Preparation method for high-activity humic acid biofertilizer
A high-activity humic acid and biological fertilizer technology, which is applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, organic fertilizers, fertilizer mixtures, etc., can solve the problems of low content of effective bacteria in inoculants, low biological activity of humic acid, and single preparation technology. The effect of excellent fecundity, comprehensive and reasonable nutrients, and high reproductive ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
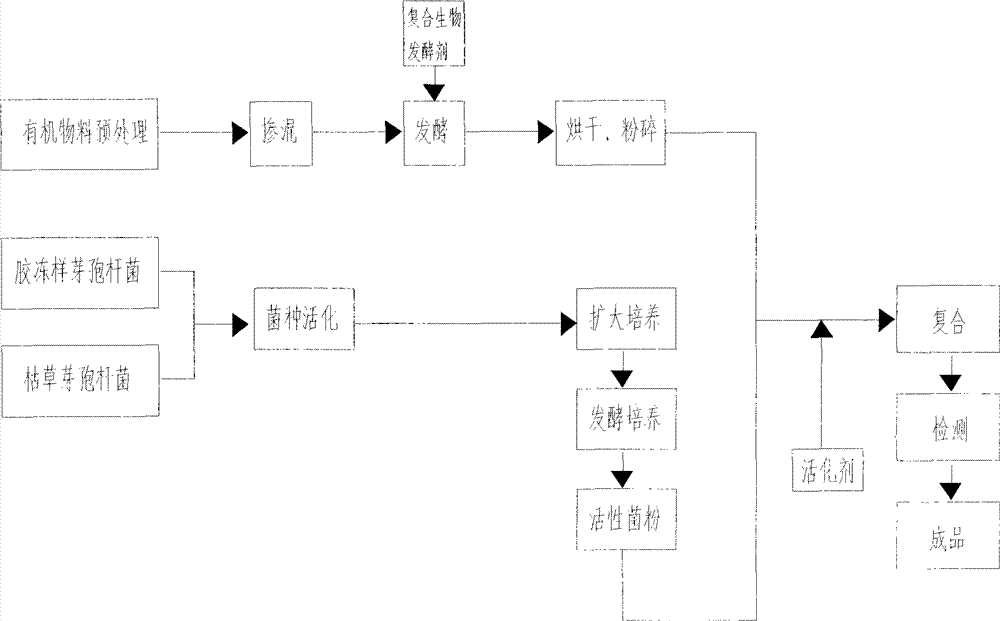
[0052] Embodiment 1: the preparation of humic acid biological organic fertilizer
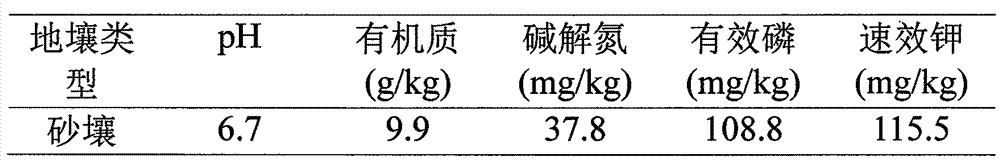
[0053] (1) Organic material pretreatment: dry and dry the duck manure; crush the straw into 2 cm long straw segments; coarsely crush the mixture of corncobs and grape seeds; break up the waste fungus sticks with a mixer dry;
[0054] (2) Extraction of active humic acid (salt): pulverize lignite (or peat) to 60 mesh. Add 3% sodium hydroxide solution at a weight ratio of 1:10, extract at 60°C for 2 hours, and then add 30% hydrogen peroxide at a weight ratio of 100:1 after the extract is centrifuged to remove residue. Activate at 70°C for 1.5h to become an activation solution. Then use 1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution and 0.2‰ polyacrylamide solution in a volume ratio of 10:2 to compound the composite precipitant, and use the above-mentioned per 1m 3 Add 70L composite precipitant to the activation solution to precipitate and separate brown and black humic acids, concentrate and dry the supernat...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: the preparation of humic acid biological organic fertilizer
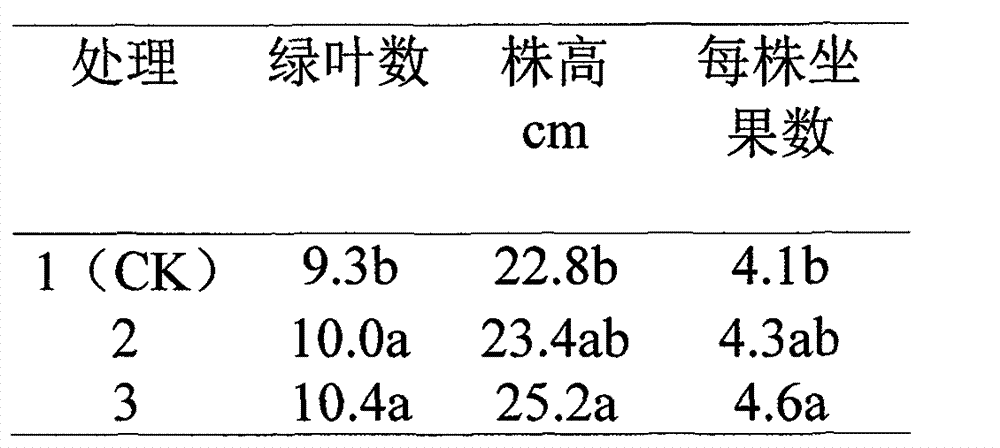
[0059] The production method is the same as that in Example 1, and the ratio of main materials is as follows: 40% of dried cow dung, 5% of straw, 5% of waste fungus sticks, and 5% of corncobs. Then add 3% ammonium sulfate, 2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, 0.5% zinc sulfate, humic acid (salt) 20%, finally add 0.1% eucalyptol, 0.3% sodium lauryl sulfate, 1% alkyl aryl poly Glycol ethers. Stir evenly and adjust the moisture content to 50%. Add and mix the total amount of organic material 1% compound biological starter (organic material decomposing agent: photosynthetic bacteria: Lactobacillus casei: Bacillus subtilis: yeast = 5: 3: 1: 1.5: 1.5). Under normal temperature, carry out biological aerobic solid fermentation for 7 days. The fermentation temperature is controlled during the process, and when the temperature reaches 70°C, mechanical turning and throwing is carried out. After t...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Secondary addition of the preparation of the bacterial agent used
[0061] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0062] Preparation of culture medium: Weigh 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.3% beef extract, and 0.5 peptone expressed in weight percent respectively, dissolve them in distilled water or tap water after mixing, and use a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid to dissolve the culture medium solution. Adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5, then add 2% agar, heat to melt, then sterilize at 121°C and 0.11MPa pressure for 30 minutes, and make a slant solid medium after cooling for later use.
[0063] Pick a little jelly-like bacillus lawn from the slope of the original strain under sterile conditions and put it on the solid medium of the slope for activation. Cultivate it at a culture temperature of 29-30°C for 24 hours, and no bacteria are found after inspection. 1. The bacteria grow neatly, and then cultured in an incubator at 29-30°C for 24 hours. Observed with ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com