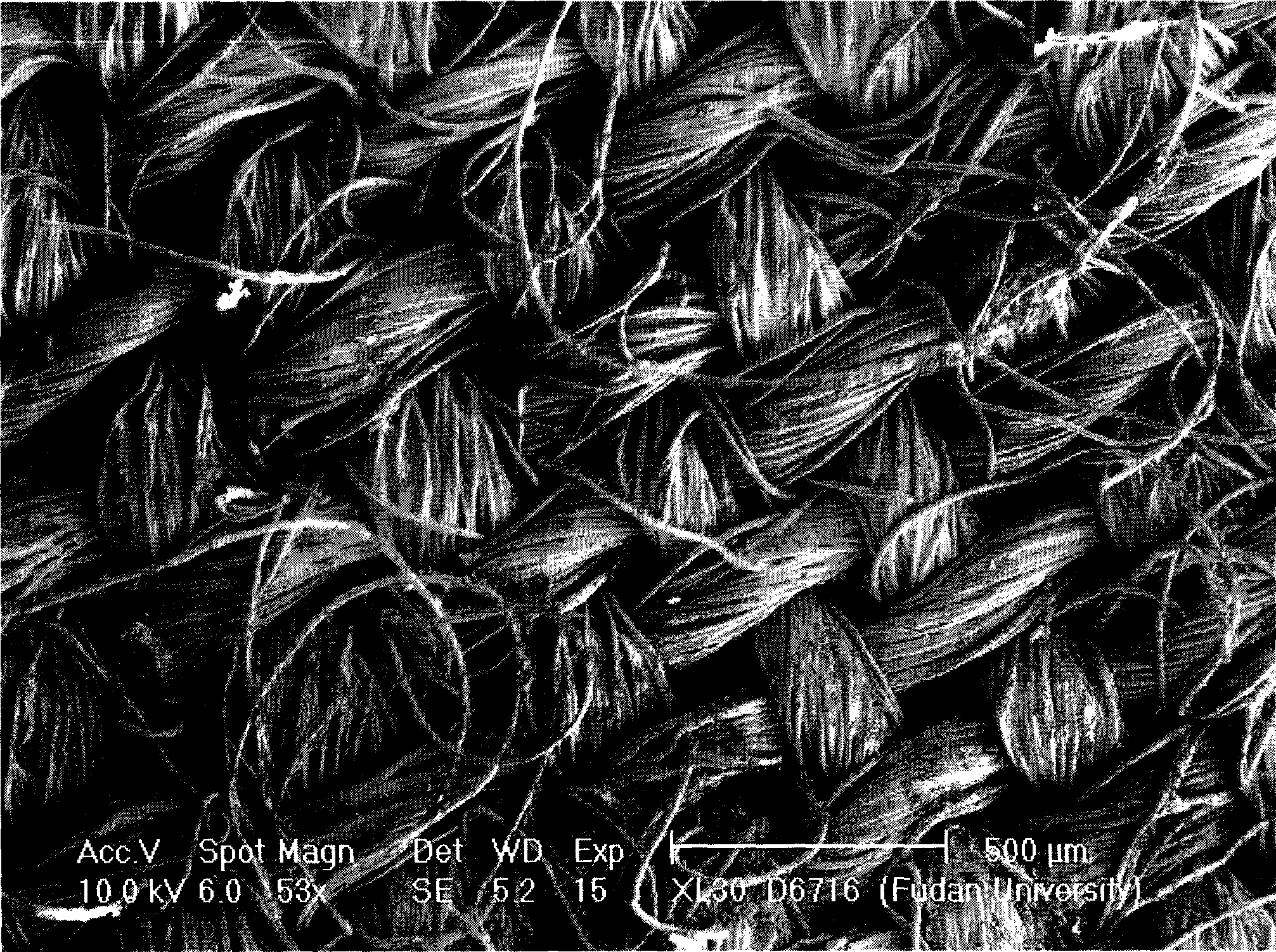Preparation method of copper-clad electromagnetic wave shielding fabric
An electromagnetic wave and fabric technology, which is applied in shielding, liquid chemical plating, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as limited application range, reduced shielding efficiency, and short service life, and achieves simple and environmentally friendly process flow, high electromagnetic wave shielding efficiency, The effect of high bond strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Wash the Nylon polyester cloth with a weight of 4g and an area of 20 cm × 25 cm with deionized water, dry it, and place it in 0.01% 3-(2-aminoethyl)-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane in ethanol solution, soak for 25 minutes, take it out, rinse with ethanol, and dry to obtain nylon-polyester cloth with surface hydroxylation.
[0020] Arrange the surface hydroxylated nylon and polyester in the acetone solution with a concentration of 1% 2-mercaptoethyltrimethoxysilane, soak for 60 minutes, take it out, rinse with ethanol, and dry to obtain the surface mercaptolated nylon and polyester cloth .
[0021] Dissolve 4g of copper sulfate, 10g of sodium potassium tartrate, 8g of sodium citrate, 6g of sodium borohydride, 6g of boric acid, and 1.5g of sodium hydroxide in 500mL of deionized water. After the dissolution is completed, add deionized water until the volume of the solution is 1L, to obtain Copper electroless plating solution.
[0022] Arrange the mercapto-coated brocade an...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Wash the polyester cotton cloth with a weight of 4 g and an area of 20 cm × 25 cm with deionized water, dry it, and place it in 0.1% 3-(2-aminoethyl)-aminopropyltriethoxysilane in methanol solution, soak for 5 minutes, take it out, rinse with ethanol, and dry to obtain polyester-cotton cloth with surface hydroxylation.
[0025] Arrange the surface-hydroxylated polyester cotton in a cyclohexanone solution with a concentration of 0.01% 2-mercaptoethyltriethoxysilane, soak for 60 minutes, take it out, rinse with ethanol, and dry to obtain the surface-mercaptolated polyester cotton. Polyester cotton.
[0026] Dissolve 6g of copper sulfate, 8g of sodium potassium tartrate, 10g of sodium citrate, 5g of sodium borohydride, 3g of boric acid, and 1g of sodium hydroxide in 500mL of deionized water. After the dissolution is complete, add deionized water until the volume of the solution is 1L to obtain copper Electroless plating solution.
[0027] Arrange the mercapto-coated po...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Wash a polyester cloth with a weight of 4 g and an area of 20 cm × 25 cm with deionized water, dry it, place it in a 0.5% ethylene glycol solution of 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane, soak it After 15 minutes, take it out, rinse it with ethanol, and dry it to get a hydroxylated polyester cloth.
[0030] Arrange the surface hydroxylated polyester in a tetrahydrofuran solution of 5% 3-mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane, soak for 45 minutes, take it out, rinse with ethanol, and dry to obtain the surface mercaptolated polyester cloth.
[0031] Dissolve 5g of copper sulfate, 9g of sodium potassium tartrate, 8g of sodium citrate, 6g of sodium borohydride, 5g of boric acid, and 2g of sodium hydroxide in 500mL of deionized water; Electroless plating solution.
[0032] Arrange the mercapto-coated polyester cloth in the above-mentioned plating solution, and chemically plate it at 40°C for 4 hours, take it out, wash it with water, and dry it to obtain a copper-clad polyester cloth, we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com