Composite ceramic fiber and preparation method thereof
A technology of multiphase ceramics and fibers, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of low mass fraction, high oxygen content, difficult to achieve uniform dispersion, etc., and achieve low melt spinning temperature and non-melting temperature. , The effect of improving high temperature creep resistance and broadening the scope of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
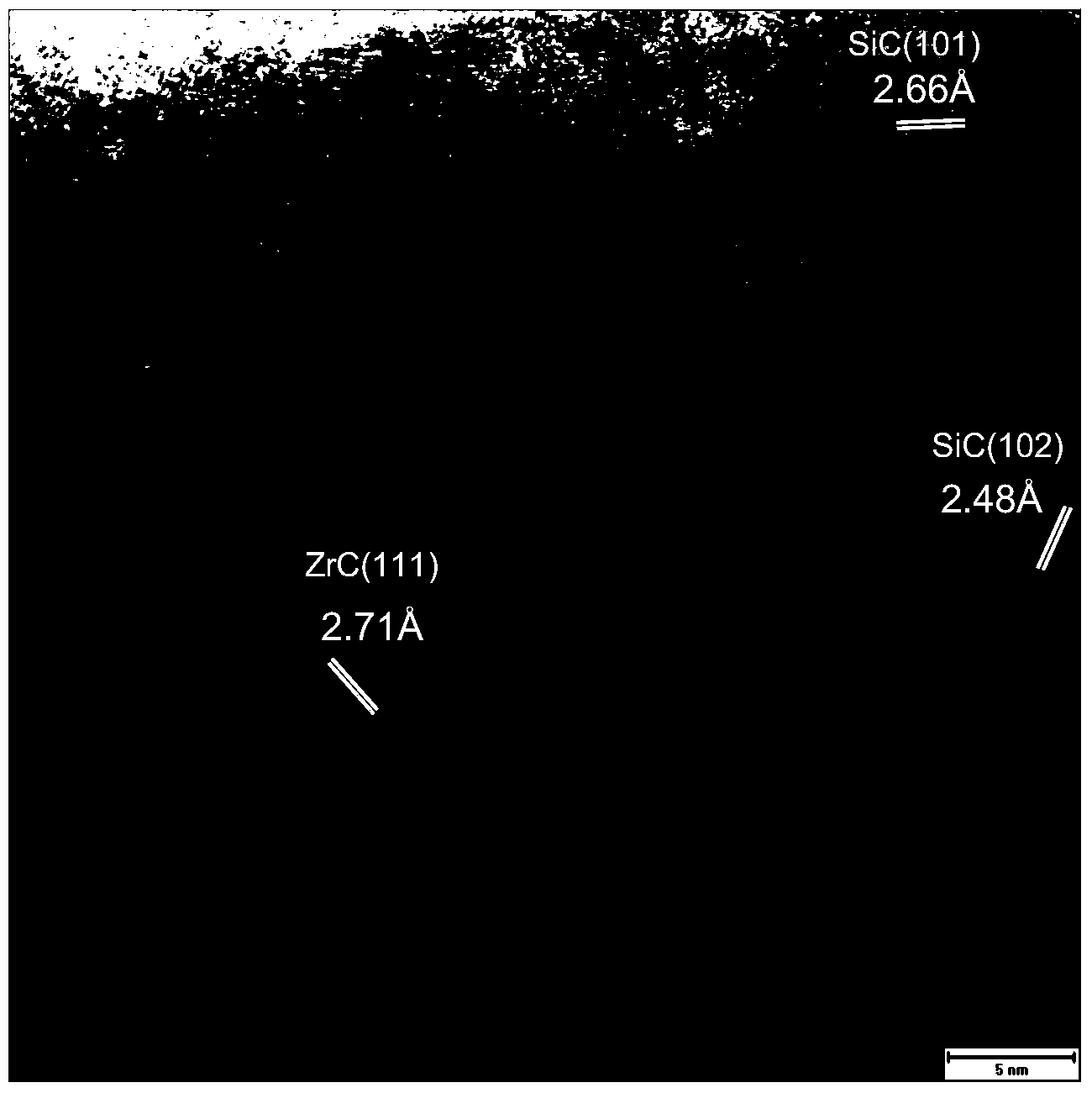
[0034] Add polyzirconium carbosilane (containing Zr, Si, C, H) with a softening point of 70°C, a molecular weight of 1500, and a molecular weight distribution of 1.2 into the melt spinning tank, melt at 160°C, keep the temperature for 4 hours, and perform defoaming After treatment, the temperature was lowered to 120° C., and the pressure was increased to 0.5 MPa with nitrogen, and spinning was carried out on a spinning machine, and fibrils were obtained at a spinning speed of 2 m / s. The microscopic morphology of the prepared fibrils is as follows figure 1 As can be seen from the figure, the resulting fibrils have a smooth surface and a diameter of about 20 microns. 2 g of the fibrils obtained in Example 1 were aged in oxygen at 200°C for 20 minutes, then heated up to 1100°C at 0.5°C / min under an Ar atmosphere, kept for 1 hour, and then cooled to obtain 1.25 g of gray-black solid fibers.
[0035] The content of Zr element in the obtained fiber was measured by an inductively co...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The softening point is 75 ° C, the molecular weight is 2400, and the polyzirconium carbosilane-polyborazane (containing Zr, Si, C, B, H) composite precursor with a molecular weight distribution of 1.3 is added to the melt-spinning feed tank, at 180 Melting at ℃, constant temperature for 6h, defoaming treatment, then cooling to 110℃, using nitrogen to pressurize to 0.7MPa, spinning on a spinning machine, and obtaining fibrils at a spinning speed of 2.5m / s. The microscopic morphology of the prepared fibrils is as follows: Figure 4 As can be seen from the figure, the resulting fibrils have a smooth surface and a diameter of about 25 microns. 2 g of the obtained fibrils were aged in oxygen at 150°C for 40 min, then heated up to 1400°C at 1.5°C / min under an Ar atmosphere, kept for 1 h, and then cooled to obtain 1.30 g of gray-black solid fibers.
[0038] The content of Zr element in the fiber was measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Add polytitanium carbosilane (containing Ti, Si, C, H) with a softening point of 80°C, a molecular weight of 1850, and a molecular weight distribution of 1.2 into the melt spinning tank, melt at 140°C, keep the temperature for 8 hours, and perform defoaming After treatment, the temperature was lowered to 100° C., and the pressure was increased to 0.3 MPa with nitrogen, and spinning was carried out on a spinning machine. Fibrils were obtained at a spinning speed of 2.8 m / s, and the diameter of the obtained fibrils was about 18 microns. 2 g of the obtained fibrils were aged in oxygen at 110 °C for 60 min, then heated up to 1500 °C at 3 °C / min under an Ar atmosphere, kept for 1 h, and then cooled to obtain 0.92 g of gray-black solid fibers.
[0041] The content of Ti element in the obtained fiber was measured by an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, and the test result was 12.2%. XRD was used for detection, and the results showed that the obtained fib...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com