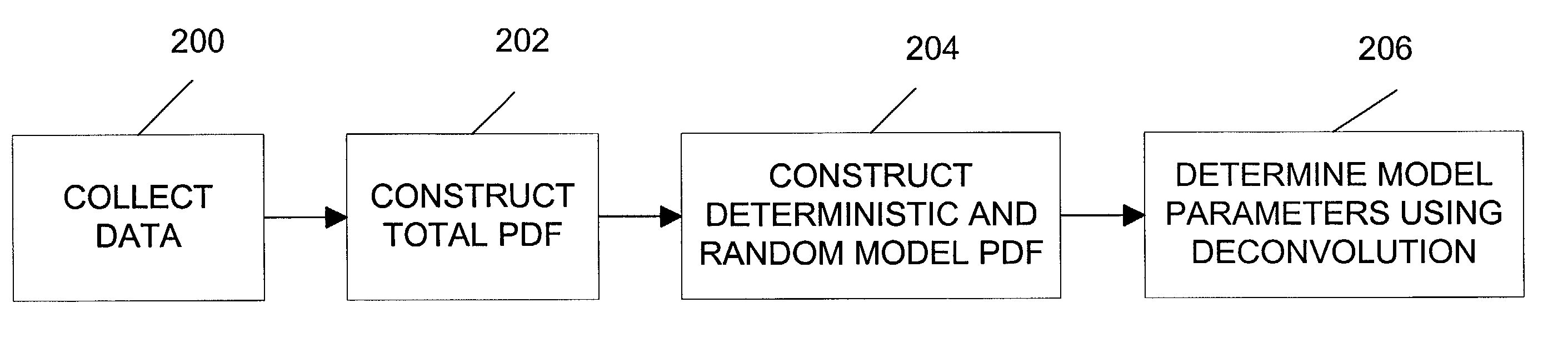
Method and apparatus for analyzing a distribution
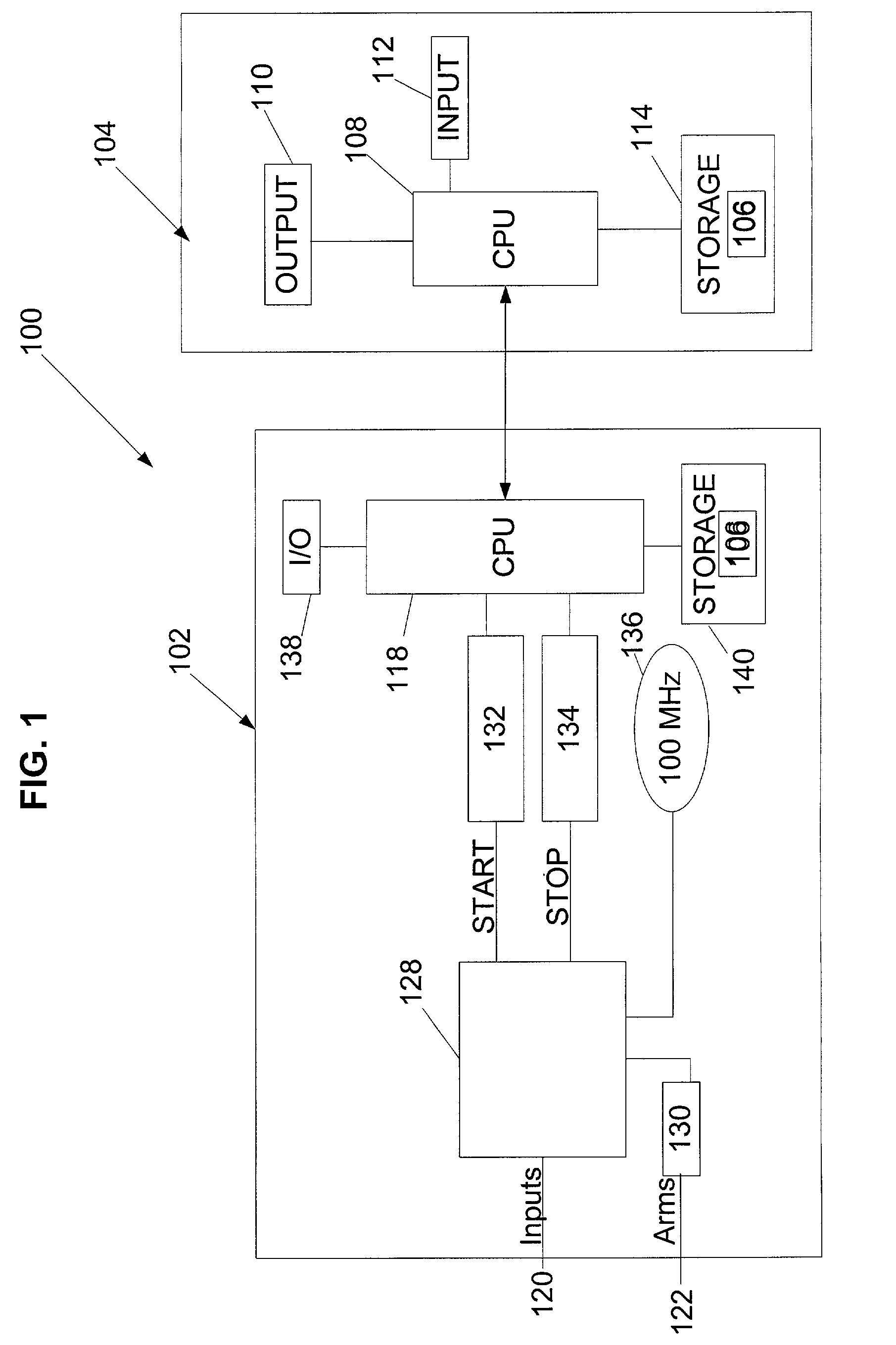
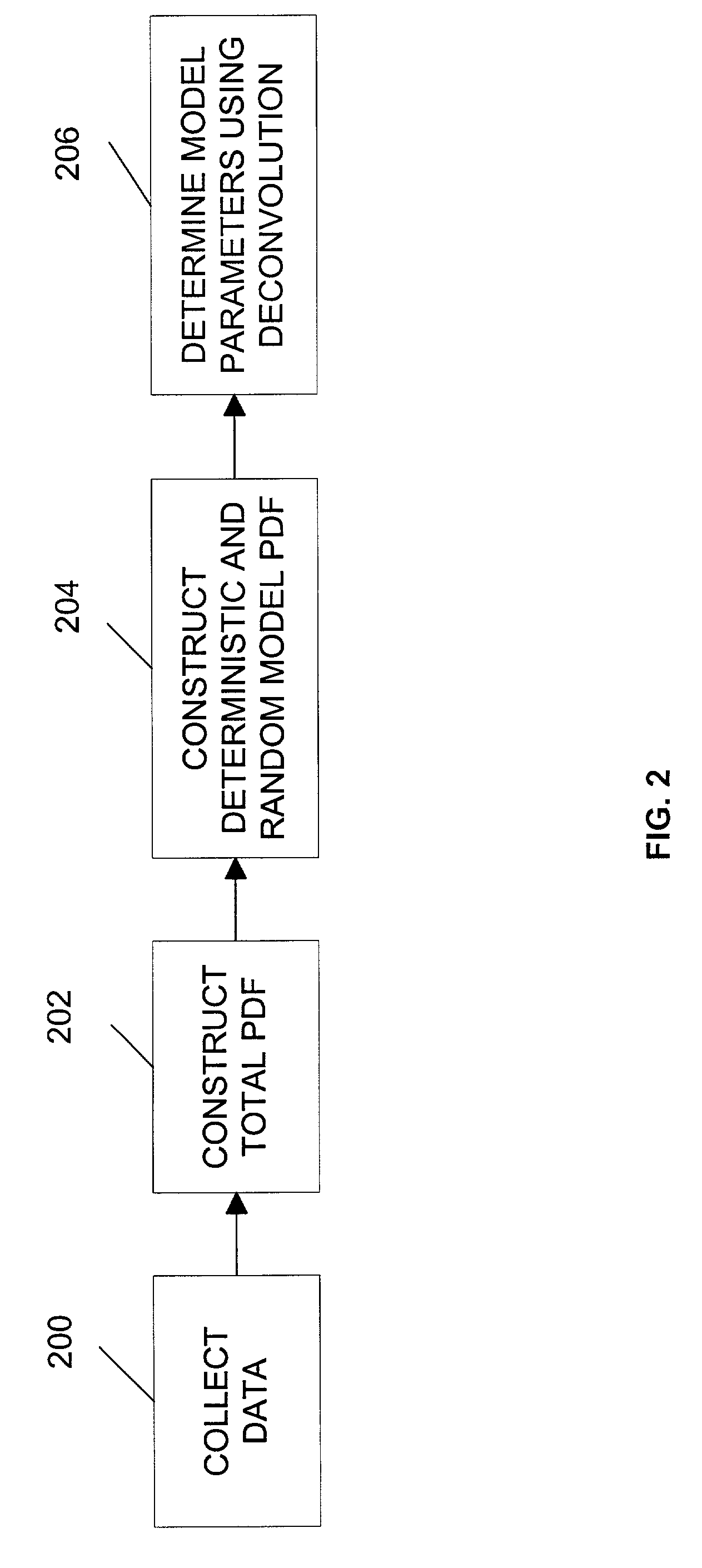
InactiveUS7016805B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementNormal densityDeterministic function
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for analyzing a measurable distribution having random components and deterministic components. The method includes the steps of collecting data, constructing a probability density function based on the data such that the probability density function is a convolution of deterministic functions and random functions, constructing a probability density function based on a deterministic and random convolution model having three or more parameters wherein at least one of the parameters are unknown, and determining unknown parameters by using a deconvolution process.
Owner:GIGAMAX TECH
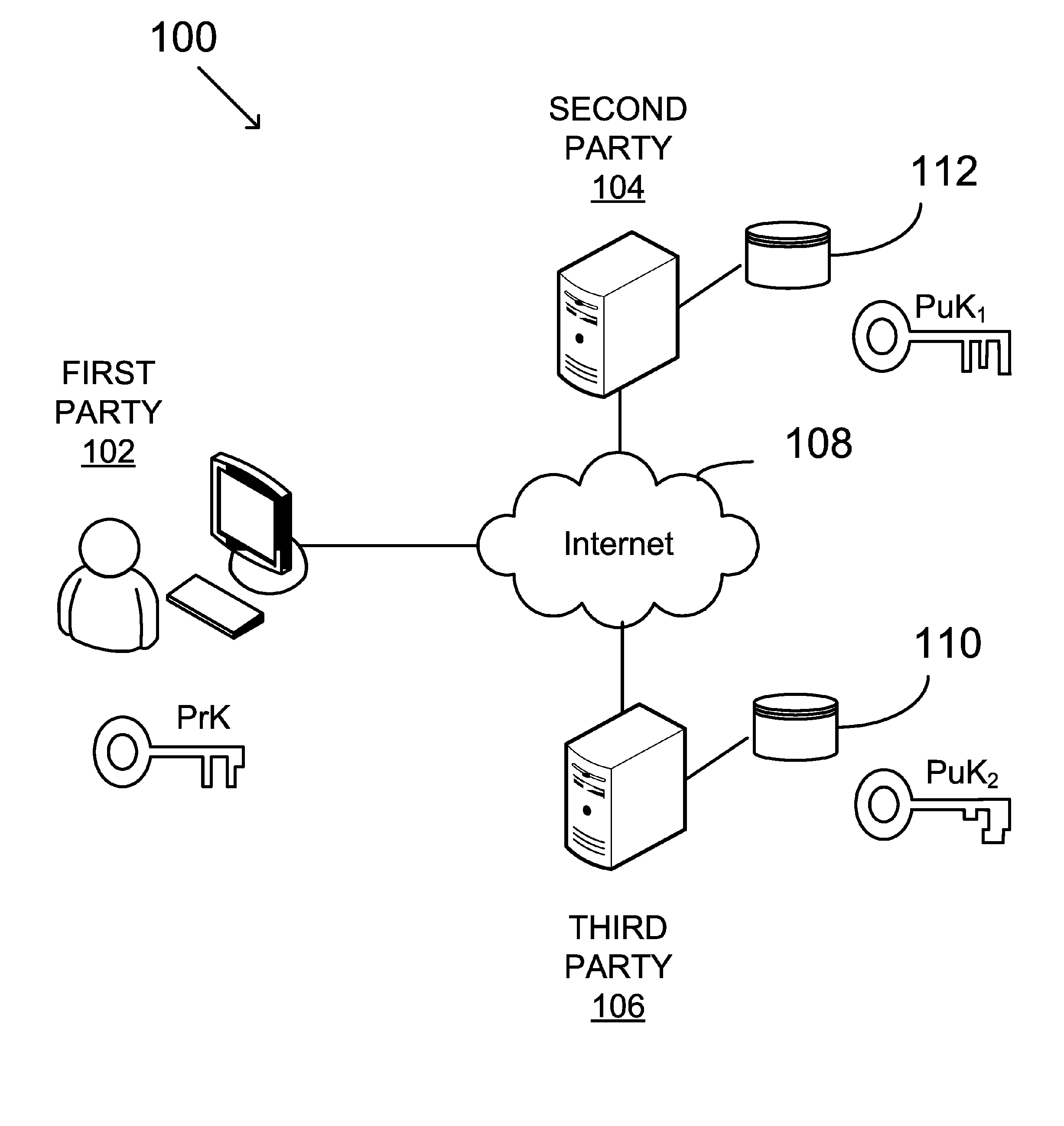
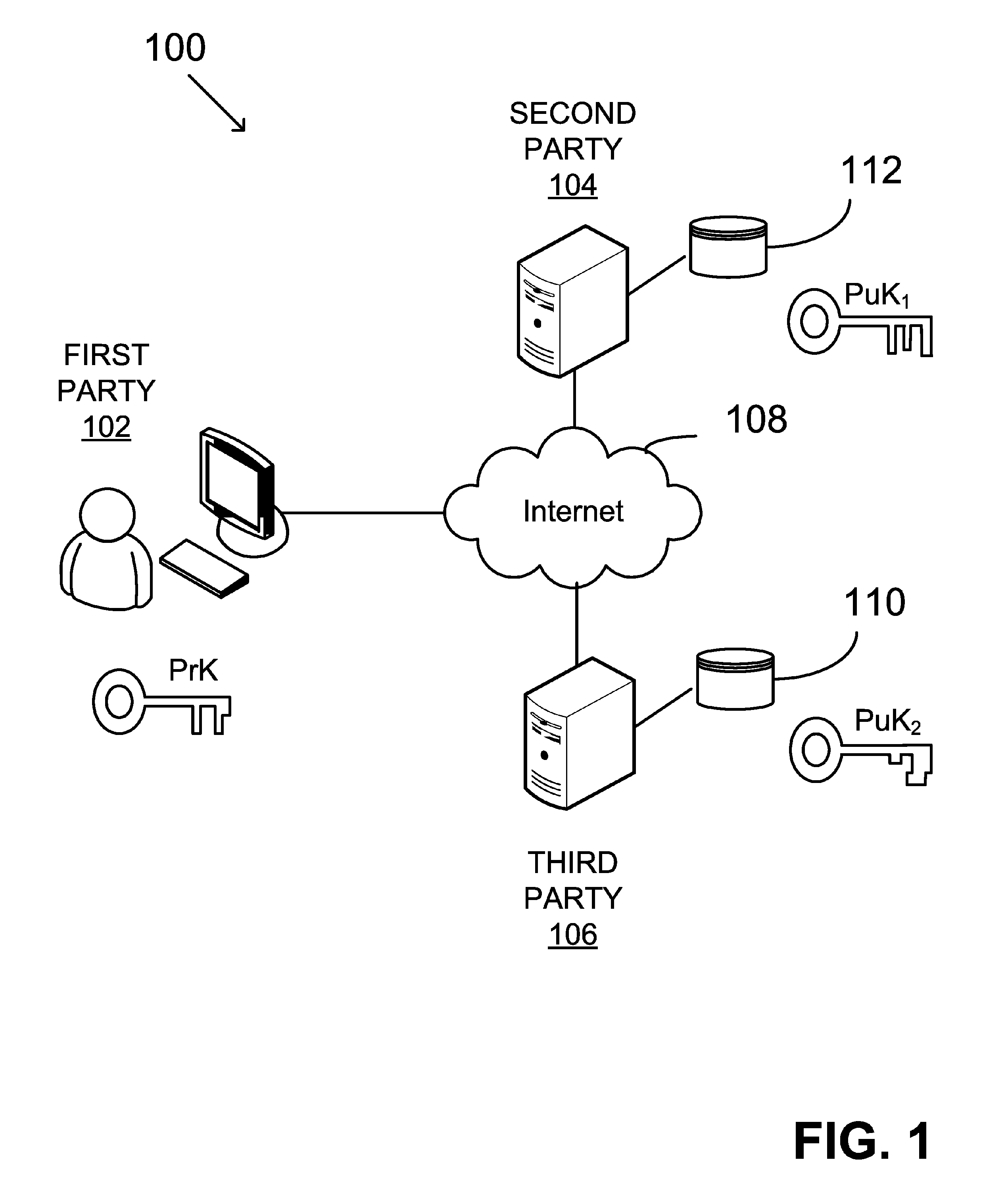
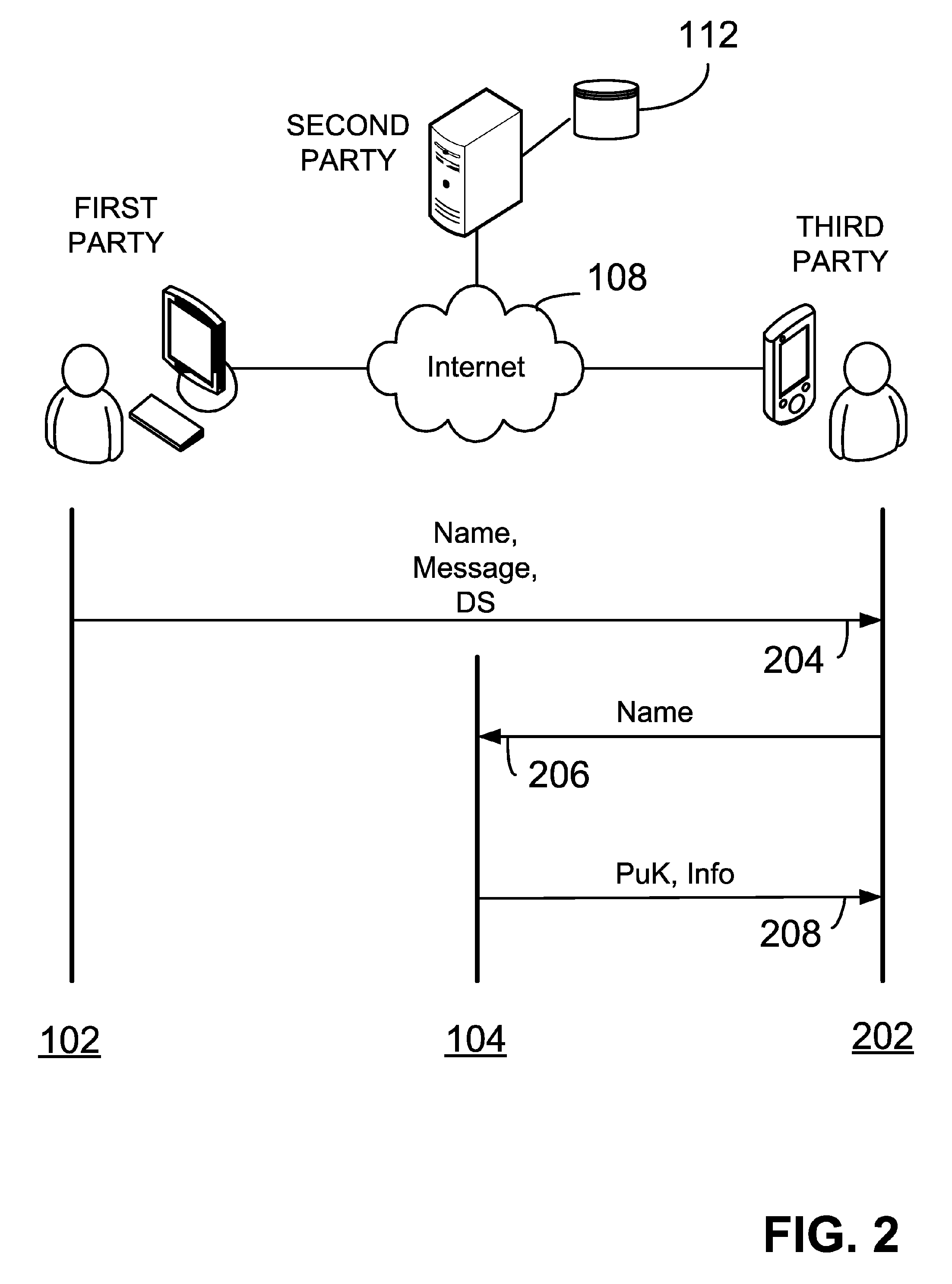
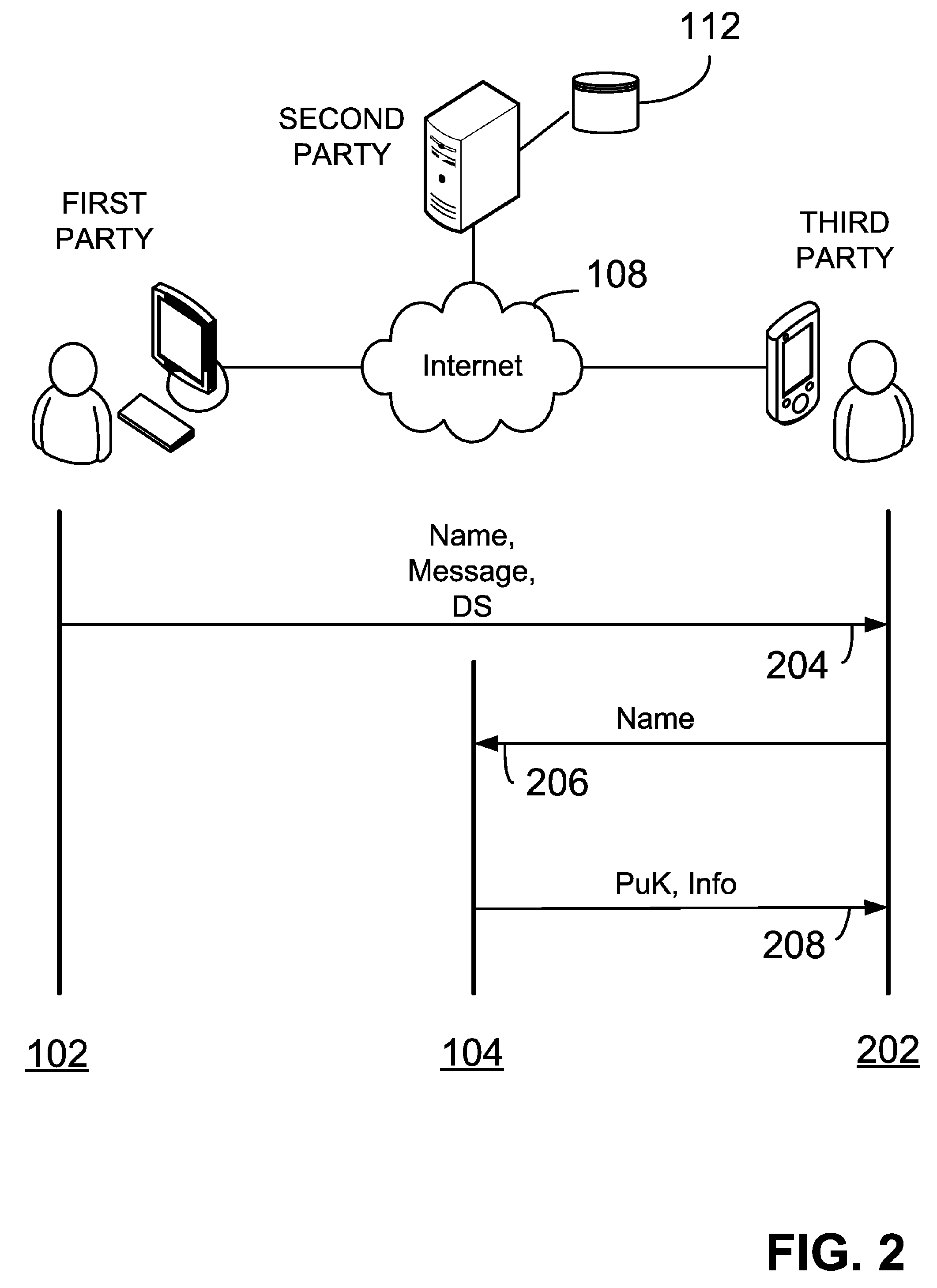
Verifying digital signature based on shared knowledge
InactiveUS20060153366A1Facilitating adoptionEasy to useKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDigital signatureDeterministic function
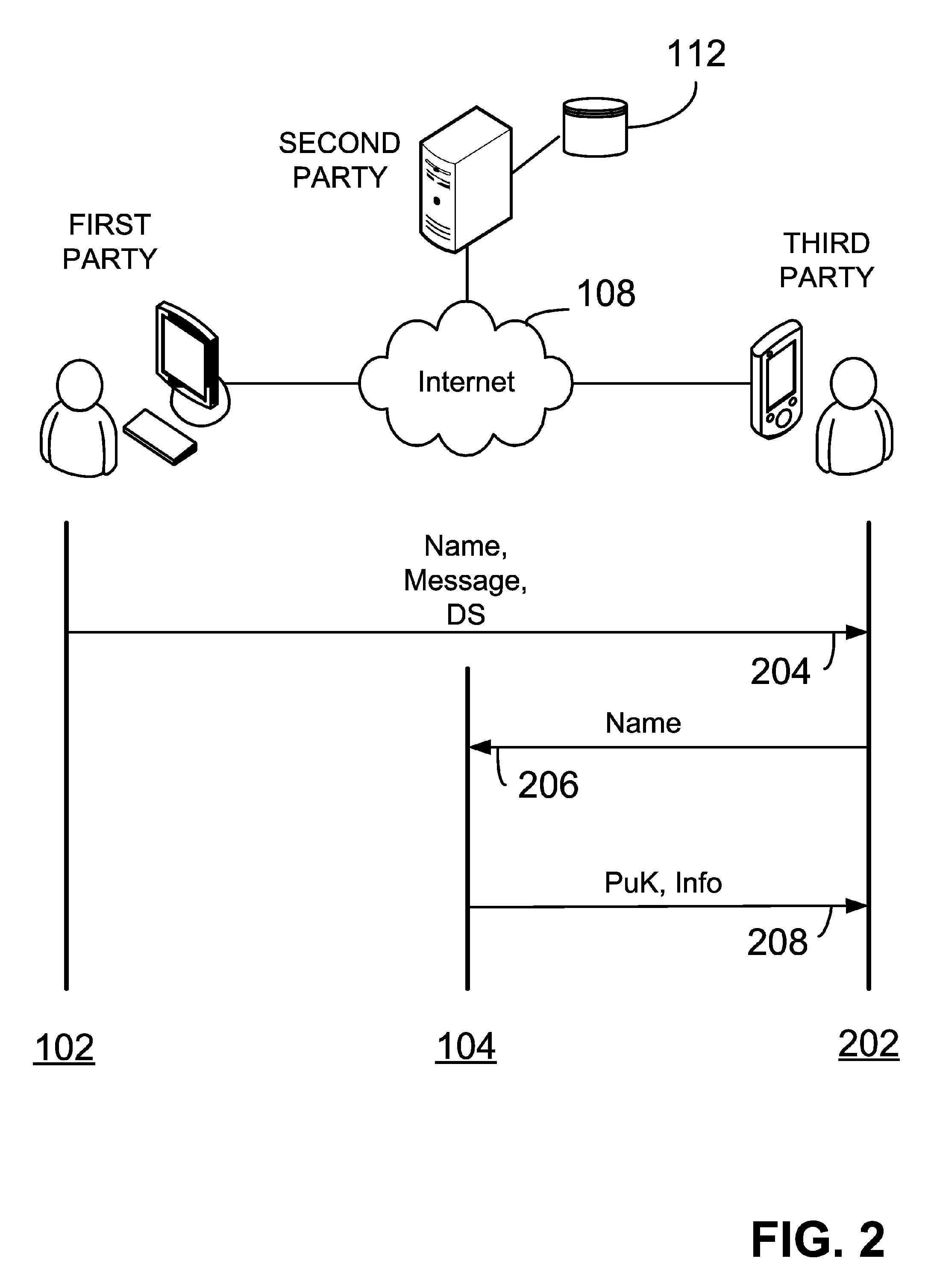
A method of verifying a digital signature of a first party that was generated using an elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) includes the steps of receiving a public key from the first party; receiving a digital signature from the first party, the digital signature being for an electronic message; identifying domain parameters of an elliptic curve used in elliptic curve cryptography, including identifying a generating point of the elliptic curve; transforming the identified generating point into a second generating point as a deterministic function of shared knowledge known to and between the first party and a second party; and verifying the received digital signature as a deterministic function of the received public key, the electronic message, and the identified domain parameters, in which the second generating point is substituted for the identified generating point.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Facilitating digital signature based on ephemeral private key
InactiveUS7490239B2Facilitating adoption and useUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionUser inputDigital signature
Facilitating communication using a digital signature includes: receiving user input data (UID); generating a first key as a deterministic function of the UID; clearing the UID; generating a second key as a deterministic function of the first key; clearing the first key following generation of the second key; and exporting the second key. Neither the UID nor the first key is exported. Thereafter, a digital signature is generated by again receiving the UID; regenerating the first key using the deterministic function and the UID; clearing the UID; generating a digital signature as a function of the regenerated first key; clearing the regenerated first key following generation of the digital signature; and exporting the generated digital signature.
Owner:FIRST DATA
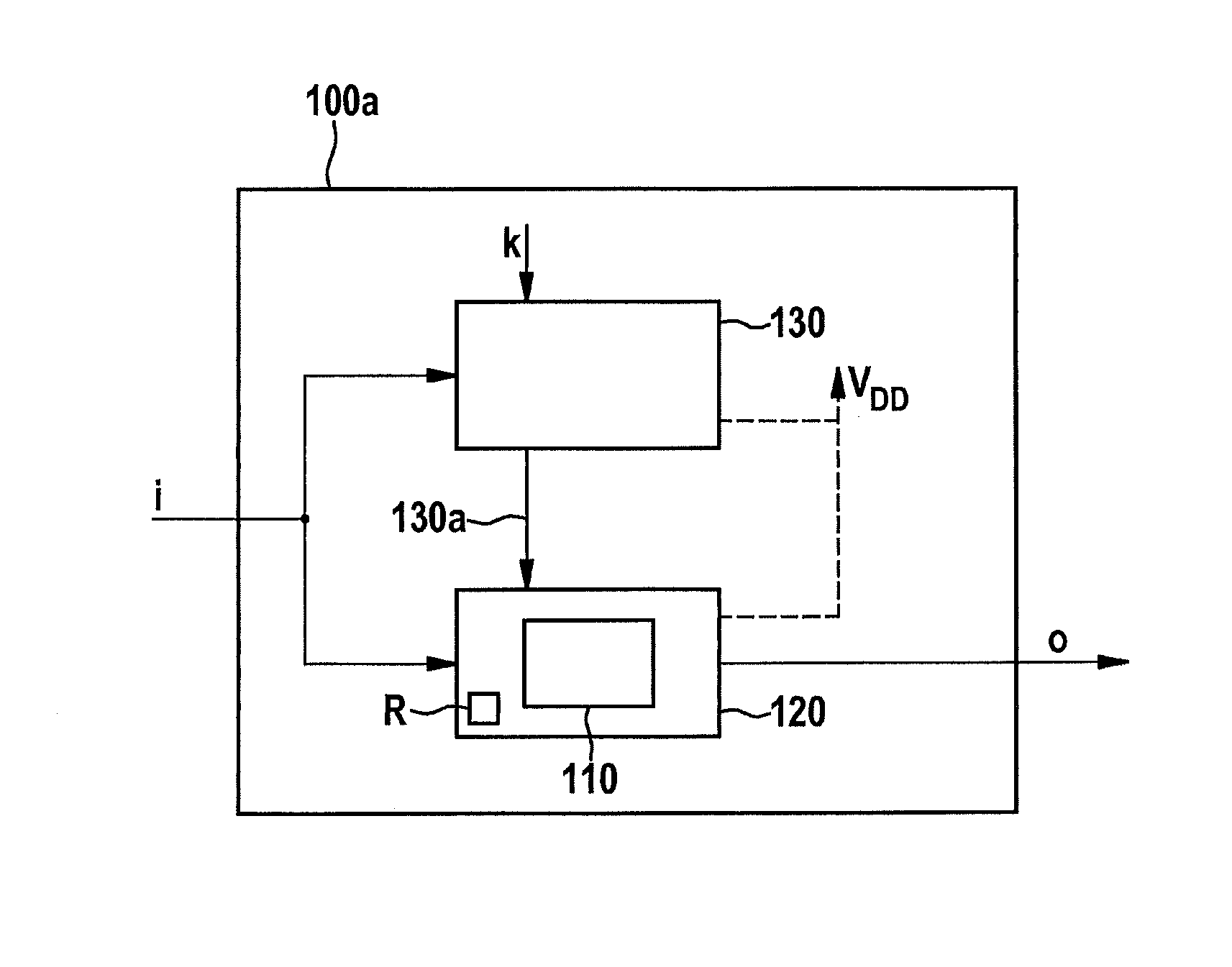
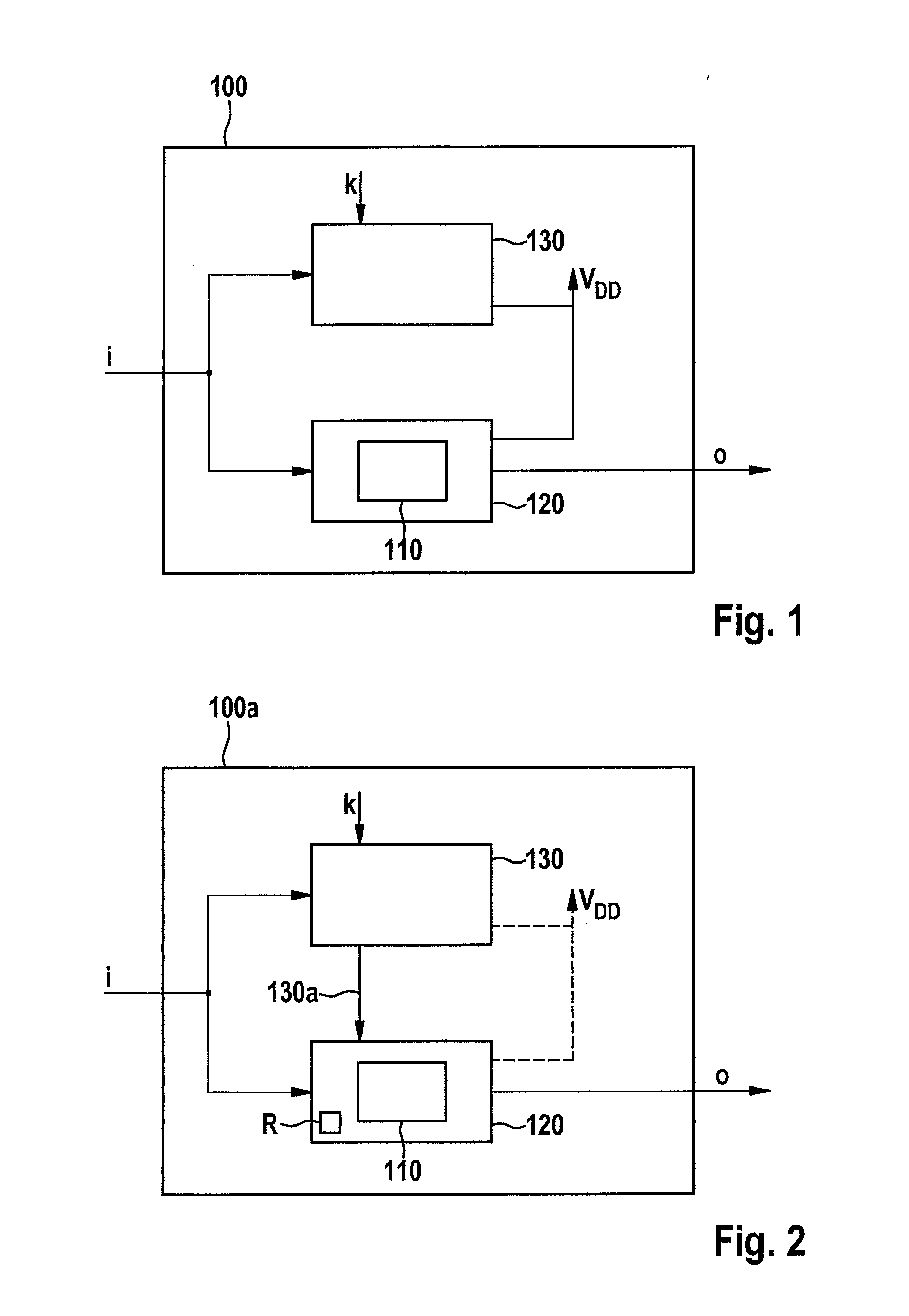
Countermeasure method for protecting stored data
ActiveUS20110033045A1Digital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer hardwareCountermeasure
A method of read or write access by an electronic component of data, including generating a first secret key for a first data of an ordered list of data to access, and for each data of the list, following the first data, generating a distinct secret key by means of a deterministic function applied to a secret key generated for a previous data of the list, and the application of a cryptographic operation to each data to be read or to be written of the list, carried out by using the secret key generated for the data.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
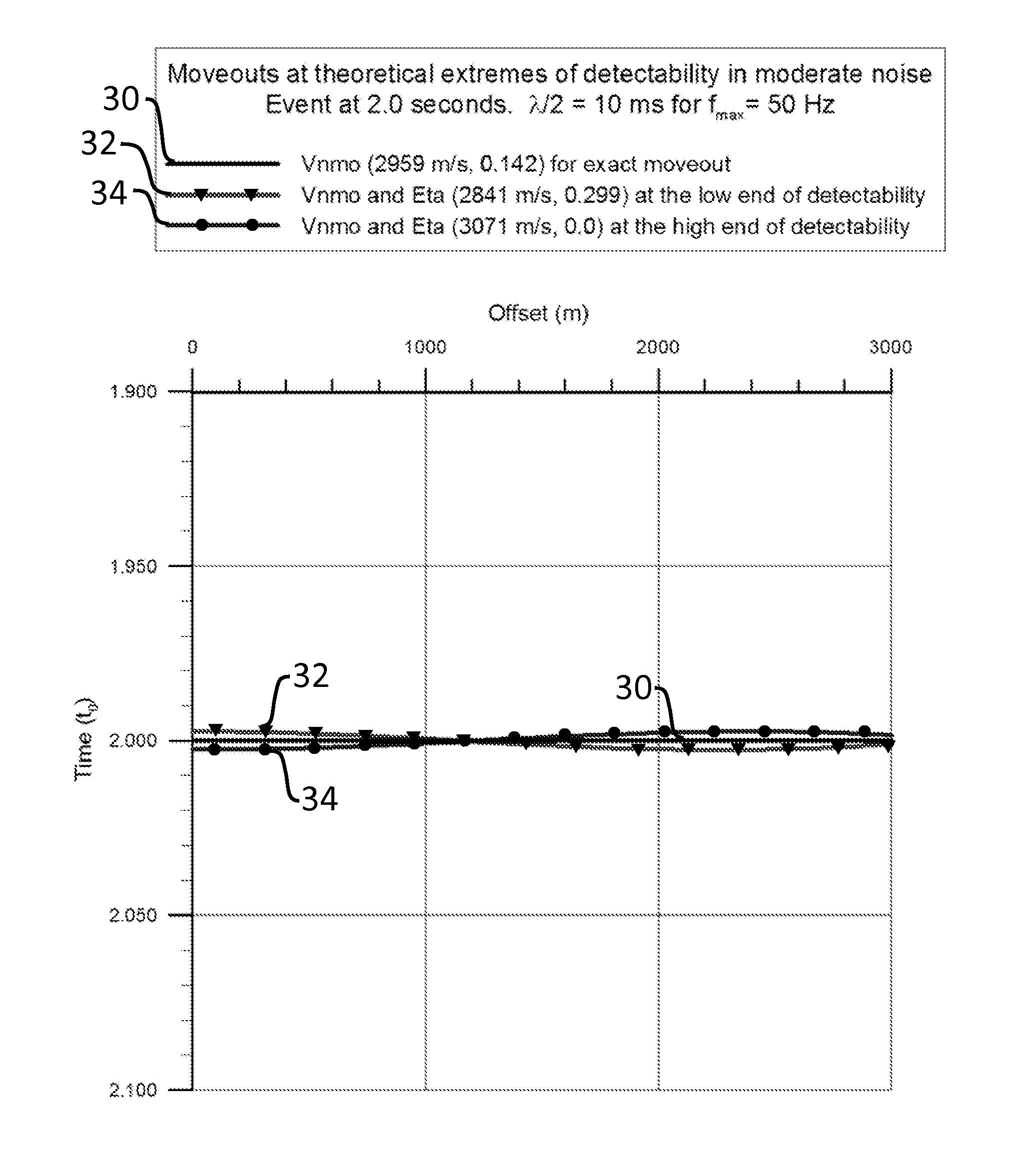
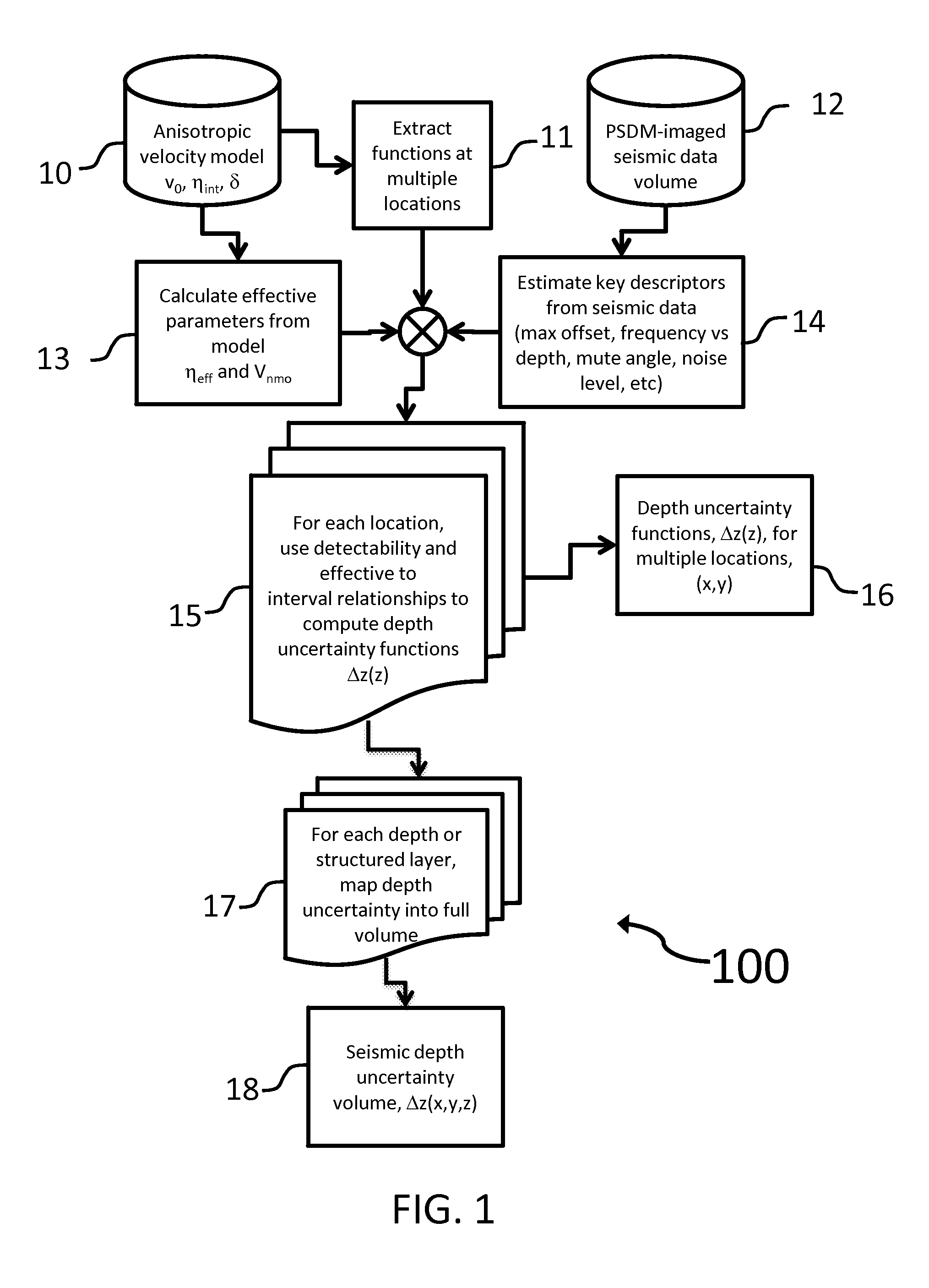
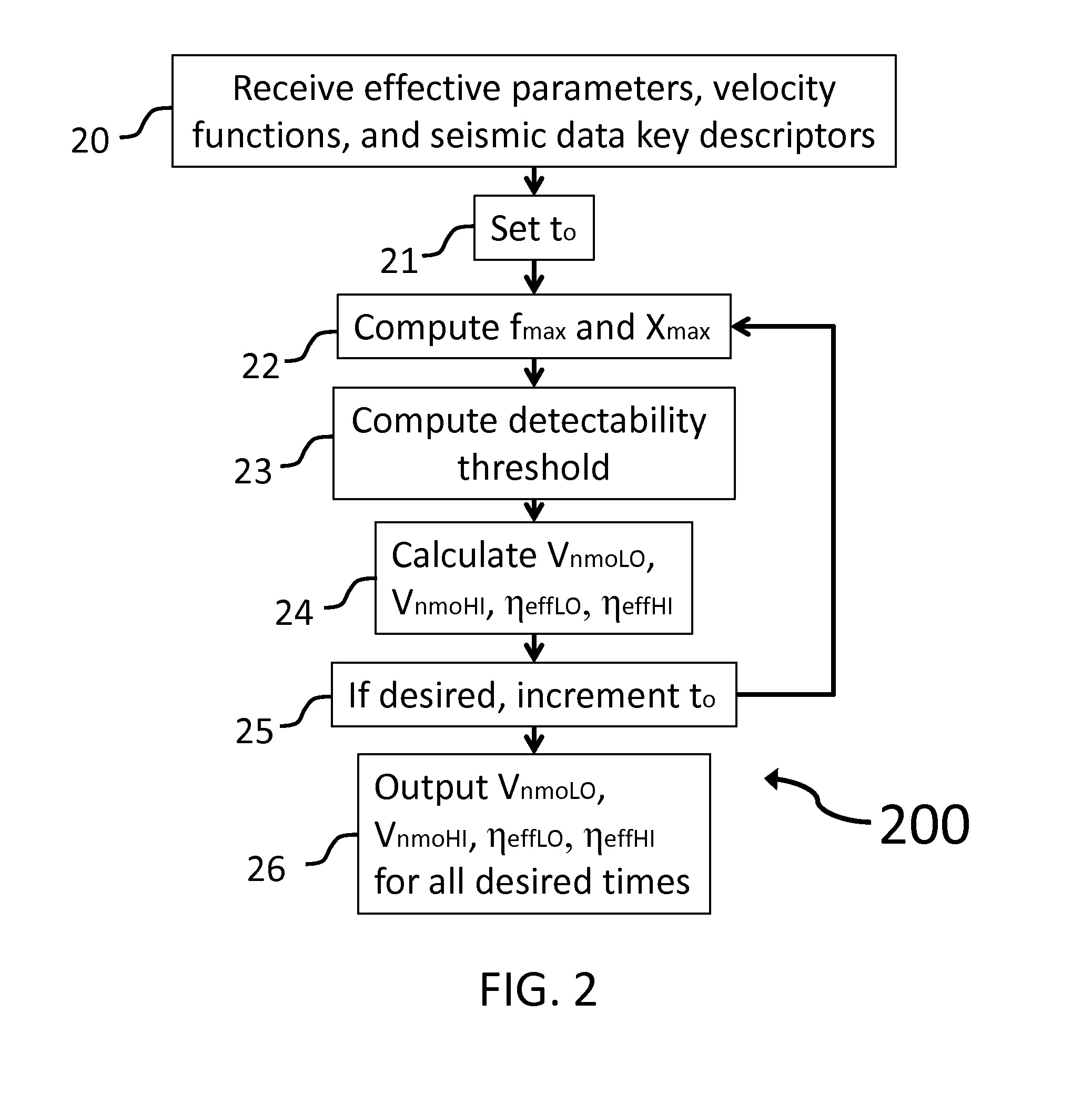
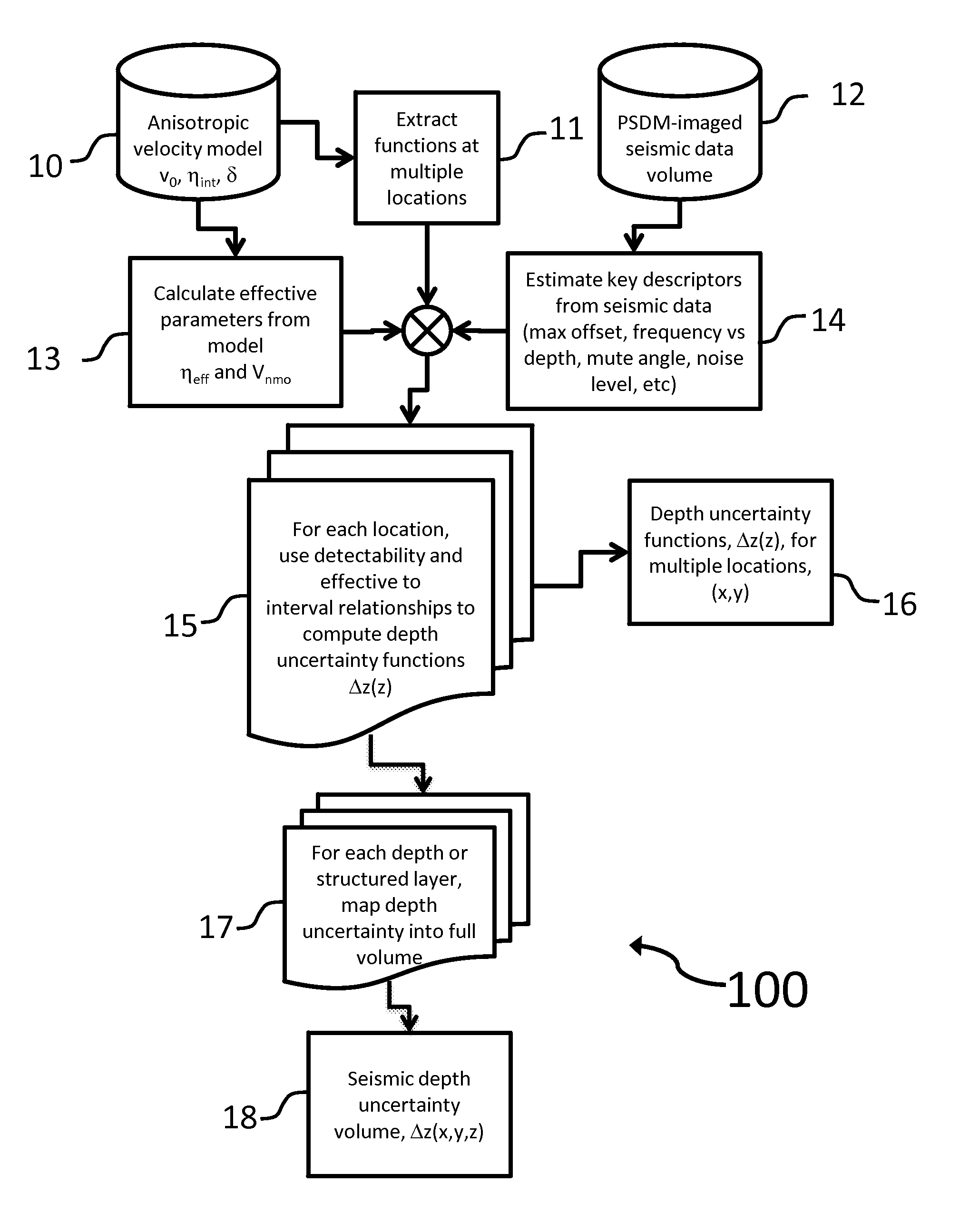
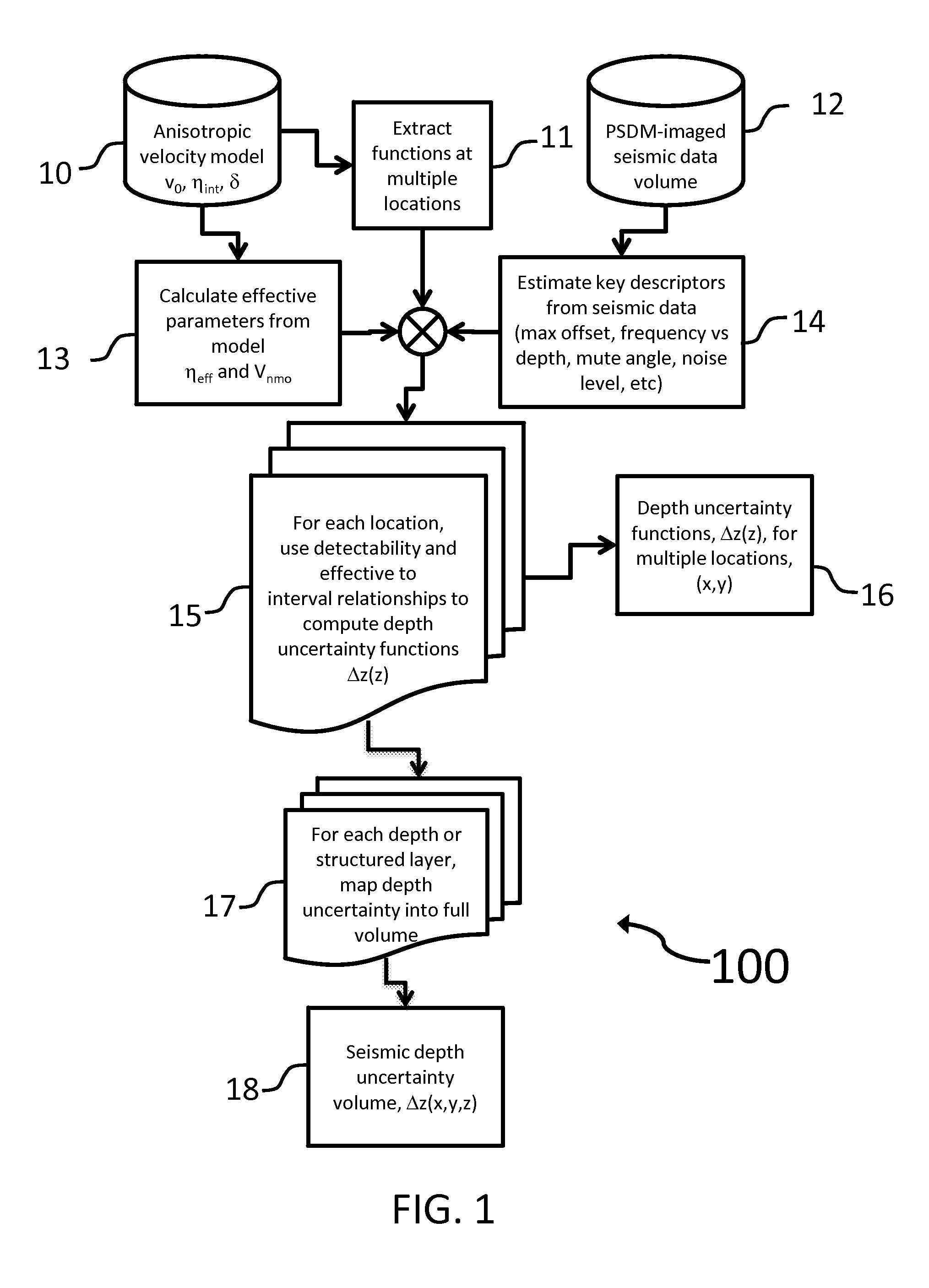
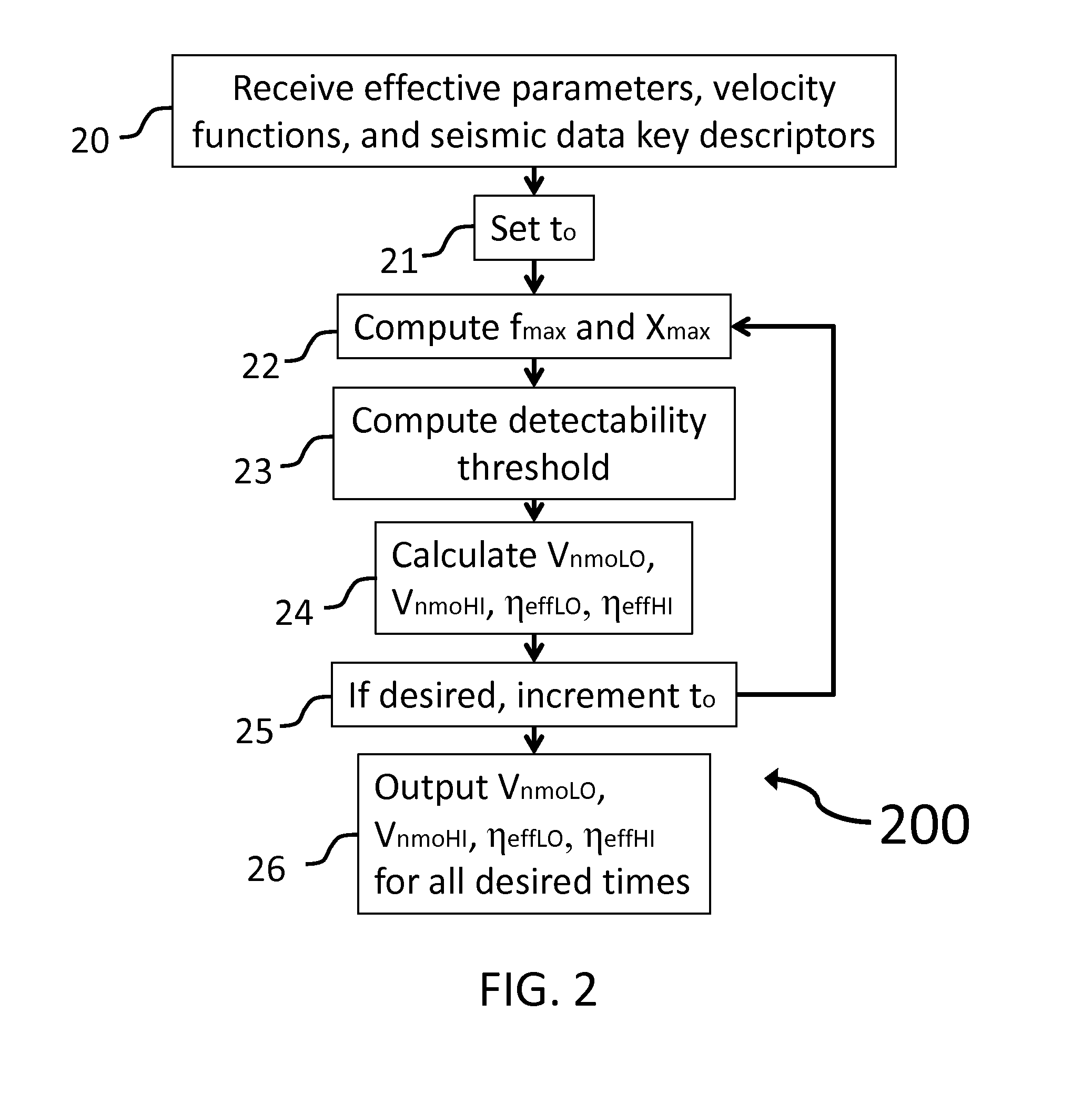
System and method for subsurface characterization including uncertainty estimation
ActiveUS20130046476A1Well formedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsHorizonUncertainty function
A system and method for subsurface characterization including depth and structural uncertainty estimation is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method may include determining a detectability threshold for moveout in a seismic data gather based on the seismic data and computing a depth uncertainty function, wherein the depth uncertainty function represents an error estimate that is used to analyze an interpretation of the seismic data. In another embodiment, the method may include receiving a depth uncertainty volume and at least one interpreted horizon from seismic data, extracting a depth uncertainty cage for each of the interpreted horizons based on the depth uncertainty volume, and simulating multiple realizations for each of the interpreted horizons, constrained by the depth uncertainty cage. The multiple realizations may be used for analyzing changes to geometrical or structural properties of the at least one interpreted horizon. The changes may be plotted as at least one distribution and may be used to make P10, P50 and P90 estimates.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Verifying digital signature based on shared knowledge
InactiveUS7936869B2Facilitating adoption and useKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDigital signatureDeterministic function
A method of verifying a digital signature of a first party that was generated using an elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) includes the steps of receiving a public key from the first party; receiving a digital signature from the first party, the digital signature being for an electronic message; identifying domain parameters of an elliptic curve used in elliptic curve cryptography, including identifying a generating point of the elliptic curve; transforming the identified generating point into a second generating point as a deterministic function of shared knowledge known to and between the first party and a second party; and verifying the received digital signature as a deterministic function of the received public key, the electronic message, and the identified domain parameters, in which the second generating point is substituted for the identified generating point.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Generating digital signatures using ephemeral cryptographic key
InactiveUS7693277B2Facilitating adoption and useKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic key generationComputer network
Generating a digital signature utilizing a cryptograph key includes: receiving into a computer system input data from a user (UID); generating within the computer system a cryptographic key as a deterministic function of the UID; clearing from the computer system the UID; generating within the computer system a digital signature as a function of the generated cryptographic key; and clearing the generated cryptographic key from the computer system following generation of the digital signature. The digital signature further may be generated as a function of whether a digital signature has yet been generated using the generated cryptographic key following receipt of the UID. Neither the received UID nor the generated cryptographic key is exported from the computer system.
Owner:FIRST DATA
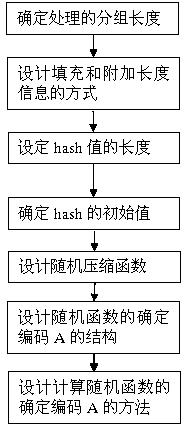
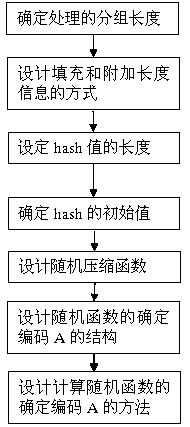
Method for structuring one-way Hash function based on random function
ActiveCN102542070AIncrease the lengthEasy to increase in lengthSpecial data processing applicationsDecoding methodsHash function
The invention belongs to the field of information security, in particular to the field of cryptology. The invention relates to a method for structuring a one-way Hash function based on a random function. The method uses a random function as a Hash function, or rather, the method uses the random function as a compression function, namely the compression function is indeterminate and has various possible concrete function forms, and the concrete form of the function is determined through clear text messages during calculation. The Hash function structured by the method brings various obstacles for decoding, a forged clear text needs to conform to the requirements of the traditional deterministic Hash function, and the definite code of the concrete function form of the deterministic random Hash function corresponding to the clear text must be consistent. The current cryptanalysis generally aims at the deterministic Hash function. When a cryptanalyst only knows a Hash value, decoding is even more difficult. As the concrete function form of the random function is not known, the cryptanalyst is unable to start by adopting a general decoding method.
Owner:南通信甲天下科技有限公司
Digital signature system based on shared knowledge
InactiveUS20060153367A1Facilitating adoptionEasy to usePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationDigital signatureDeterministic function
A method in a digital signature system includes providing a public key of a first party to a second party for later verification of a digital signature. The method includes: identifying domain parameters of an elliptic curve, including a generating point; transforming the generating point into a second generating point as a deterministic function of shared knowledge; and generating the public key as a deterministic function of a private key and the domain parameters, in which the second generating point is substituted for the identified generating point. The public key and private key constitute a public-private key pair of elliptic curve cryptography. A digital signature is generated as a function of the private key and the domain parameters, in which the second generating point again is substituted for the initial generating point identified. The shared knowledge is known to and shared between the first party and the second party.
Owner:FIRST DATA
System and method for subsurface characterization including uncertainty estimation
ActiveUS8694262B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsUncertainty functionDeterministic function
A system and method for subsurface characterization including depth and structural uncertainty estimation is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method may include determining a detectability threshold for moveout in a seismic data gather based on the seismic data and computing a depth uncertainty function, wherein the depth uncertainty function represents an error estimate that is used to analyze an interpretation of the seismic data. In another embodiment, the method may include receiving a depth uncertainty volume and at least one interpreted horizon from seismic data, extracting a depth uncertainty cage for each of the interpreted horizons based on the depth uncertainty volume, and simulating multiple realizations for each of the interpreted horizons, constrained by the depth uncertainty cage. The multiple realizations may be used for analyzing changes to geometrical or structural properties of the at least one interpreted horizon. The changes may be plotted as at least one distribution and may be used to make P10, P50 and P90 estimates.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
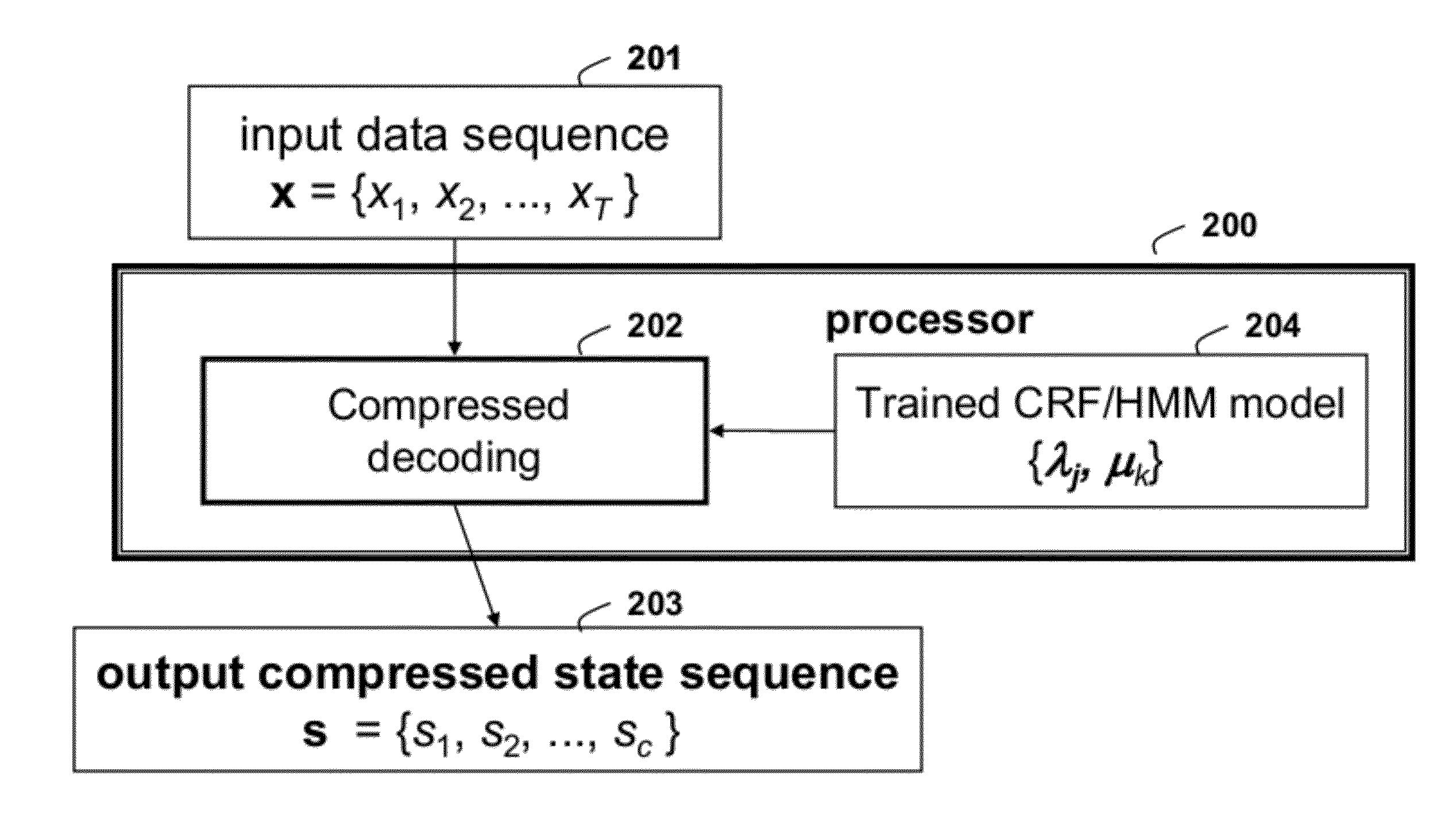
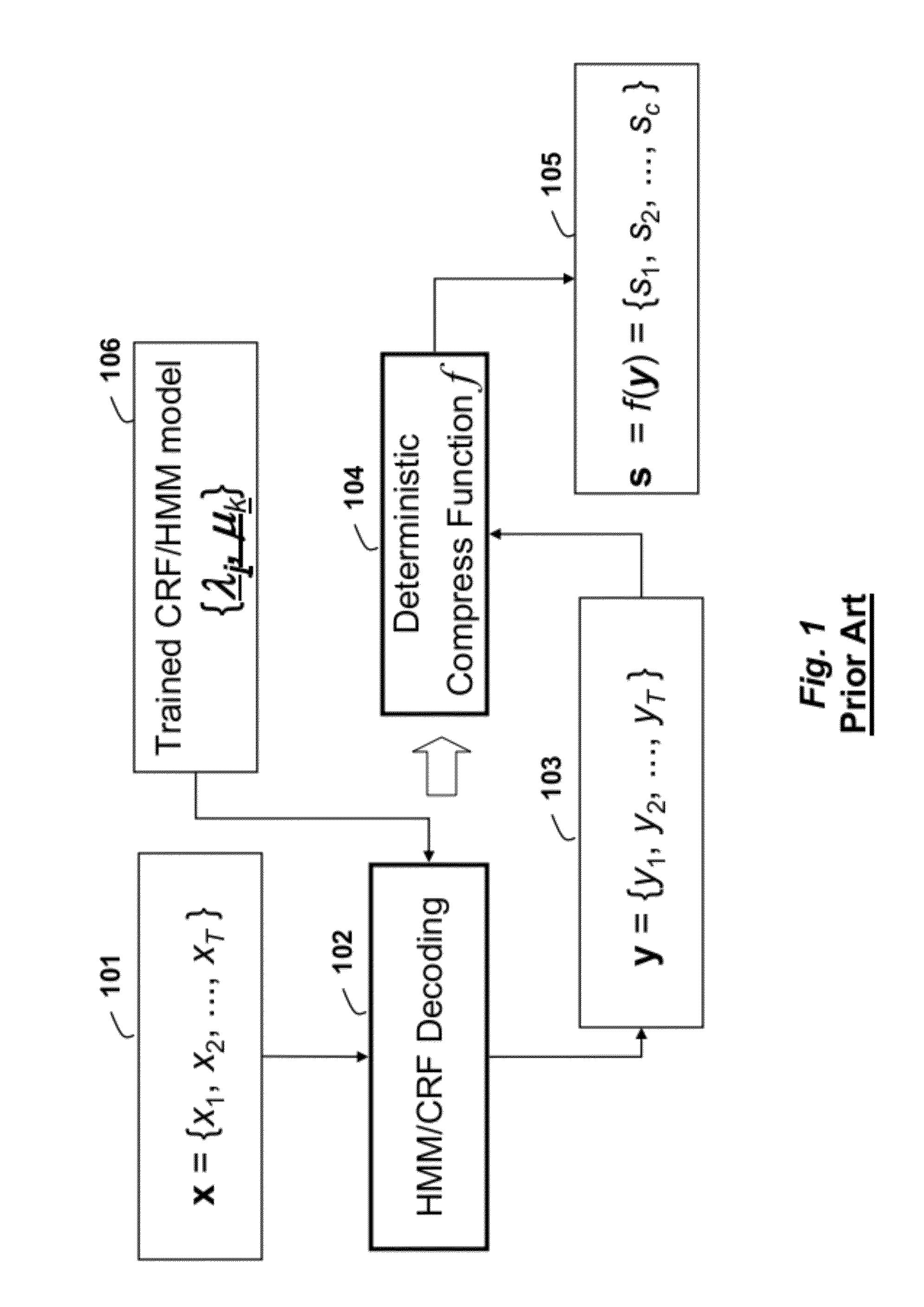
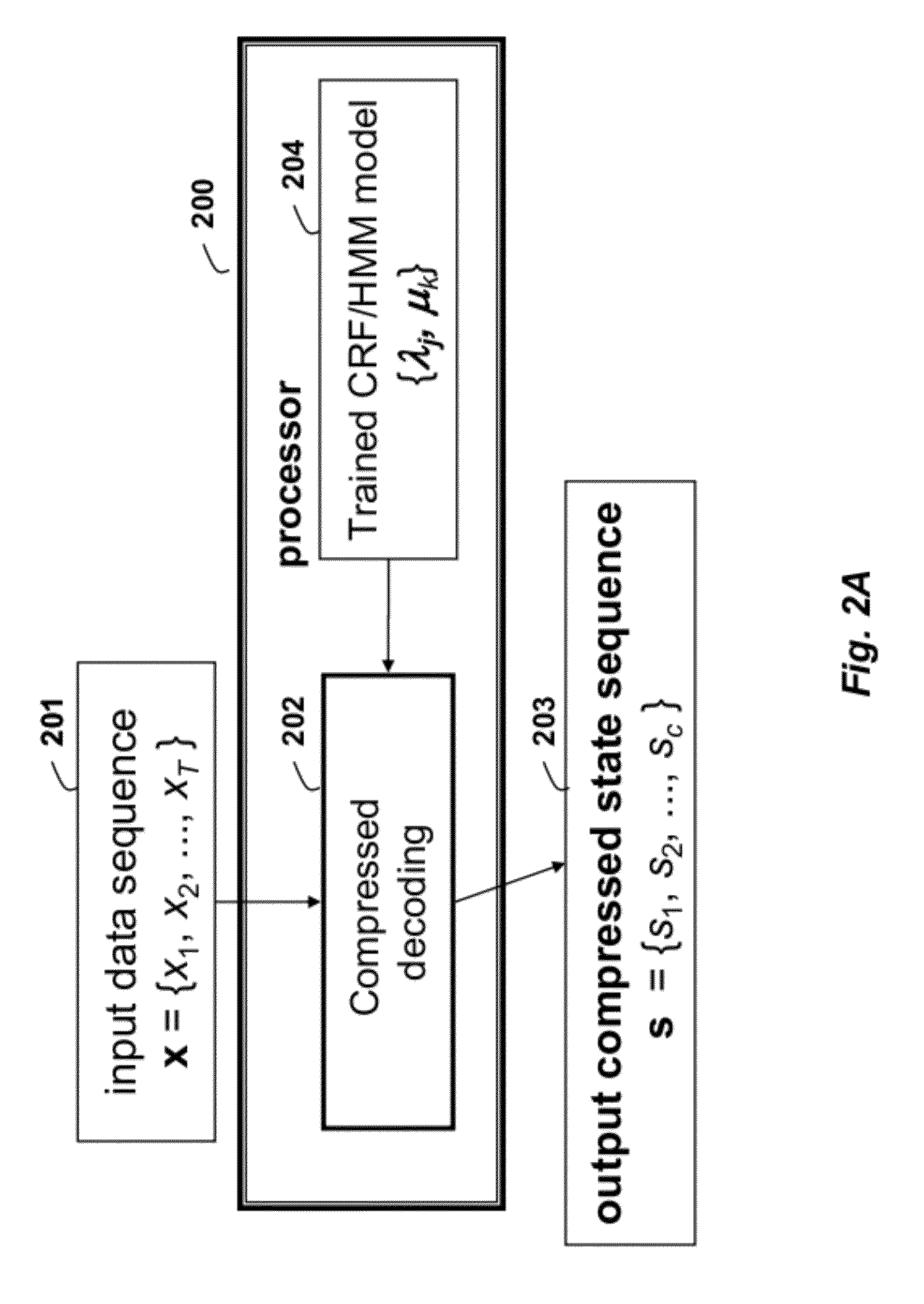
Method for Determining Compressed State Sequences
InactiveUS20120053944A1Code conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDeterministic function
A compressed state sequence s is determined directly from the input sequence of data x. A deterministic function ƒ(x) only tracks unique state transitions, and not the dwell times in each state. A polynomial time compressed state sequence inference method outperforms conventional compressed state sequence inference techniques.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Password augmented all-or-nothing transform
ActiveUS20180247071A1Key distribution for secure communicationInput/output to record carriersPasswordAll-or-nothing transform
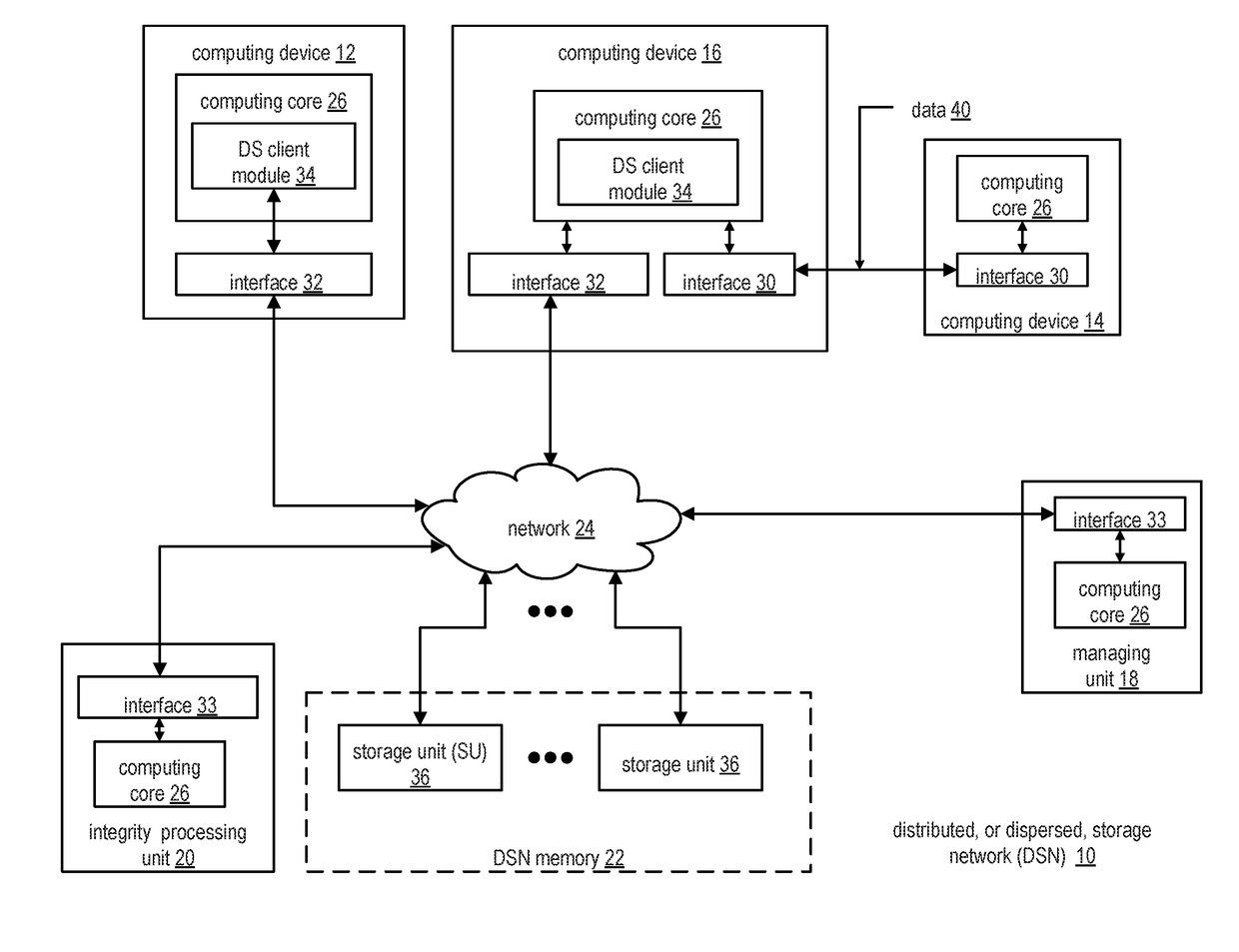
A computing device includes an interface configured to interface and communicate with a dispersed storage network (DSN), a memory that stores operational instructions, and processing circuitry operably coupled to the interface and to the memory. The processing circuitry is configured to execute the operational instructions to perform various operations and functions. The computing device encrypts data using a key to generate encrypted data and processes it and a password based on a deterministic function to generate transformed data. The computing device masks the key based on a masking function based on the transformed data to generate a masked key, and then combines the encrypted data and the masked key to generate a secure package that is encoded in accordance with dispersed error encoding parameters produce a set of encoded data slices (EDSs) and transmits the set of EDSs to a plurality of storage units (SUs) to be distributedly stored therein.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
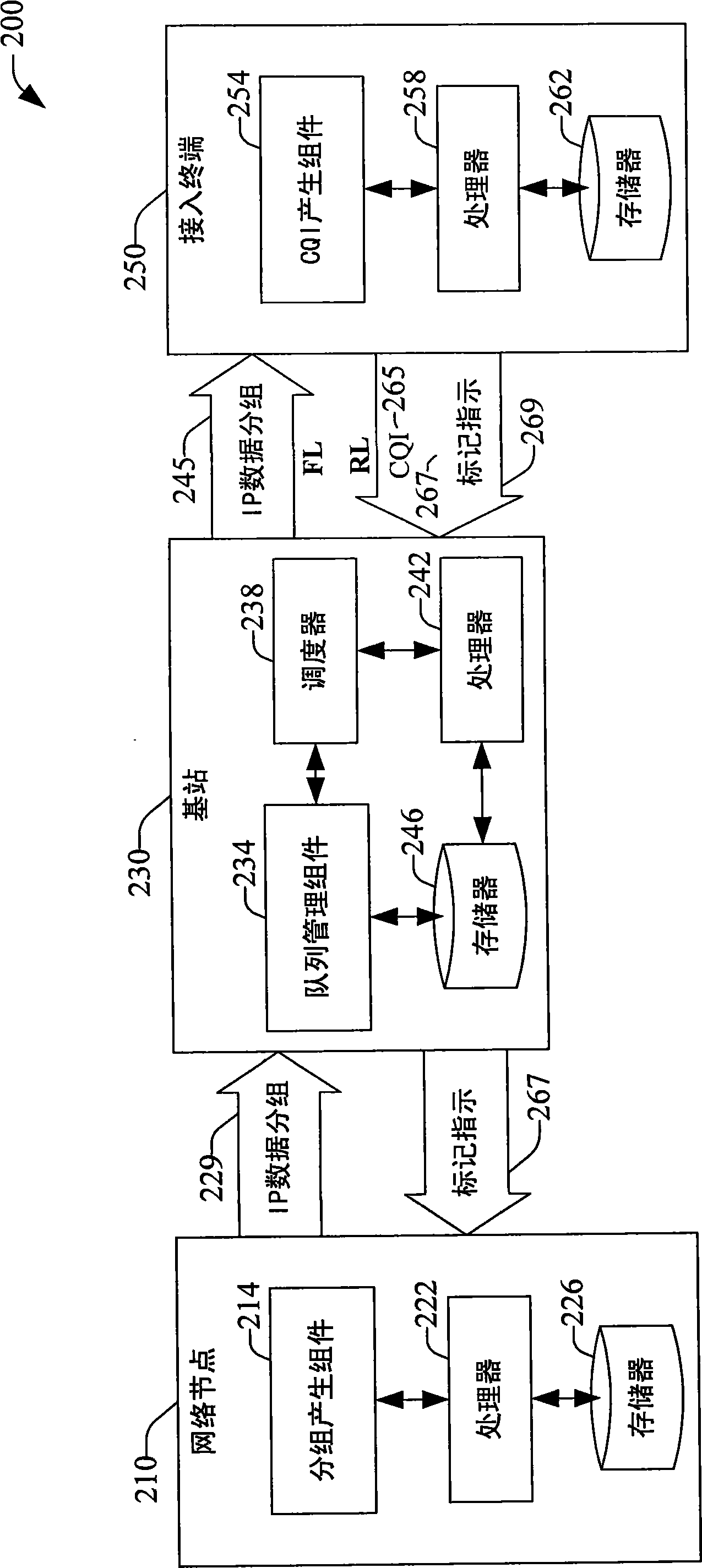
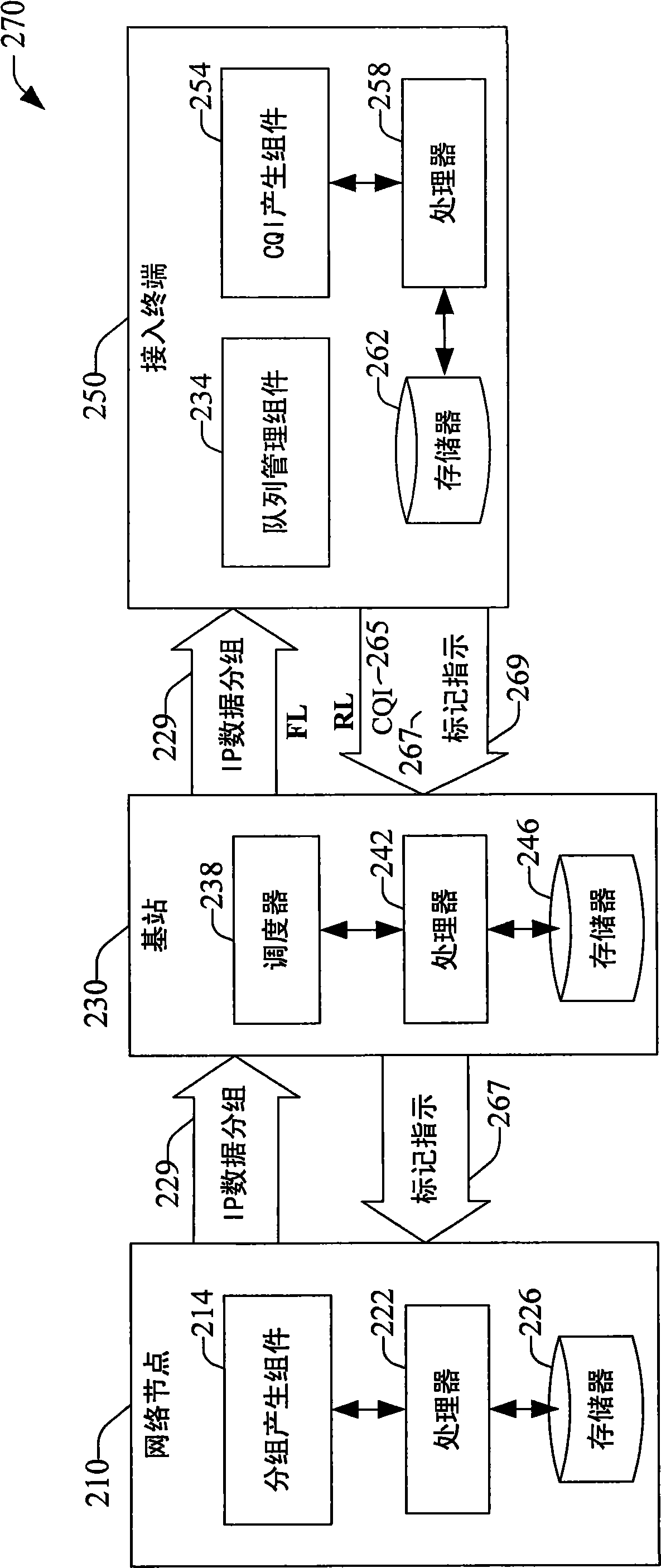
Method and system for reducing backhaul utilization during base station handoff in wireless networks
InactiveCN101548512AEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless mesh networkFrequency reuse
Systems and methods are provided that facilitate active queue management of internet-protocol data packets generated in a data packet switched wireless network. Queue management can be effected in a serving base station as well as in an access terminal, and the application that generates the data packets can be executed locally or remotely to either the base station or access terminal. Management of the generated data packets is effected via a marking / dropping of data packets according to an adaptive response function that can be deterministic or stochastic, and can depend of multiple communication generalized indicators, which include packet queue size, queue delay, channel conditions, frequency reuse, operation bandwidth, and bandwidth-delay product. Historical data related to the communication generalized indicators can be employed to determine response functions via thresholds and rates for marking / dropping data packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Device and method for carrying out a cryptographic method
InactiveUS20150270973A1High degreeNot easy to attackUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationComputer hardwareDeterministic function
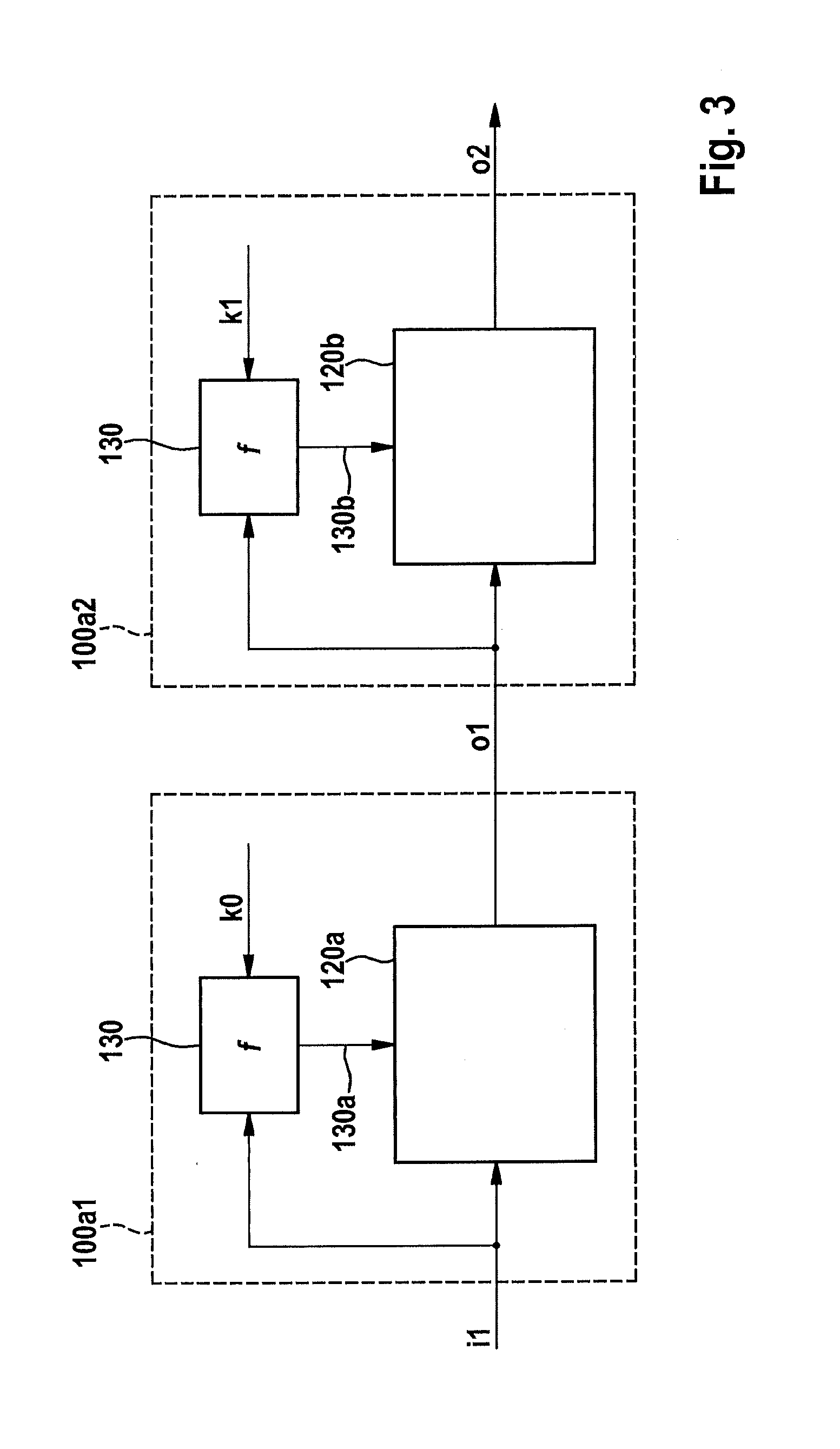
A device for carrying out a cryptographic method includes: a cryptographic unit carrying out at least one step of the cryptographic method; and a functional unit carrying out a deterministic function as a function of input data supplied to the device and at least one secret key.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Printing press with several operating zones
ActiveCN101177064AReduce stepsConfirm existenceSafety arrangmentsSheet bindingDeterministic functionEngineering
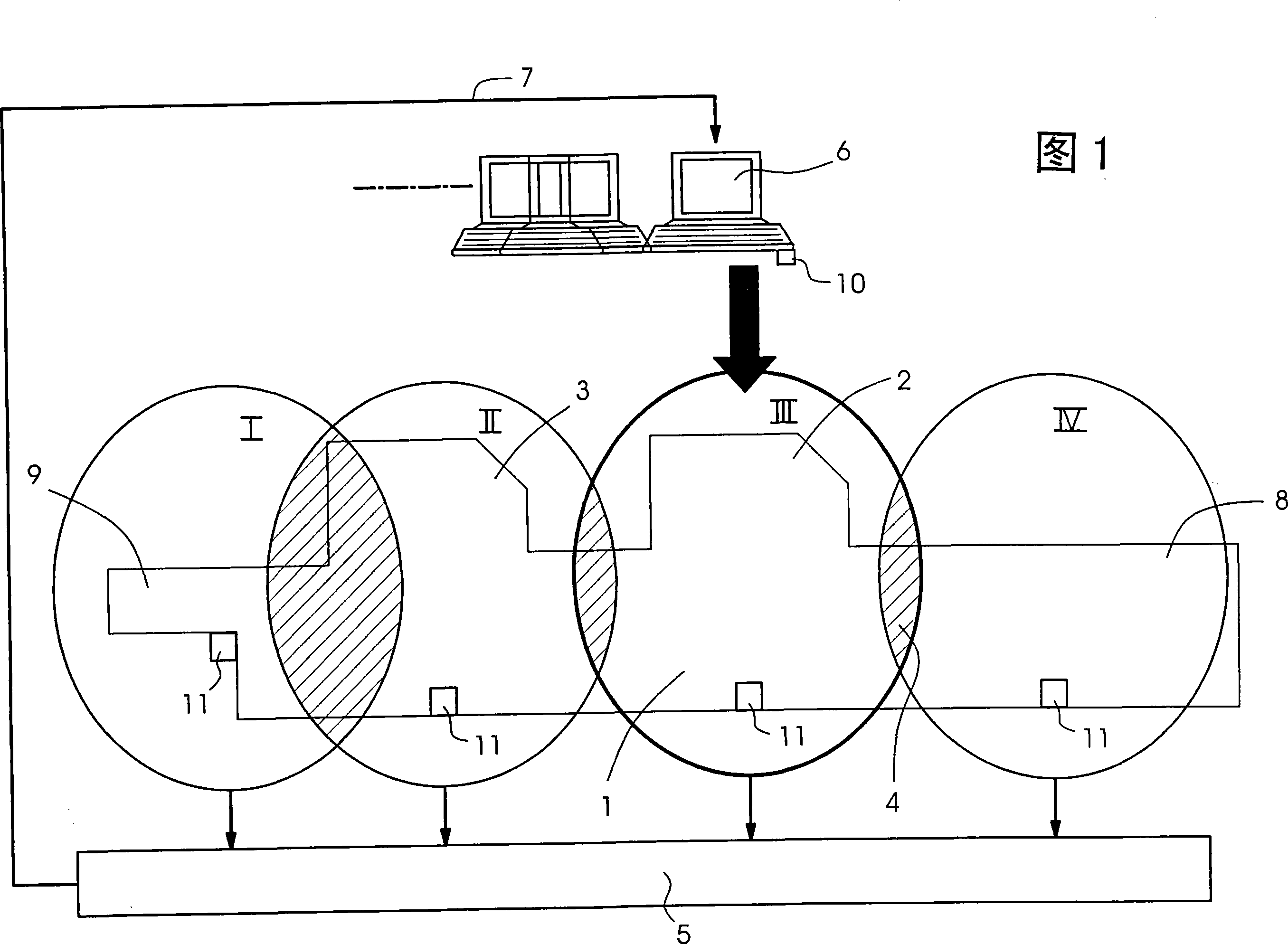
The present invention relates to a printing press provided with a plurality of operating spaces and is characterized in that the machine (1) used for treating printing materials is divided into a plurality of definite districts (I, II, III, IV) in room, and a control device's (6) position relative to the plural districts (I, II, III, IV) can be explored, wherein, by means of the position of the control device (6), the district (III) in which the control device (6) is located can be determined, and the deterministic functions of the machine (1) used for treating printing materials can be freely communicated or shut according to the district (III) obtained.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com