Titanium carbide-based hard alloy taking nickel-molybdenum alloy as adhesive and preparation method thereof
A nickel-molybdenum alloy and cemented carbide technology, which is applied in the field of titanium carbide-based cemented carbide and its preparation, can solve the problems of reducing the bending strength of the alloy, the thickness of the annular phase, and the poor toughness of the cemented carbide, so as to improve the wettability. , The effect of improving strength and low porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
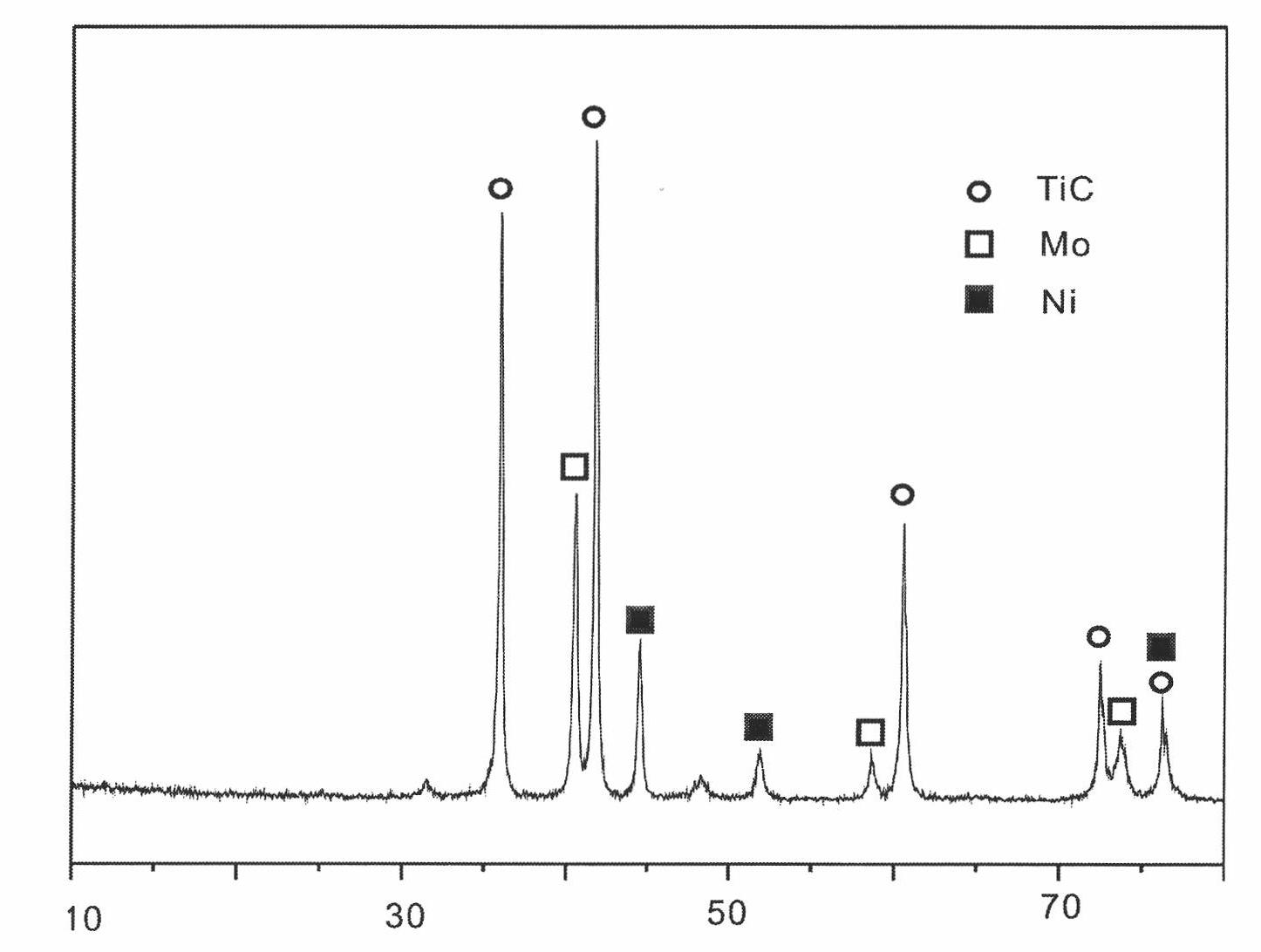
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] In this embodiment, the titanium carbide-based cemented carbide with nickel-molybdenum alloy as the binder is composed of 20% nickel powder, 10% molybdenum powder, and 70% titanium carbide powder in terms of mass percentage.
[0025] In the present embodiment, the preparation method of titanium carbide-based cemented carbide using nickel-molybdenum alloy as a binder, operates in the following steps:
[0026] a, nickel powder, molybdenum powder and titanium carbide powder are added in the planetary ball mill, and the ball mill rotating speed is 240r / min, and the ball milling ball is the WC-8wt%Co cemented carbide ball milling ball of diameter 5mm and 10mm, and ball material ratio is 6: 1. The ball milling time is 48 hours, the solvent used for wet milling is absolute ethanol, and the mixed slurry is obtained by wet milling until the powder particle size is 1-1.5 μm;
[0027] b. After filtering and drying the mixed slurry, add paraffin wax of 2% of the total mass of raw m...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In this embodiment, the titanium carbide-based cemented carbide with nickel-molybdenum alloy as the binder is composed of 13% nickel powder, 7% molybdenum powder and 80% titanium carbide powder in terms of mass percentage.
[0032] In this embodiment, the preparation method of titanium carbide-based cemented carbide using nickel-molybdenum alloy as a binder is the same as in Example 1, except that the vacuum degree during sintering in step b is 3 × 10 -2 Pa.
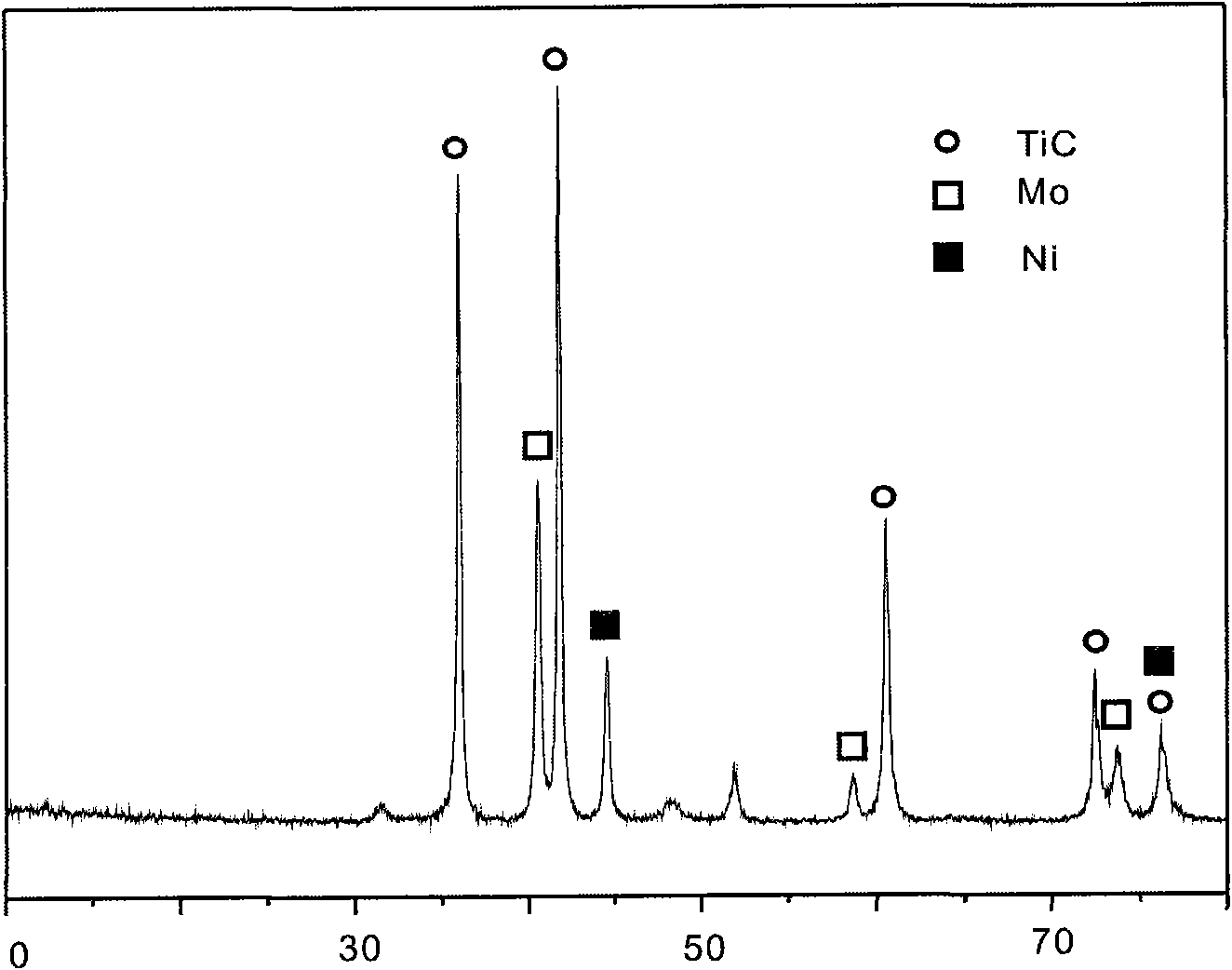
[0033] The TiC-based cemented carbide prepared according to the above composition and process has a uniform structure, its grain size is about 0.8-1.0 μm, its flexural strength is 1387.2 MPa, and its hardness is 92.1 HRA. Its X-ray diffraction pattern is shown in figure 2 , microscopic morphology see Figure 4 . The cemented carbide of this composition can be used for continuous cutting and finishing of low carbon steel, and can also be used as a substrate for diamond-coated cemented carbide.
Embodiment 3
[0035] In this embodiment, the titanium carbide-based cemented carbide with nickel-molybdenum alloy as the binder is composed of 17% nickel powder, 8% molybdenum powder, and 75% titanium carbide powder in terms of mass percentage.
[0036] In this embodiment, the preparation method of the titanium carbide-based cemented carbide with nickel-molybdenum alloy as the binder is the same as that in Example 1, except that the vacuum degree during sintering in step b is 5 × 10 -2 Pa.
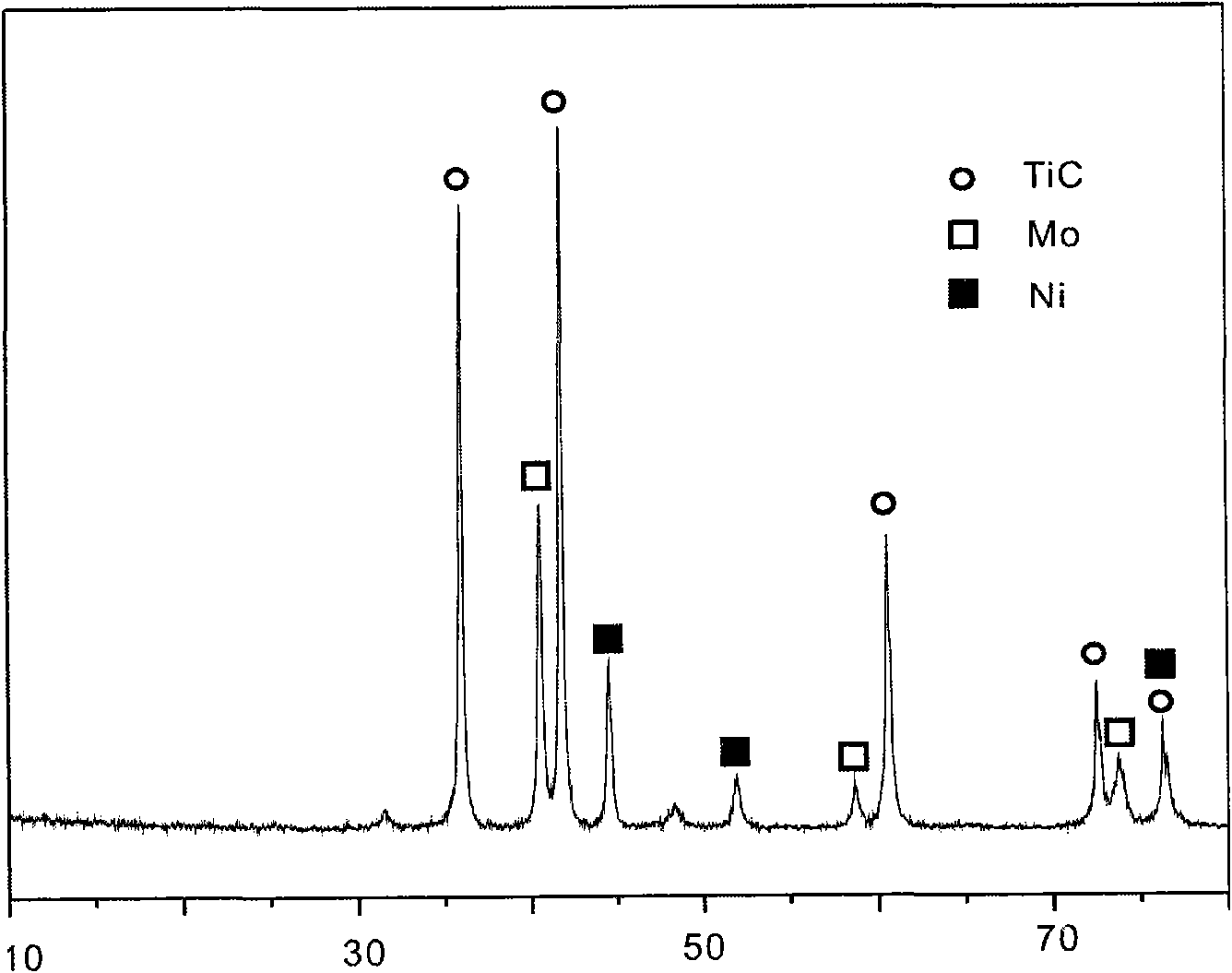
[0037] The TiC-based cemented carbide prepared according to the above composition and process has a uniform structure, its grain size is about 0.8-1.0 μm, its flexural strength is 1467.3 MPa, and its hardness is 92.0 HRA. Its X-ray diffraction pattern is shown in image 3 , microscopic morphology see Figure 6 . The cemented carbide of this composition can be used for continuous cutting and finishing of low carbon steel, and can also be used as a substrate for diamond-coated cemented carbide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com