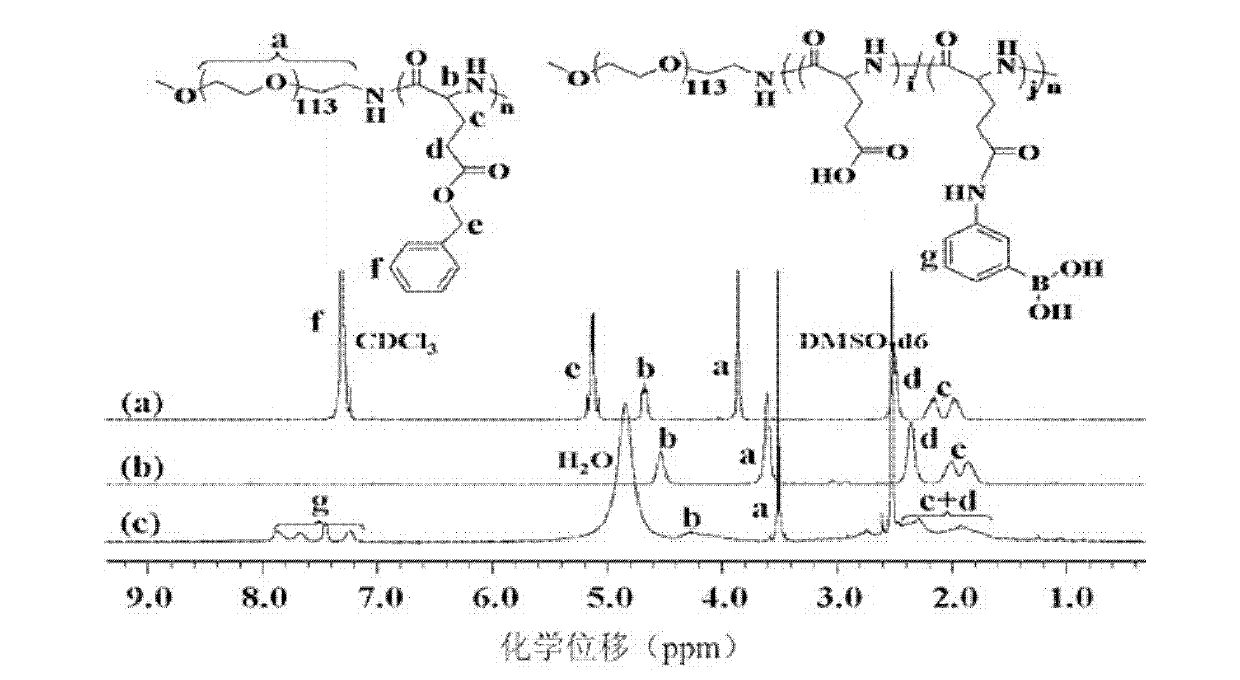
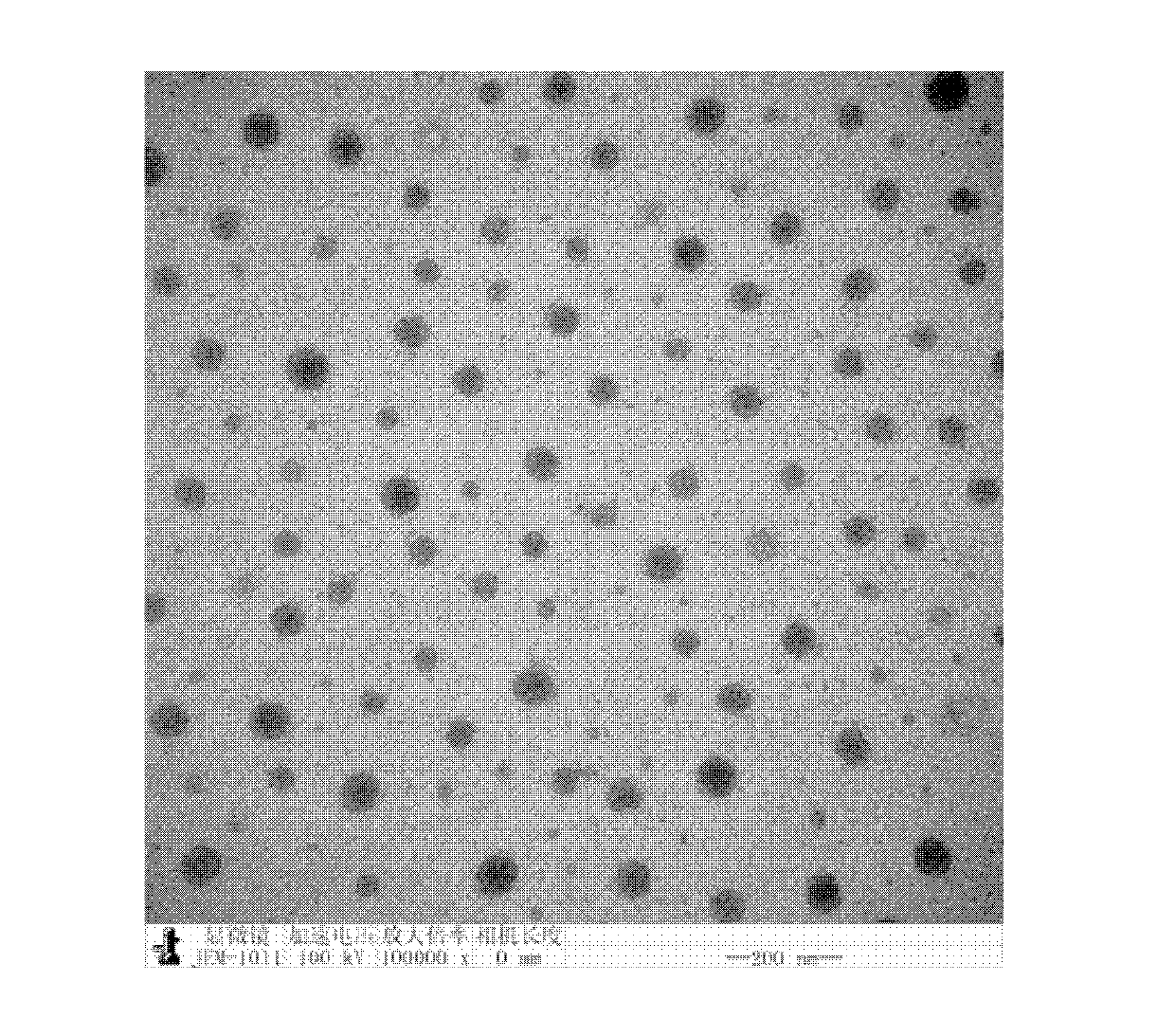
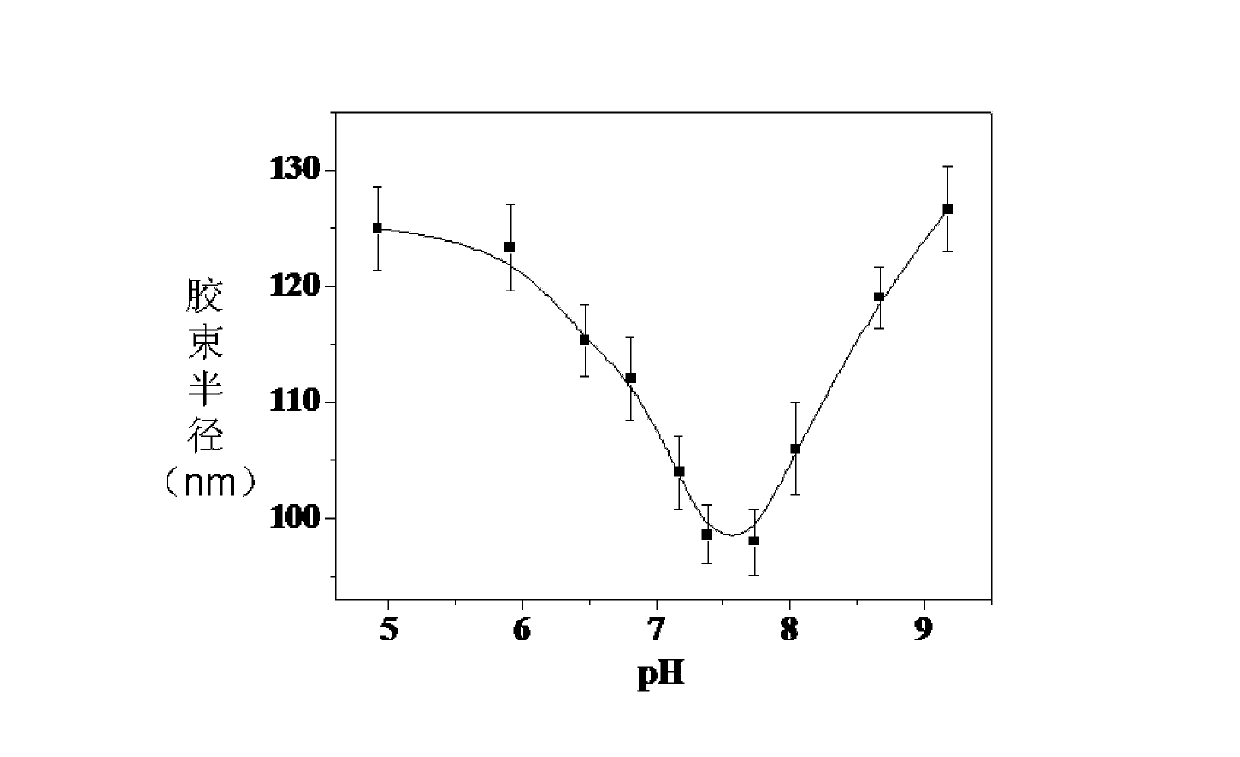
Copolymer, glucose sensitive micelle, glucose sensitive medicine-carrying micelle and preparation method thereof
A technology of glucose-sensitive and drug-loaded micelles, which is applied in the field of glucose-sensitive materials, can solve problems such as limitations in the field of bioavailability of glucose-sensitive materials, and achieve good biodegradability and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] The present invention also provides a kind of preparation method of copolymer, comprises the following steps:
[0048] γ-benzyl-L-glutamate-N-internal carboxylic acid anhydride undergoes ring-opening polymerization under the initiation of amino-terminated polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether hydrochloride to obtain poly(ethylene glycol monomethyl ether )-b-poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate);
[0049] The poly(ethylene glycol monomethyl ether)-b-poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) is deprotected to obtain poly(ethylene glycol monomethyl ether)-b-poly(L- glutamic acid);
[0050] Add 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide carries out activation reaction, then adds 3-aminophenylboronic acid and carries out condensation reaction, obtains the copolymer with formula (1) structure:
[0051]
[0052] Wherein, m is the degree of polymerization, 55≤m≤250; n is the degree of polymerization, 30≤n≤300; i and j are relative molar numbers, 0.1≤j / (i+j)...
Embodiment 1
[0097] After 25g of polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether with a molecular weight of 5000 was azeotroped with toluene to remove water, it was dissolved in 150mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, and 3.5mL of triethylamine was added at 0°C under anhydrous conditions, and 8mL of formaldehyde was added dropwise. Methylsulfonyl chloride and methanesulfonyl chloride were reacted at 0°C for 2 hours after the addition of methanesulfonyl chloride, returned to 25°C, and continued to react for 48 hours under stirring with a stirrer. , Vacuum drying at 25°C for 24h to obtain polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether methanesulfonate.
[0098] Dissolve 3g of polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether methanesulfonate and 1g of ammonium chloride in 80mL of ammonia water with a mass concentration of 25%, and react at 25°C for 72h. After the reaction, extract the aminated product with dichloromethane. Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, and washed with 4% sodium chloride aqueous solution by mass percentag...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Add 0.5 g (0.1 mmol) of the amino-terminated polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether hydrochloride (mPEG-NH2HCl) prepared in Example 1 to 3 reaction flasks under anhydrous conditions, and use toluene to azeotropically remove water and use Anhydrous N, N-dimethylformamide was dissolved to obtain amino-terminated polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether hydrochloride solution; 3.948g (15mmol), 5.791g (22mmol) and 6.581g (25mmol) Methyl-L-glutamate-N-internal carboxylic acid anhydride (BLG-NCA) was dissolved with anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide, and added to the amino-terminated polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether hydrochloride In the salt solution, react for 72h at 25°C under the condition of stirring with a stirrer. After the reaction is over, pour the solution into diethyl ether whose volume is 10 times that of the solvent to settle, filter, wash, and vacuum-dry at 25°C for 24h to obtain poly(ethyl ether) respectively. Glycol monomethyl ether)-b-poly(γ-benzyl-L-glutamate) (mP...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com