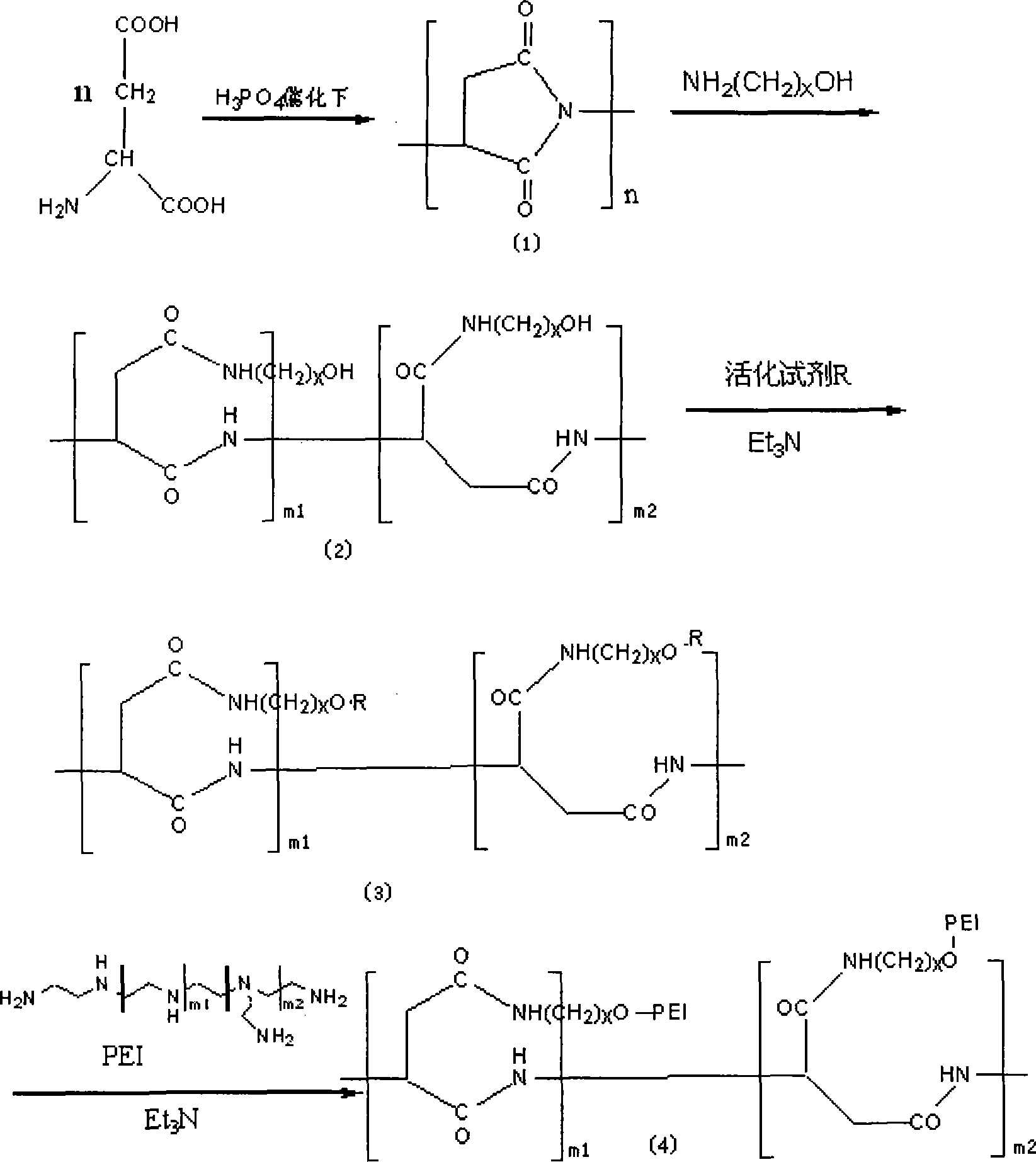
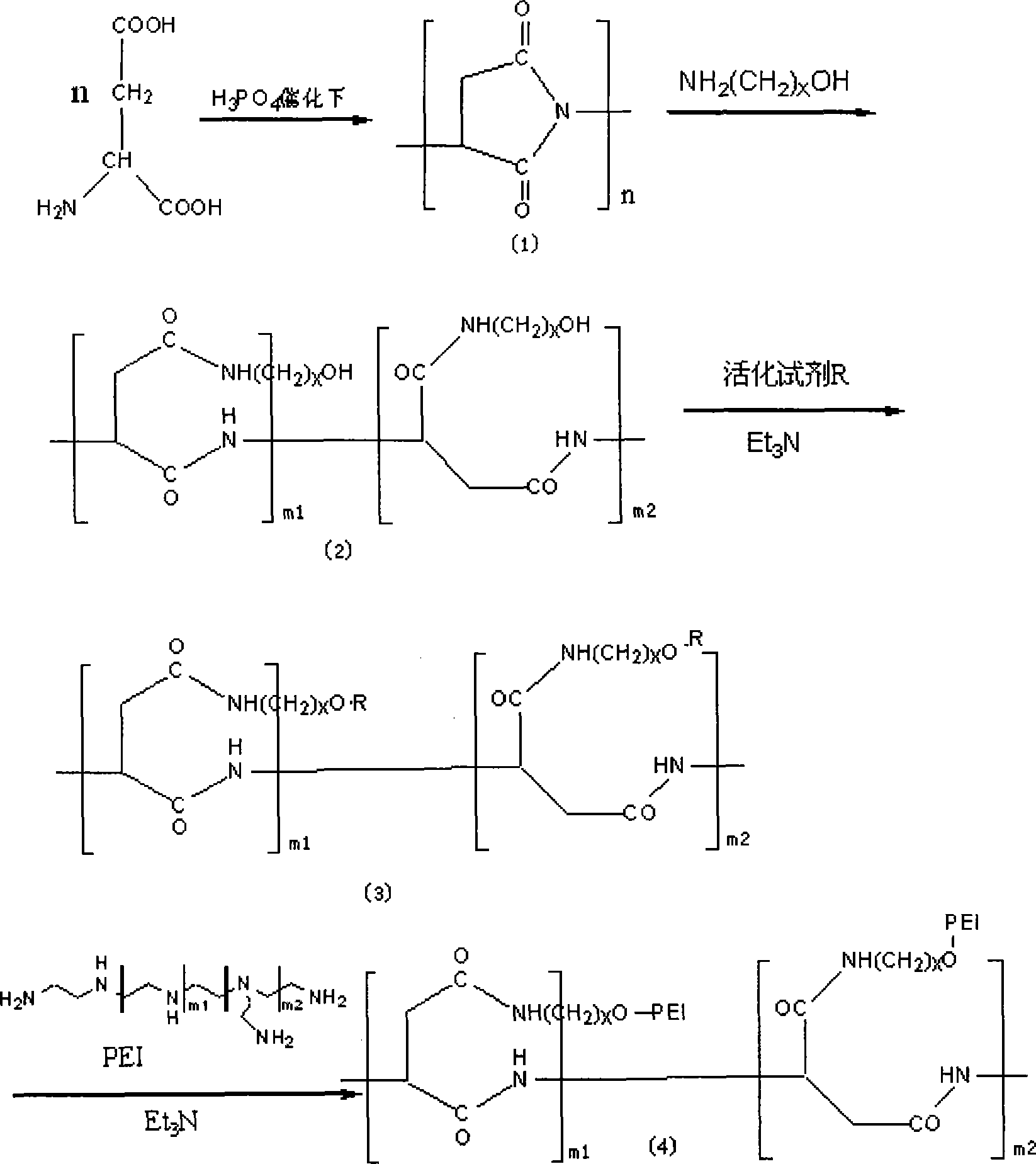
Method for preparing non-viral gene vector of amino acid material
An amino acid, non-viral technology, applied in the field of non-viral gene therapy vectors, can solve the problems of no transfection efficiency and low toxicity, and achieve the effects of high gene transfection efficiency and high recovery rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Take polyaspartic acid as an example.
[0030] 1) Preparation of polyaspartic acid-iminopropanol polymer
[0031] ● 10g of aspartic acid is catalyzed by 85% phosphoric acid, and dehydrated for 2h at 160-180℃ and reduced to 3mmHg under vacuum. Remove the vacuum pump and add N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) while it is hot to fully dissolve the solids. Add the reaction solution dropwise to 500 ml of distilled water to get a white flake precipitate, filter, and wash with distilled water To neutrality, dry to obtain 6.8 g of polyamino acid.
[0032]●Take 3 g of polyaspartic acid, dissolve it in 20 ml of DMF, cool, add 7 ml of 3-aminopropanol dropwise under an ice bath, stir for 4 hours at room temperature, and add the reaction solution dropwise to 100 ml of n-propanol During the precipitation, the precipitate was washed with acetone and filtered with suction to obtain a solid. The solid was placed in a round-bottomed flask, pumped with a water pump for 3 hours, and then p...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Take glutamic acid as an example to synthesize polyglutamic acid, and the synthesis process is the same as in Example 1.
[0039] Take 3 g of polyglutamic acid, dissolve it in 18 ml of DMF, cool, add 5 ml of 3-aminoethanol dropwise under an ice bath, stir for 4 hours at room temperature, add the reaction solution dropwise to 100 ml of n-propanol, and precipitate Precipitate, wash with acetone, and filter with suction to obtain a solid. The solid was placed in a round-bottomed flask, pumped with a water pump for 3 hours, and then pumped with an oil pump to completely dry, to obtain a polyglutamic acid-iminoethanol polymer.
[0040] Take 0.5 g of polyglutamic acid-iminoethanol polymer and dissolve it in 6 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Take 0.8 g of benzotriazole carbonate, dissolve it in 4 ml of DMSO, add it to the polymer solution under nitrogen protection and light-proof conditions, stir while adding, and react for 3 hours to obtain an activated polymer.
[0041] Take 1....
Embodiment 3
[0044] Take lysine as an example to synthesize polylysine, and the synthesis process is the same as in Example 1.
[0045] Take 3 grams of polylysine, dissolve it in 18 ml of DMF, cool, add 8 ml of 3-aminopentanol dropwise under an ice bath, stir for 4 hours at room temperature, and add the reaction solution dropwise to 100 ml of n-propanol. The precipitate was separated out, washed with acetone, and filtered with suction to obtain a solid. The solid was placed in a round bottom flask, pumped with a water pump for 3 hours, and then pumped with an oil pump to completely dry, to obtain a polylysine-iminopentanol polymer.
[0046] Take 0.5 g of polylysine-iminopentanol polymer and dissolve it in 6 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Take 1.0 g of N-hydroxysuccinimide chloroformate, dissolve it in 5 ml of DMSO, add it to the polymer solution under nitrogen protection and dark conditions, stir while adding, and react for 3 hours to obtain an activated polymerization Things.
[0047] Take ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com