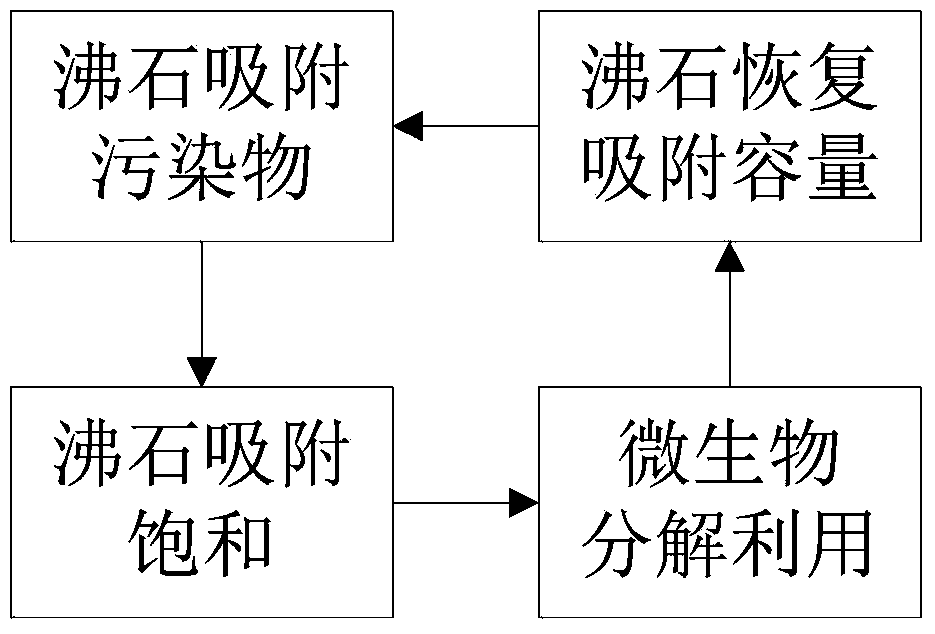
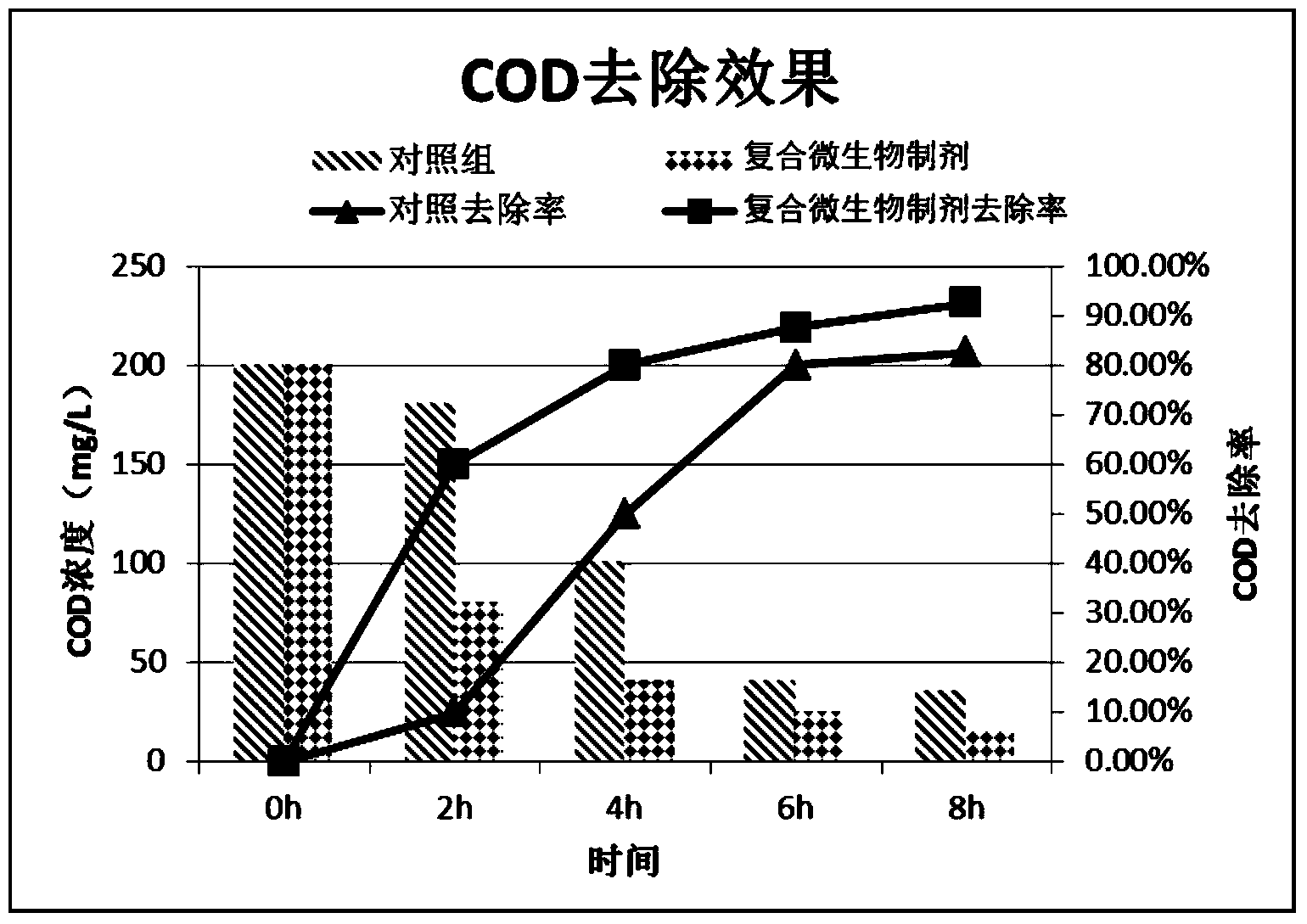
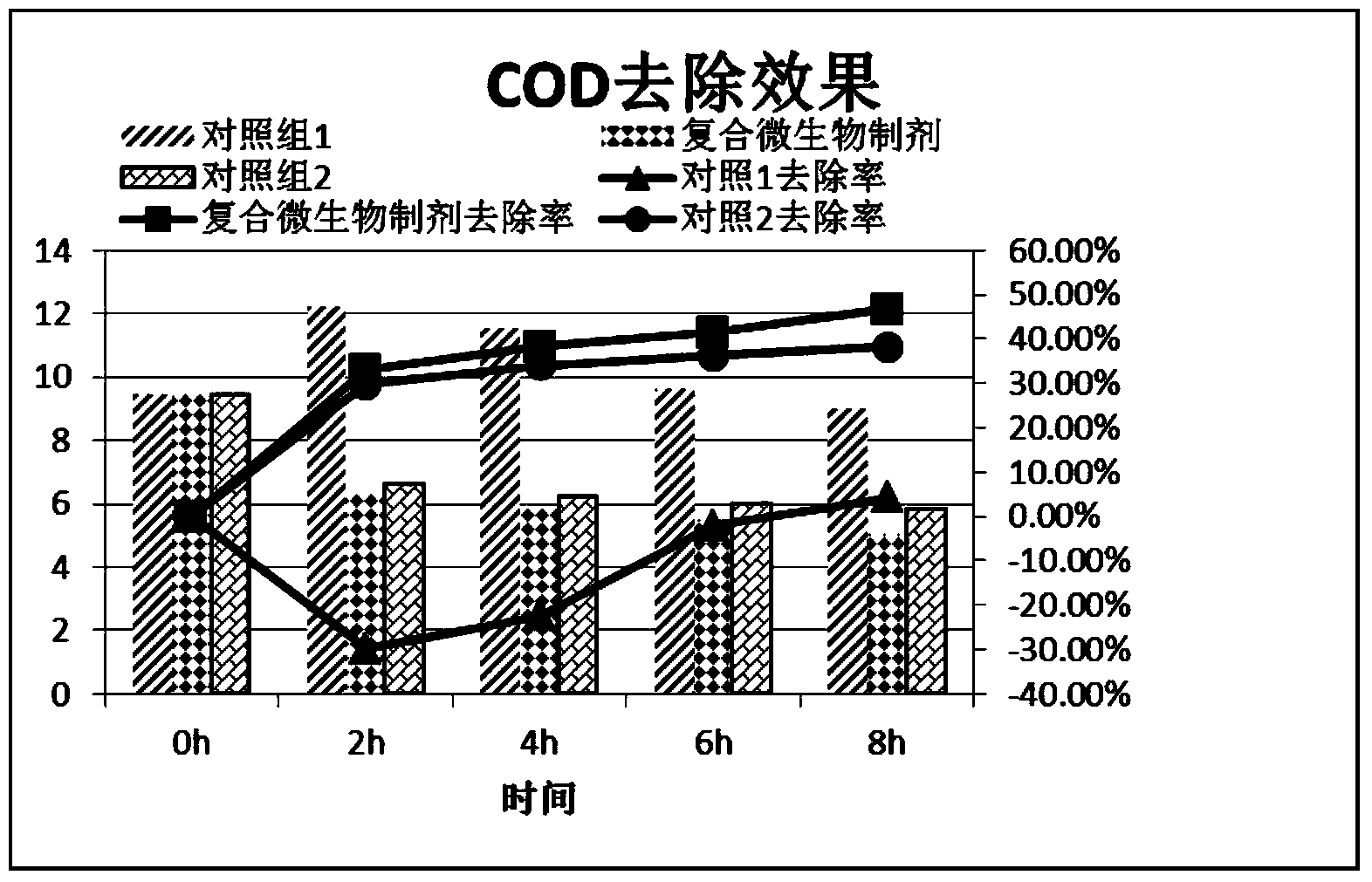
Composite microbial preparation for watershed bioremediation as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of compound microorganisms and microbial preparations, applied in the field of compound microorganism preparations, can solve the problems of reducing the concentration of inoculants, liquid inoculants and powdery inoculants are easily washed away by water flow, and water quality treatment cannot achieve expected results, etc. Environmentally friendly, non-toxic and environmentally friendly, and the effect of improving acid resistance and thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Select commercially available Bacillus natto, Candida utilis, and Rhodop seudanonas palustris, and mix them at a ratio of 1:1:1 by volume .
[0034] (2) adding the compound microbial preparations into fresh water culture solution and seawater culture solution respectively for cultivation, sedimentation, and removing the supernatant by siphon method to obtain fresh water mixed bacterial solution D and seawater mixed bacterial solution H; 1000ml contains 1.5g of ammonium chloride, 0.5g of sodium chloride, 1.5g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 5.0g of peptone, 8.0g of glucose, 5.0g of yeast extract, and the pH is 7.5. The seawater culture solution contains 24g of sodium chloride per 1000ml, 7.0g of magnesium sulfate, 1.0g of ammonium nitrate, 0.7g of potassium chloride, 2.0g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3.0g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, and the pH is 7.4.
[0035] (3) Mix the fresh water mixed bacterial solution D obtained in step 2), the seawater mixed bac...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Select commercially available Bacillus natto, Candida utilis, and Rhodop seudanonas palustris, and mix them at a ratio of 1:1:1 by volume .
[0041](2) The compound microbial preparation is added to fresh water culture solution and seawater culture solution respectively for cultivation, sedimentation, and siphon method to remove the supernatant to obtain fresh water mixed bacterial solution D and seawater mixed bacterial solution H; 1000ml contains 1.5g of ammonium chloride, 0.5g of sodium chloride, 1.5g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 5.0g of peptone, 8.0g of glucose, 5.0g of yeast extract, and the pH is 7.5. The seawater culture solution contains 24g of sodium chloride per 1000ml, 7.0g of magnesium sulfate, 1.0g of ammonium nitrate, 0.7g of potassium chloride, 2.0g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3.0g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, and the pH is 7.4.
[0042] (3) Mix the fresh water mixed bacterial solution D obtained in step 2), the seawater mixed bacteri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com