Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device
A device and anti-reflection layer technology, applied in the field of OLED devices, can solve the problems of poor light transmittance, low work function light transmittance, and high work function of the transparent cathode structure, so as to improve stability, improve quantum efficiency, and improve luminous efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
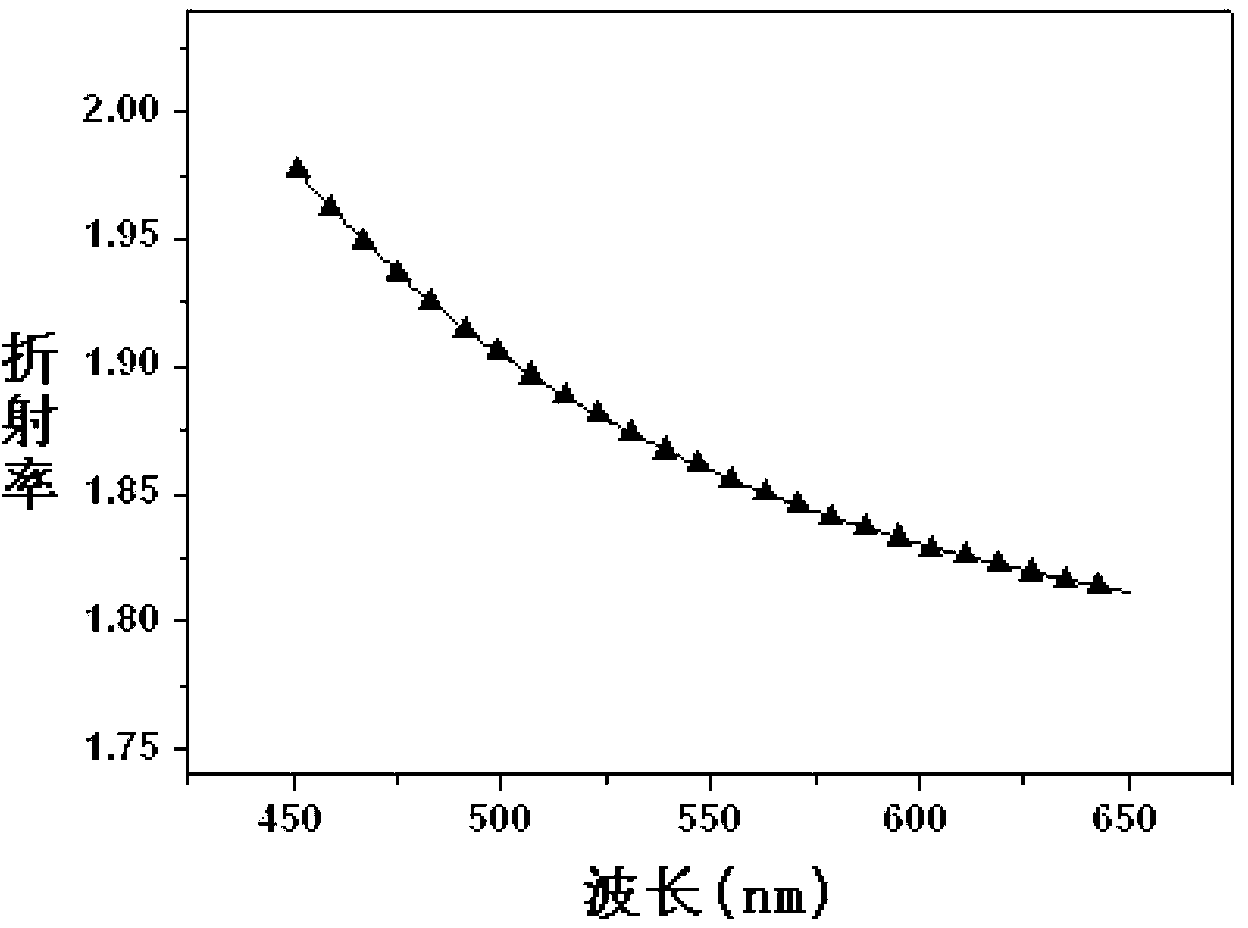
[0042] This embodiment is an embodiment of the preparation of the anti-reflection layer material F1.
[0043] The reaction route is divided into two steps. The first step is the preparation of the intermediate dibromoindenofluorene. The synthetic route is shown in the following formula:
[0044]
[0045] The specific method is:
[0046]Dissolve 26.4g 1,4-dibromo-2,5-dimethylbenzene and 24.4g phenylboronic acid in 300.0mL toluene and 100.0mL ethanol, add 27.6g K 2 CO 3 and 0.65g of tetrabutylammonium bromide, 1.5g of tetrakis(3-phenylphosphine)palladium, and reflux for 2h to finally obtain 22.5g of 2,5-dimethyl-4-phenylbiphenyl with a yield of 87.2%. Continue the reaction of the obtained product in the next step, dissolve it in 200.0 mL of pyridine, add 41.2 g of potassium permanganate and 50.0 mL of water, reflux for 2 h, and the reaction is complete. After filtering, the pyridine layer was made acidic with hydrochloric acid, and a large amount of white solid was found t...
Embodiment 2
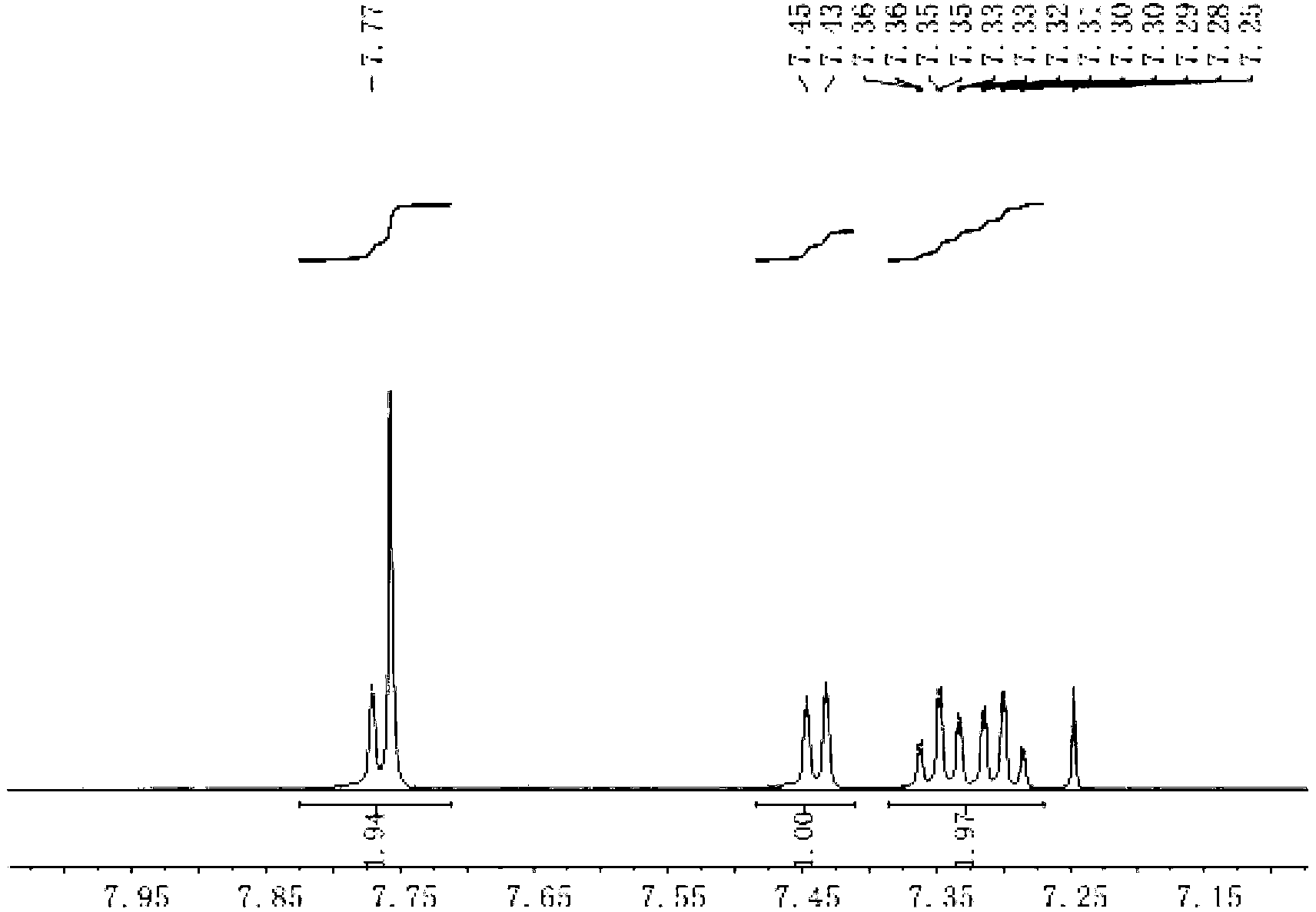
[0057] This example is a preparation example of compound F2. The preparation of F2 includes two steps. The first step is the preparation of the intermediate dibromoindenofluorene, which is the same as in Example 1. The second step is the preparation of compound F2. Synthetic route As shown in the following formula:
[0058]
[0059] The specific method is:
[0060] A.25.2g (75mmol) N-p-tolyl-3-bromocarbazole was dissolved in 300ml redistilled THF, cooled the reaction system to -78°C with a cold bath, and slowly added 37.5ml of 2.4 M n-BuLi solution, after the dropwise addition is complete, keep this temperature for about 1 hour. Then 28ml of triisopropyl borate was added dropwise. After the drop, the reaction was stirred for 30 minutes, the cold bath was removed, the reaction system was slowly raised to room temperature and continued to stir at room temperature for 1.5 hours. Add 20ml of 1:1 hydrochloric acid solution dropwise to neutralize the reaction system, continue s...
Embodiment 3
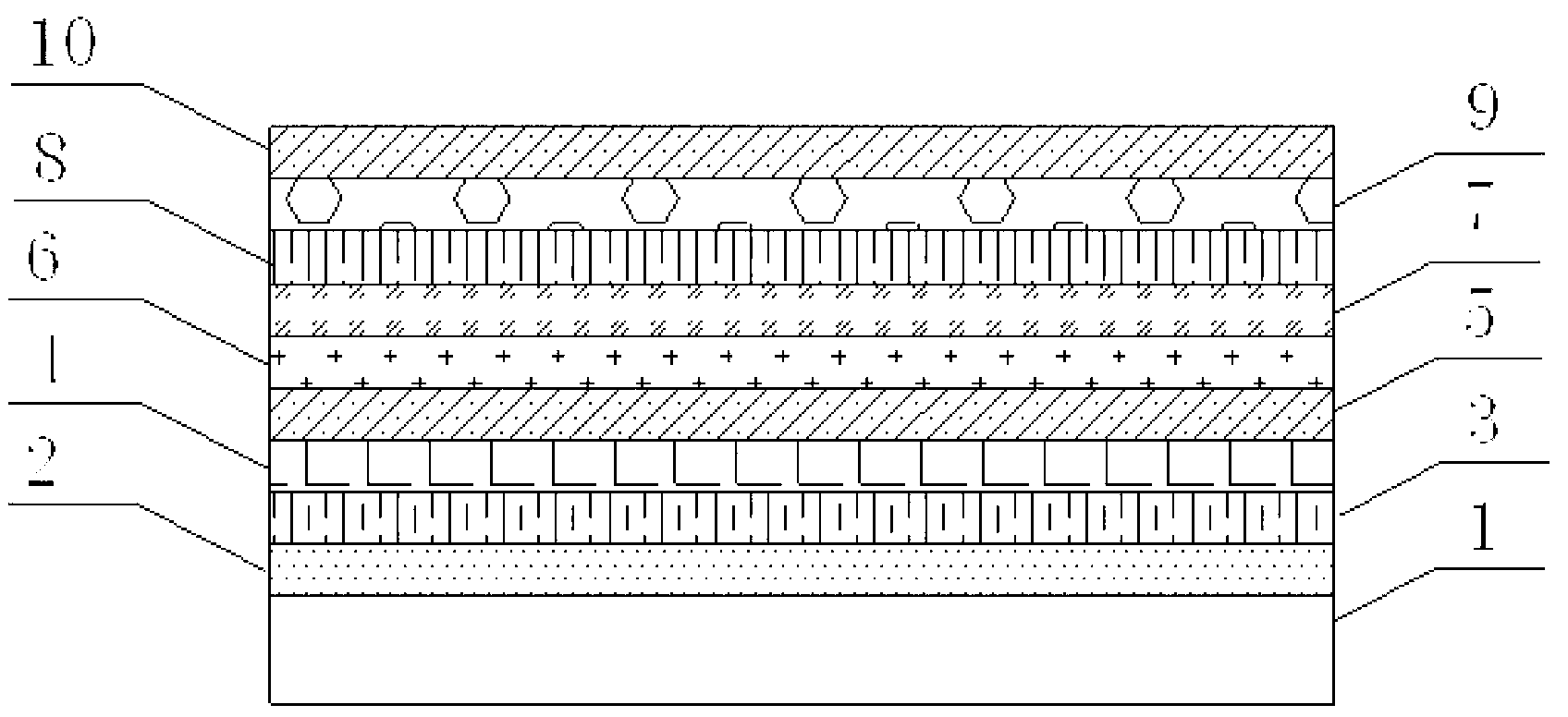
[0064] This embodiment is an example of OLED device preparation. The device in this embodiment is a top-emitting organic electroluminescent device. The structure includes: a substrate 1, and a reflective layer 2, an anode 3, and a hole injection layer formed by plating on the substrate 1 in sequence. layer (HIL) 4 , hole transport layer (HTL) 5 , light emitting layer (EML) 6 , electron transport layer (ETL) 7 , electron injection layer (EIL) 8 , cathode 9 and cover layer 10 .
[0065] Among them, the substrate 1 is a glass substrate, a quartz substrate or a flexible polymer substrate (plastic or polyimide, etc.); the reflective layer 2 can be metal silver or silver alloy, metal aluminum or aluminum alloy layer, used to reflect the direction of the incident substrate light; the anode layer 3 can be organic semiconductor materials such as ITO (indium tin oxide), IZO (indium zinc oxide), high work function metals or alloys, and C60; all of which can achieve the purpose of the pres...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com