Aldolase mutant
A ‐phosphate aldolase and transformant technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of substrate concentration limitation, product separation difficulty, DERA enzyme inactivation, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the addition amount
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Construction of E.coli mutant deoC library
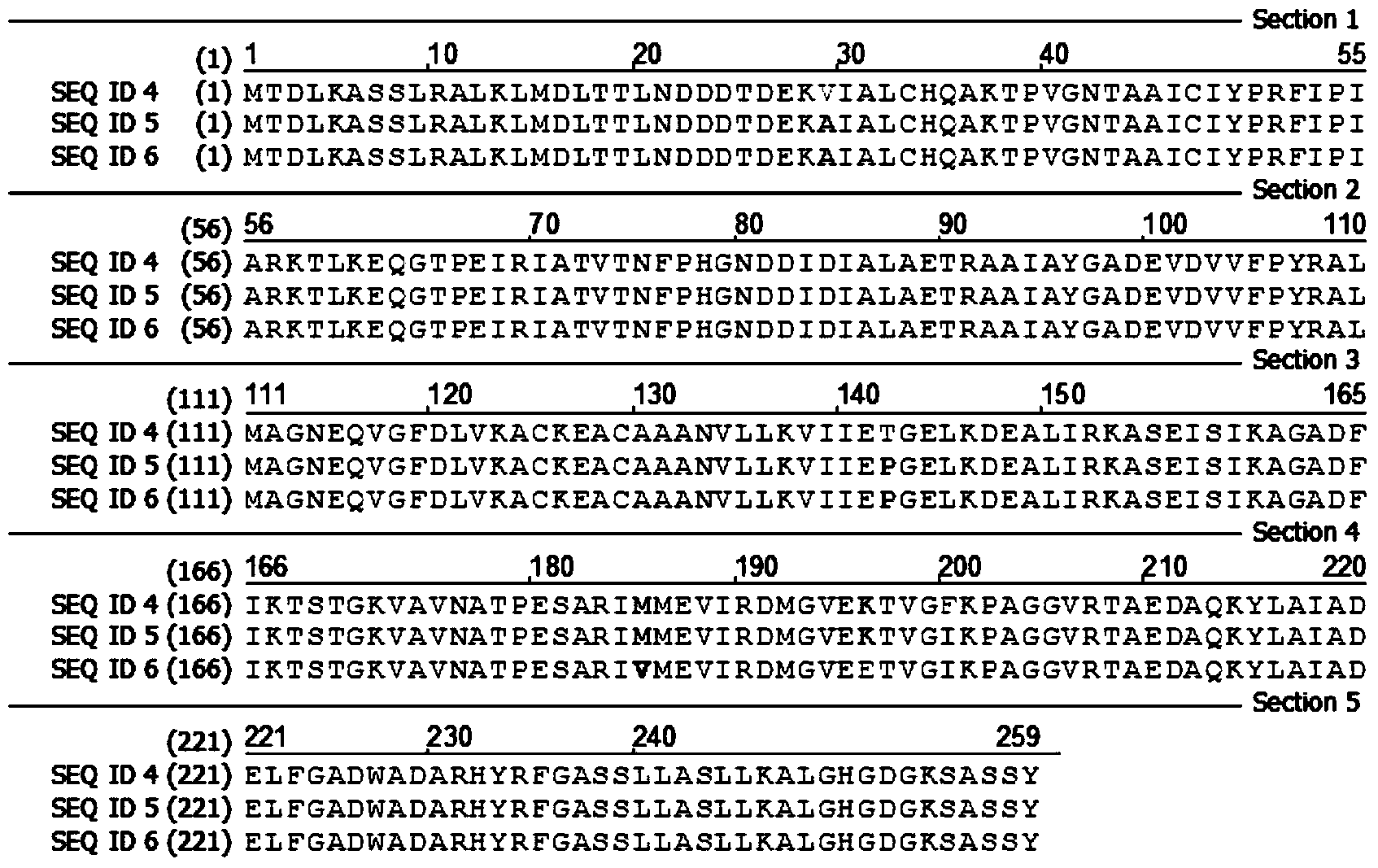
[0039] Using a random mutagenesis kit, multiple reactions were performed by changing the concentration of MnSO4, thereby introducing 1 to 3 point mutations into the E.coli deoC gene (SEQ ID No.3), making 1 to 2 amino acids in the amino acid sequence of the DERA enzyme is replaced. To amplify the E.coli deoC gene (SEQ ID No.3) encoding the E.coli DERA enzyme (SEQ ID No.4), use primers DAI13600 (SEQ ID No.1) and DAI13465 (SEQ ID No.2) respectively as forward and reverse primers. Both primers contained sites compatible with the PCR-amplified deoC gene fragment obtained by site-directed recombination cloning using Gateway Technology. The gel electrophoresis patterns of the PCR amplification products are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0040] Sequence SEQ ID No.1 of the forward primer (DAI13600):
[0041] 5’‐GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CTT CGA AGG AGA TAG AAC CAT GAC TGA TCT GAA AGC AAG CAG CC‐3’
[0042] The...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 Expression of DERA enzyme
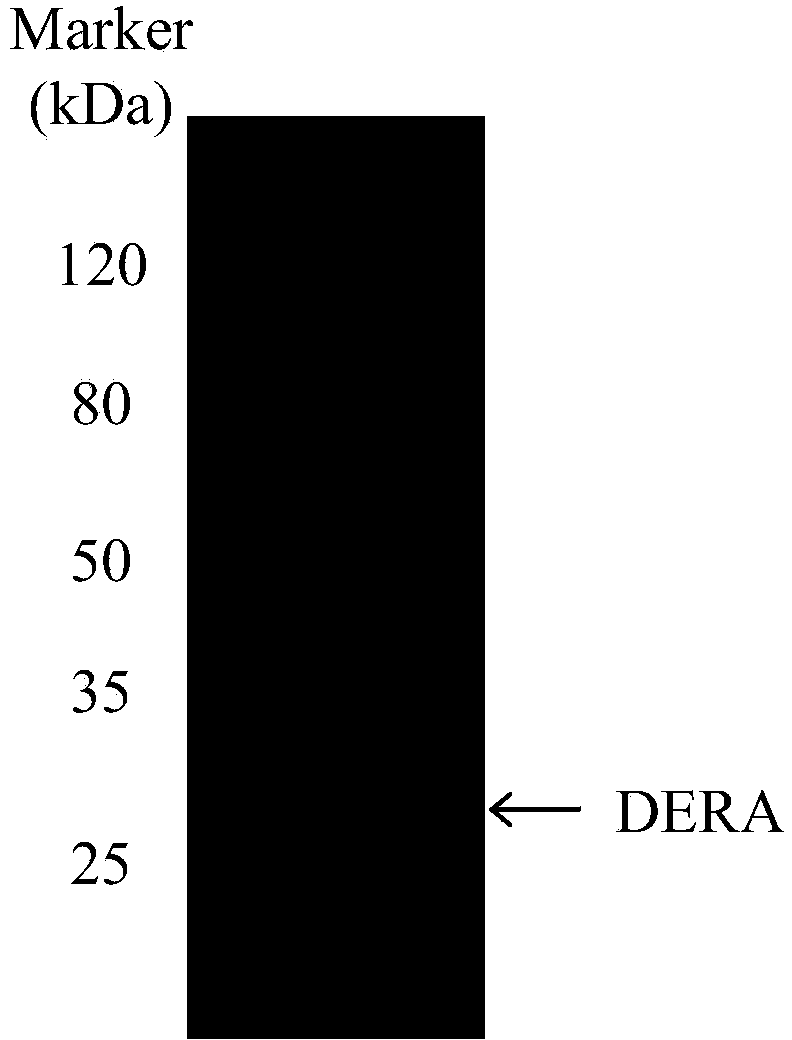
[0046] Expression of the mutated deoC gene in a deep-well microtiter plate: According to the mutant bacteria obtained in Example 1, select mutant colonies and inoculate them into 200 μl 2×YT medium (containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin) in a microtiter plate (MTP) , the culture condition is 37°C, and the time is 1 day. Then 100 μl of the above preculture was inoculated into a deep-well plate containing 500 μl of expression culture (2×YT, 100 μg / ml ampicillin, 1 mM IPTG), and then cultured on a shaker at 25°C for 24 hours. The SDS-PAGE electrophoresis pattern of the expression product is as follows: figure 2 shown. The expression of the unmutated deoC gene (SEQ ID No.4) under the same conditions was used as a control group.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Preparation of Fluorescent Substrate
[0048] The substrate is a conventional methyl-5-tosyl-2-deoxynucleotide. Dissolve 12.75 g of tosylate in 75 ml of DMF, then add 11.86 g of K to the resulting solution 2 CO 3 and 9.29 g of 4-methyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (4-methylumbelliferone, 4-MU). After the above mixture was stirred at 75°C for 16 h, 300 ml of water was added and extracted twice with 200 ml of ethyl acetate. The organic phase was back-extracted with 100ml of 0.1M NaOH, and the organic phase was dried with sodium sulfate. The crude extract obtained by concentrating the organic phase was dissolved in a mixture of 25ml of acetonitrile and 100ml of water, then 2.5g of ion exchange resin Dowex50WX8-100 was added, stirred at room temperature for 1.5h, and then methanol was distilled off under reduced pressure. After 2 days, the mixture was filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and purified with a silica gel column, using gradient elution from 100% et...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com