Method for preparing small-molecule oligomeric hyaluronic acid through enzyme method
A technology for oligomeric hyaluronic acid and enzymatic preparation, which is applied in the field of enzymatic preparation of small molecule oligomeric hyaluronic acid, can solve the problems of complex reaction conditions, influence of HA properties, and difficulty in product purification, and achieves easy purification, recovery and reaction. simple conditional effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The expression of embodiment 1 hyaluronidase
[0025] The modified hyaluronidase gene sequence (SEQ ID NO.1) was fully chemically synthesized, digested and ligated to the expression vector pPIC9K to construct the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-His-HaseA3887, transformed into E.coil DH5α, and extracted for sequencing verification. The recombinant plasmid was linearized by SalI and then electroporated into the expression host P. pastoris GS115, and the recombinant clone was verified to be correct by PCR.
[0026] Recombinant P. pastoris GS115 / pPIC9K-His-HaseA3887 clone was fermented and expressed. Single clones were inoculated in 5ml of YPD medium (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L), and cultured at 30°C and 200rpm for 16h. Transfer to 100ml induction expression medium BMGY (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, 3g / L K 2 HPO 4 , 11.8g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 10×YNB100ml / L (13.4g / L), 500×biotin 1mL (4×10 -4 g / L), glycerol 10mL), cultured to OD at 30℃200rpm 600 The v...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Purification and preparation of embodiment 2 recombinant hyaluronidase
[0028] After transcription and translation, the gene shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is fused with six consecutive histidine tags at the N-terminal of hyaluronidase. According to the principle of affinity chromatography, the tag can specifically bind to dextran nickel. Nickel dextran was first equilibrated with pH 6.0, 50mM phosphate buffer for 30min, then added the fermentation broth filtered through 0.45μm, incubated at 4°C for 2h, and then used the same buffer solution to prepare 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50mM imidazole buffer to elute impurities. Finally, the target protein was eluted with 500mM imidazole buffer. The target protein eluted with high concentration of imidazole was dialyzed overnight. A pure hyaluronidase protein with a single band is obtained, and the obtained pure hyaluronidase protein has hyaluronidase activity after determination.
Embodiment 3
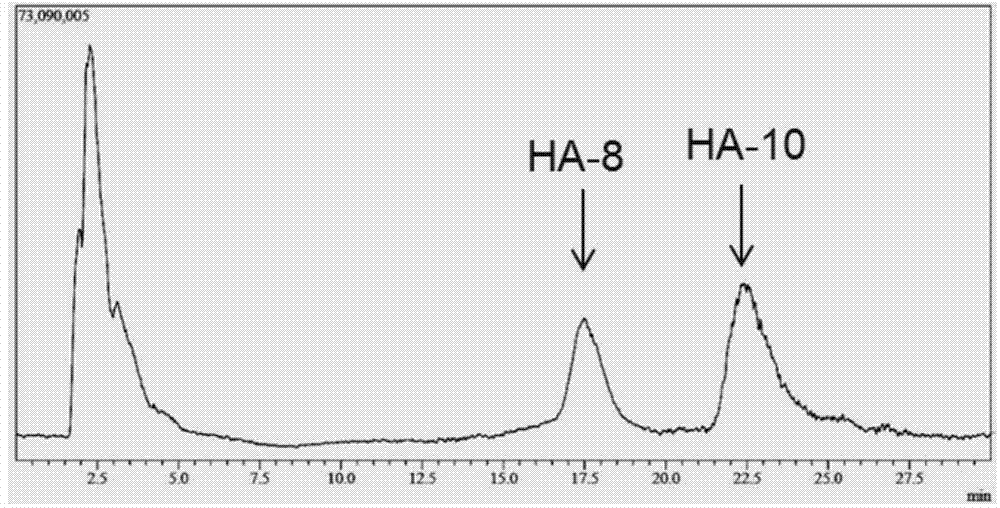
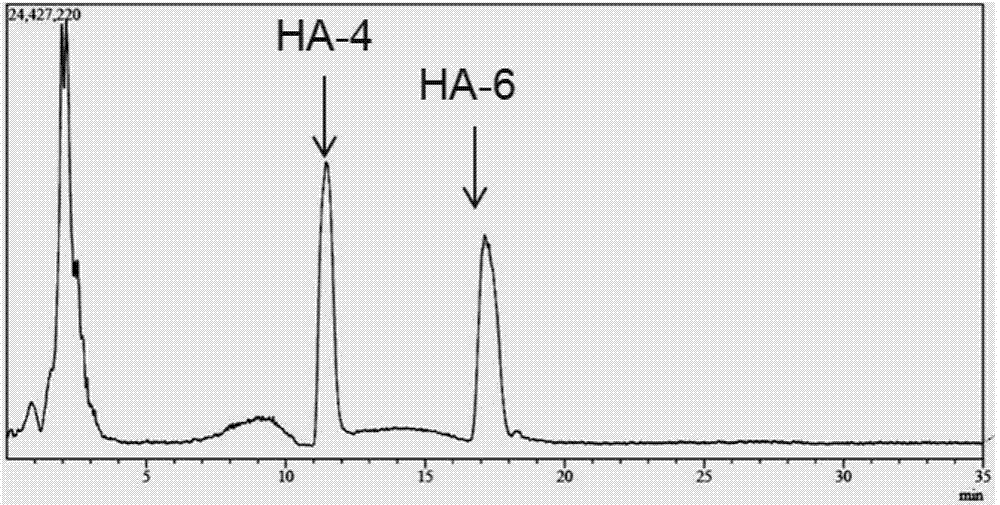
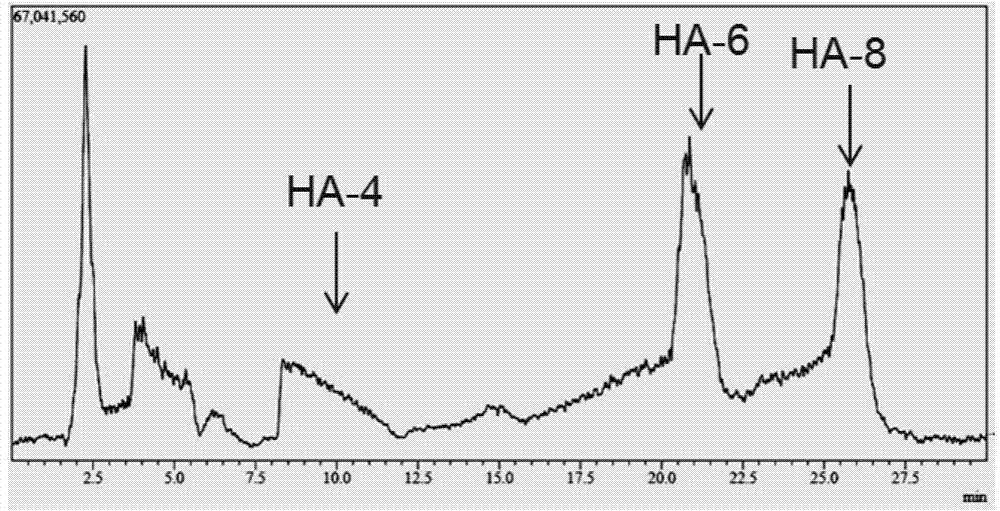
[0029] Example 3 Preparation of oligomeric hyaluronic acid octasaccharide (HA-8) and decasaccharide (HA-10)
[0030] Hyaluronidase prepared in Example 2 (pure enzyme aqueous solution, enzyme activity 2.43 × 10 5 U / mL), for large molecular weight (10 4 -10 7kDa) hyaluronic acid for hydrolysis. Hyaluronic acid (HA) was prepared at 2mg / ml with 50mM citrate buffer, pH5.5. In the 1ml reaction system, add HA solution 0.8ml, enzyme solution 8μl, and the rest with citric acid buffer (pH6.0, 50mM) to make up to 1ml system, and react at 38°C for 4h. Immediately after the reaction was completed, the enzyme was inactivated in a boiling water bath. The reaction system was filtered with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and the molecular weight of the product was analyzed by LCMS-IT-TOF mass spectrometer. The result is as figure 1 As shown, the mass spectrum peak that appeared at 17.5min on the mass spectrum total ion current peak has an M / Z of 766.22 in negative ion mode, which is [M-2H] af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com