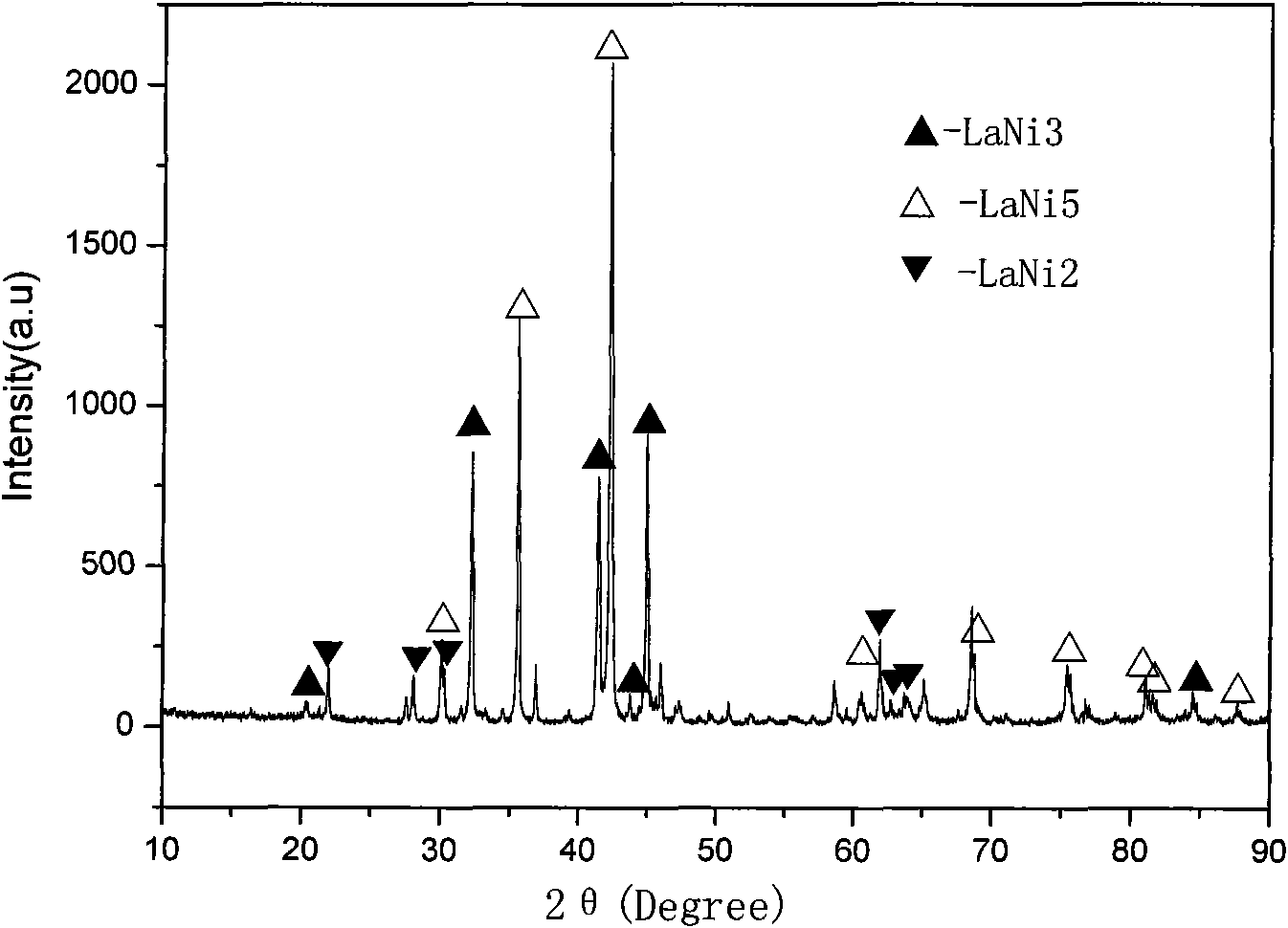
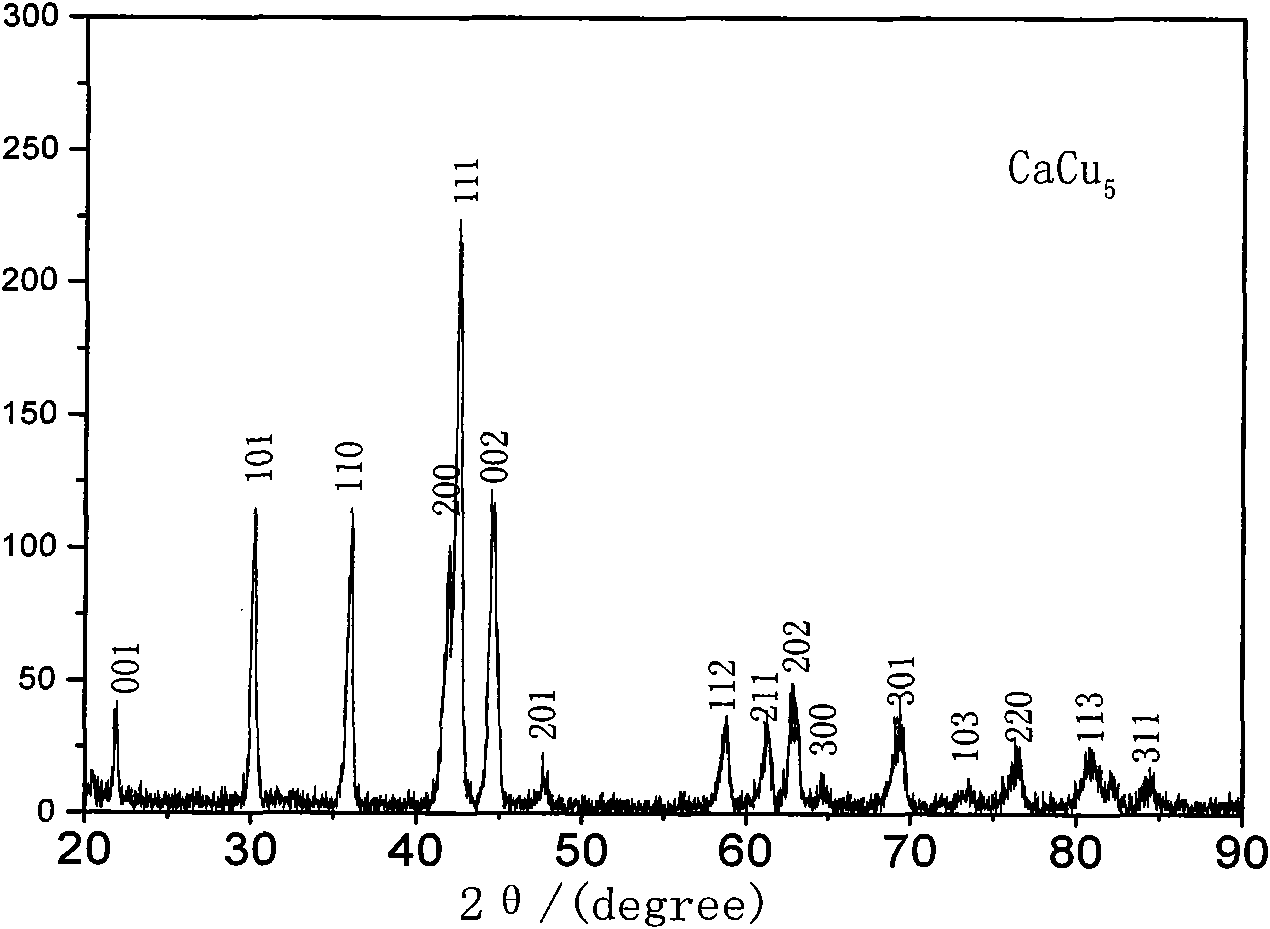
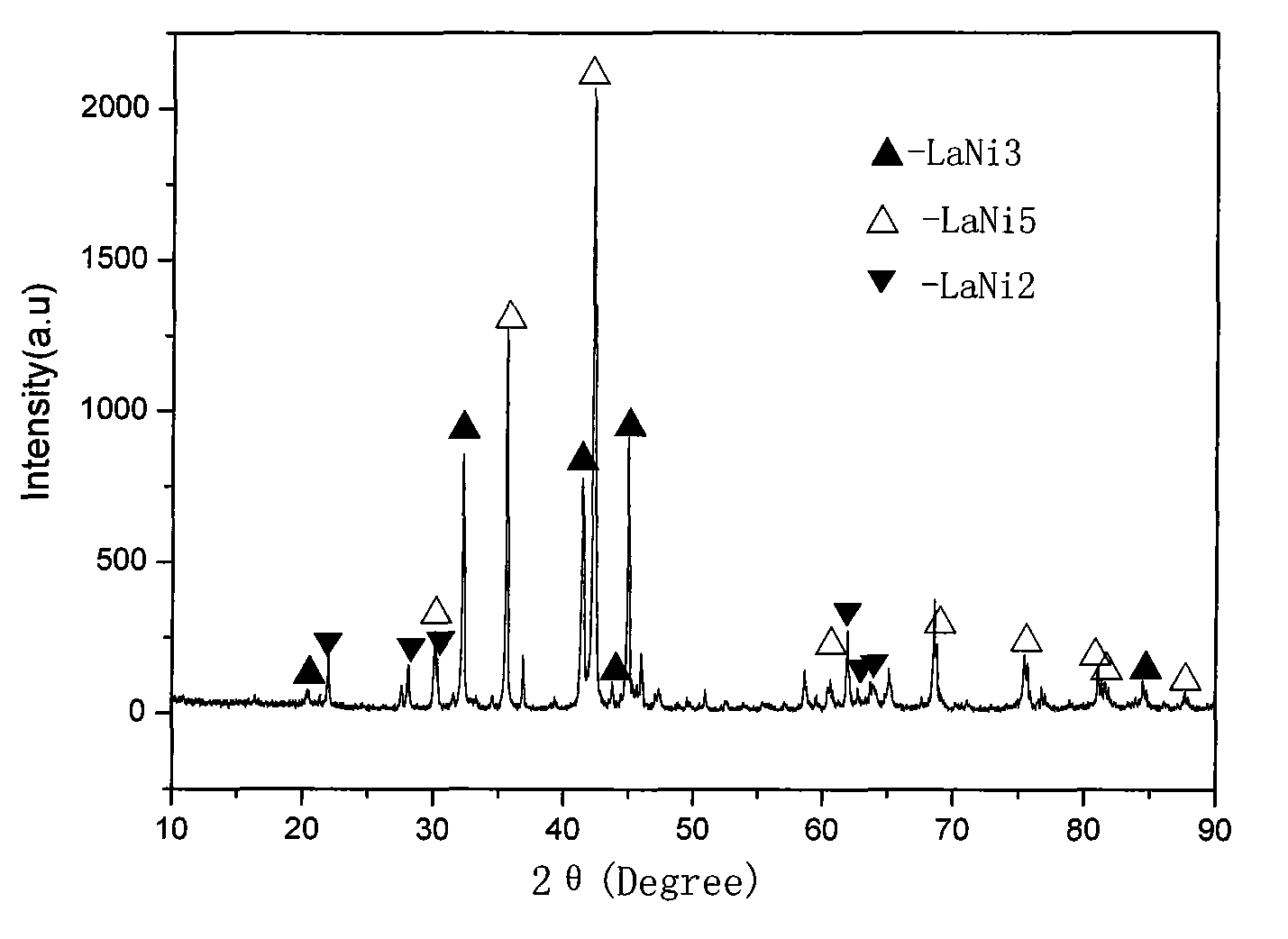
Hydrogen storage alloy for Re-Mg-Ni type metal hydride secondary battery and preparation method thereof
A hydrogen storage alloy and secondary battery technology, applied in electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as uneven alloy composition and structure, low production efficiency, and difficult control of composition and structure, and achieve uniform structure and structure , The preparation method is simple, the effect of good discharge capacity
Active Publication Date: 2010-11-03
CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
View PDF5 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
The results reported in journal literature are that the discharge capacity is mostly 330-390mAh / g, and the highest capacity can reach 410mAh / g. After 100 charge-discharge cycles, the capacity retention rate is mostly in the range of 60-80%, and the better one is 150 The capacity retention rate after one charge-discharge cycle can reach about 80%, that is, the cycle life can only reach 100-200 times, and the better one can reach about 300 times, which is far from the requirement of a practical cycle life of more than 500 times. , it is difficult to meet the requirements of Ni / MH batteries for negative electrode materials only by optimizing the electrochemical properties of the alloy
[0006] For La-Mg-Ni alloys, due to the large difference in melting point and volatility of Mg and Ni, when Mg-Ni alloys are prepared by traditional smelting methods, it is necessary to continuously add Mg for re-smelting, or by smelting intermediate alloys. To ensure the accuracy of the alloy composition; in comparison, the mechanical alloying method can overcome the shortcomings of low melting point and high vapor pressure of magnesium metal, but the preparation of magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloys by mechanical alloying requires a long ball milling time, at least 3 days, as many as 6-8 days, the preparation efficiency is low, and it is easy to introduce impurity pollution; the hydrogenation combustion method is a solid-state combustion reaction, which is usually solid-state combustion in an argon or hydrogen atmosphere to synthesize La-Mg-Ni-based alloys, which have The advantages of energy saving and simple equipment, but its main disadvantage is poor repeatability; the preparation of La-Mg-Ni-based alloys by ordinary sintering methods is not easy to bring in impurities, and when the synthesis temperature is not high, the saturated vapor pressure of magnesium is small and easy Control the composition ratio and content of the alloy, but the disadvantage is that the sintering time is long and it is difficult to produce in large quantities, generally only a few tens of grams
In addition, because Mg is a very active metal, it is easy to be oxidized and corroded, and its oxide film is loose, which is easy to be further oxidized and corroded. It is prone to oxidation, combustion and even explosion during high-temperature smelting, which leads to Mg-based hydrogen storage. There are also some difficulties in the preparation of alloys
[0007] At present, the preparation methods of La-Mg-Ni type hydrogen storage alloys are: mechanical alloying, the disadvantage is that it is difficult to produce on a large scale
The disadvantage of powder sintering method is that the experiment period is long, the alloy composition and structure are not uniform, the oxygen content is easy to exceed the standard, and it is difficult to realize large-scale production
Chinese invention patent 200610088905.4 discloses 'a preparation method of RE-Mg-Ni-M hydrogen storage alloy', using an intermediate alloy of Mg and other elements as the raw material of Mg, the disadvantage is that the process procedure is increased
Chinese invention patent 03115993.1 discloses a "new hydrogen storage alloy for nickel-metal hydride secondary battery and its preparation and annealing treatment method", which adopts magnetic levitation melting or electric arc furnace melting, and the disadvantage is that it is difficult to produce on a large scale (generally only a few Ten grams) and induction furnace smelting, the preparation of La-Mg-Ni type hydrogen storage alloy by traditional induction furnace smelting has the disadvantages of serious volatilization of Mg element, difficult control of composition and structure, etc.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: La 0.75 Mg 0.25 Ni 3.5 Si 0.05
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: La 0.75 Mg 0.25 Ni 3.5 Si 0.10
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: La 0.60 Nd 0.15 Mg 0.25 Ni 3.3 Si 0.10
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Login to View More
Abstract
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal material and preparation thereof, and more particularly relates to a hydrogen storage alloy for a Re-Mg-Ni type metal hydride secondary battery and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogen storage alloy has the chemical composition of A(1-x) Mgx Niy Siz, wherein x, y and z are atomic numbers, x is more than or equal to 0.2 and less than or equal to 0.4, y is more than or equal to 3.0 and less than or equal to 3.6, and z is more than or equal to 0.05 and less than or equal to 0.20; A is rare earth element Re or calcium, and the rare earthelement Re is at least one selected from lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium and yttrium. The key points of the preparation method are as follows: smelting is carried out in an induction furnace under the inert gas protective atmosphere; the raw materials are cast after being completely melted under the inert atmosphere, and cooled along with the furnace to room temperature under the inertgas atmosphere, so that as-cast alloy ingots can be obtained; the inert gas is one of argon, helium, neon, radon and xenon; and heat treatment step is vacuum annealing carried out in a vacuum heat treatment furnace. The method is simple and easy to produce the hydrogen storage alloy for the Re-Mg-Ni type metal hydride secondary battery in a way of large-scale industrialization, and the hydrogen storage alloy has high capacity and long service life.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of metal materials and their preparation, and in particular relates to a hydrogen storage alloy for a RE-Mg-Ni type metal hydride secondary battery and a preparation method thereof. Background technique [0002] As one of the main raw materials of nickel-metal hydride batteries, the anode material is a hydrogen storage material. After decades of research and development, its hydrogen storage capacity and cycle life have been greatly improved. Now it has been widely used in mobile communications and notebook computers. and other small portable electronic devices, and is being developed as a power source for commercialized electric vehicles. Among several typical hydrogen storage alloys, AB 5 The hydrogen storage performance of the type rare earth hydrogen storage alloy is the most ideal, but its hydrogen storage capacity is close to the theoretical capacity, the room for improvement of the cycle life is also...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): H01M4/04H01M4/38C22C19/03C22C1/02B22D21/02C22F1/10C22F1/02
CPCY02E60/12Y02E60/10
Inventor 林玉芳赵栋梁张羊换赵海花李平董小平
Owner CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com