Plant expression vector for vascular peculiar promoter to control antimicrobial protein gene and method for cultivating greensickness-resistant cotton
A plant expression vector and specific promoter technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reduced seed germination rate, reduced number of seeds, reduced formation of lateral roots, etc., to achieve the effect of inhibiting breeding and improving resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] The extraction of implementation example 1 plant DNA and RNA
[0062] 1. Extraction of plant genomic DNA
[0063] Select Arabidopsis thaliana, tobacco or cotton (tomato, rice, etc.) fresh plant tissue 0.5g, quickly ground into powder in liquid nitrogen, add 3mL 65 ℃ preheated CTAB extract (100mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH8 .0), 20mmol / LEDTA (pH8.0), 1.5mol / L NaCl, 2% CTAB (W / V), 4% PVP40 (W / V) and 2% mercaptoethanol (V / V), PVP and mercapto Add ethanol before use), shake quickly to mix. Bath at 65°C for 30min, then add 1mL 5mol / LKAc, ice-bath for 20min, extract once with an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) (10,000r / min, centrifuge at 4°C for 5min), and take the supernatant solution, add 2 / 3 times the volume of -20°C pre-cooled isopropanol, mix well, let it stand for about 30 minutes, pick out the flocculent precipitate with a glass rod, rinse repeatedly with 75% ethanol several times, and then rinse with absolute ethanol 1 time, air-dried and resuspended in 500...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Implementation example 2 Cloning of vascular specific promoter AAP2
[0067] 1. PCR cloning of vascular bundle-specific expression promoter AAP2
[0068] According to the characteristics of the Arabidopsis thaliana Amino acid permease gene2 (AAP2) gene, the Arabidopsis genomic DNA was used as a template, and the sequence 1 and sequence 2 were used as primers to amplify the promoter sequence of the AAP2 gene, and a 25 μL reaction system was constructed: 10×ExPCR buffer (no Mg 2+ 2.5 μL; 2.5 mmol / L dNTPs 2 μL; 25 mmol / L MgCl2 (magnesium chloride) 2 μL; primer 1 (5 μmol / L) 2 μL; primer 2 (5 μmol / L) 2 μL; Ex Taq DNA polymerase 1U; genomic DNA about 60 ng.
[0069] PCR reaction conditions: 94°C for 5min; 94°C for 1min; 50°C for 1min; 72°C for 2min and 30sec (1°C drop for each cycle); 94°C for 1min; 40°C for 1min; 72°C for 2min 30sec (25 cycles); 72°C 10min.
[0070] 2. Recovery of amplified products
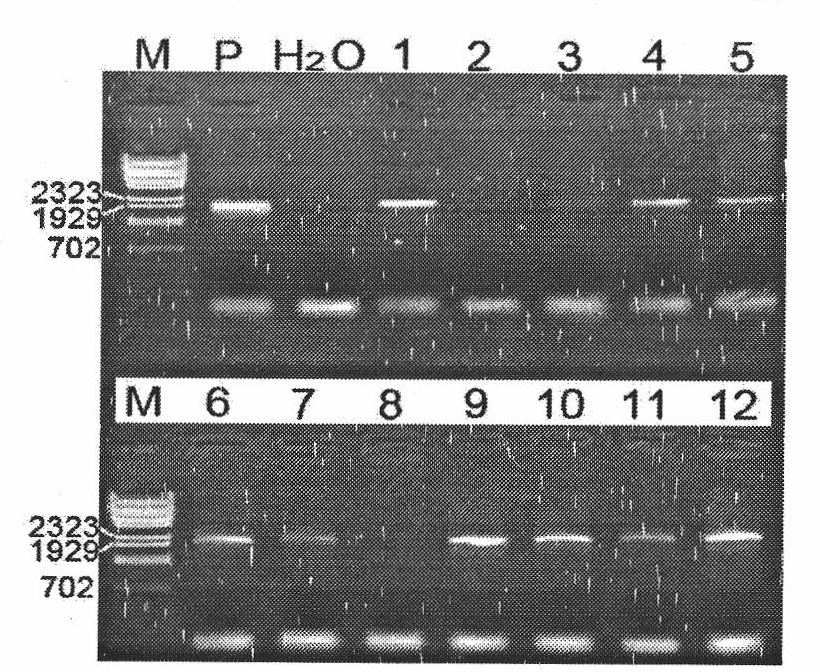
[0071] The PCR products were quantified by electrophoresis on agarose ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Implementation example 3 Construction of vascular specific promoter AAP2 plant expression vector
[0077] 1. Construction of vascular specific promoter AAP2 plant expression vector
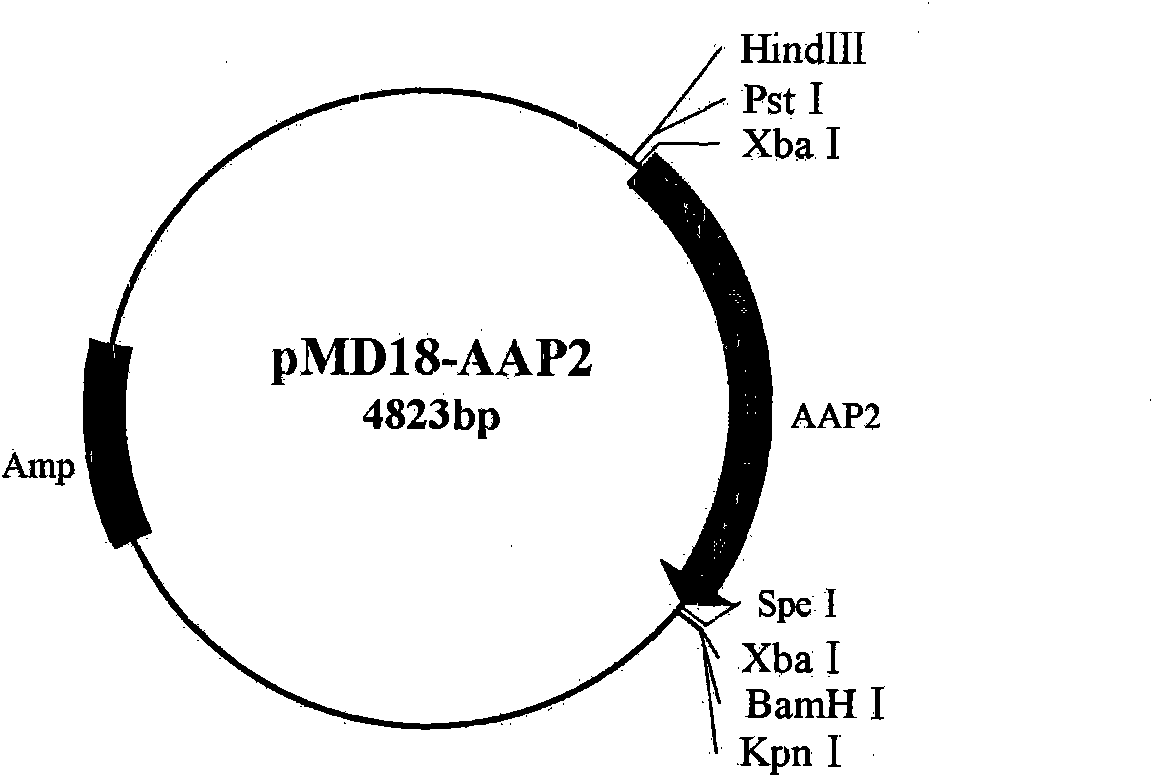
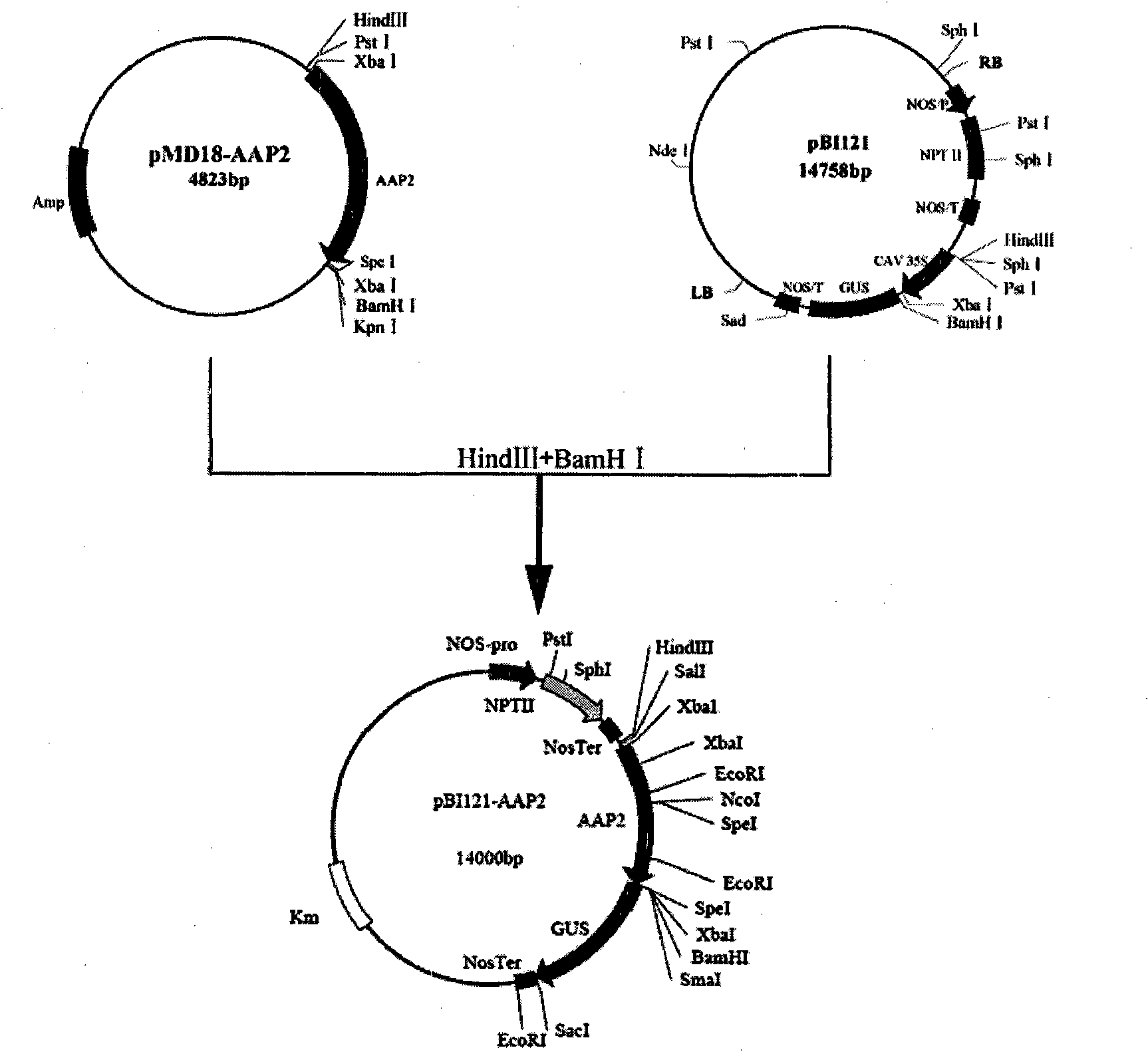
[0078] In order to analyze the expression characteristics of the AAP2 vascular-specific promoter, the AAP2 promoter sequence was substituted for the CaMV35S promoter sequence on the pBI121 vector to obtain the plant expression vector pBI121-AAP2. Vector construction flow chart see figure 2 .
[0079] 2. Transformation of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens host integrating the pBI121-AAP2 expression vector
[0080] The pBI121-AAP2 plant expression vector was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens by freeze-thaw method. The specific procedure is: add 0.5-1 μg of plasmid DNA to 100 μL of competent cells, mix well, and ice-bath for 30 minutes. After quick-freezing in liquid nitrogen for 5 minutes, incubate at 37°C for 5 minutes, and immediately ice-bath for 2 minutes. Add 1000μL liquid YEB,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com