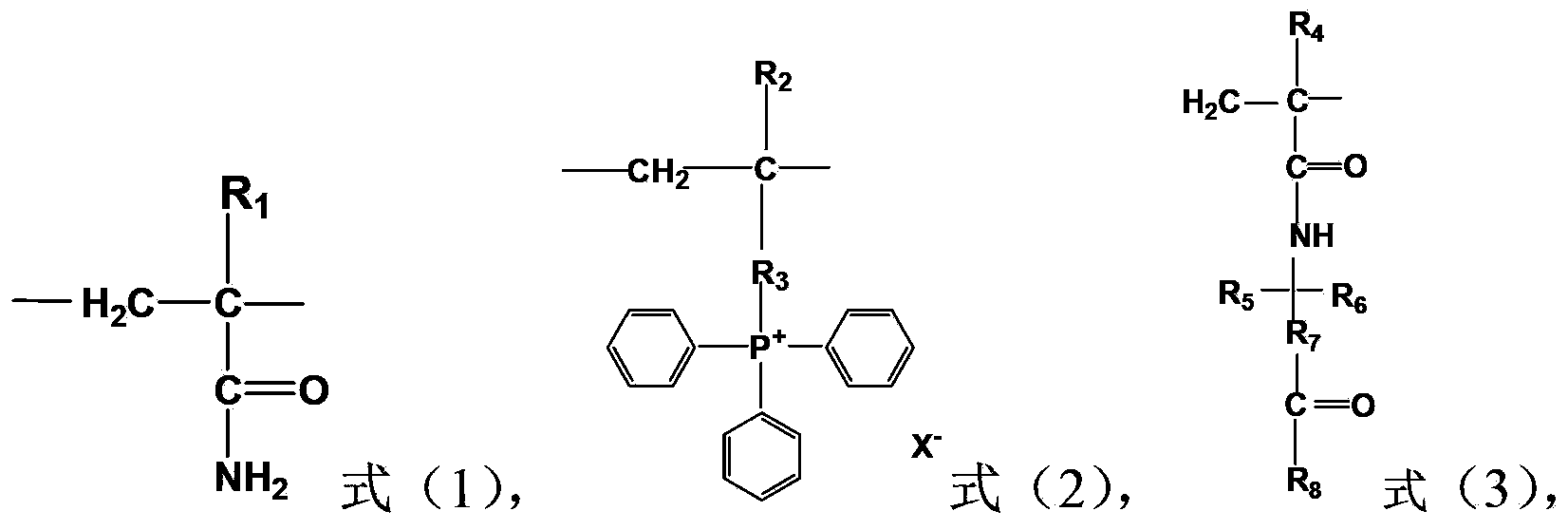
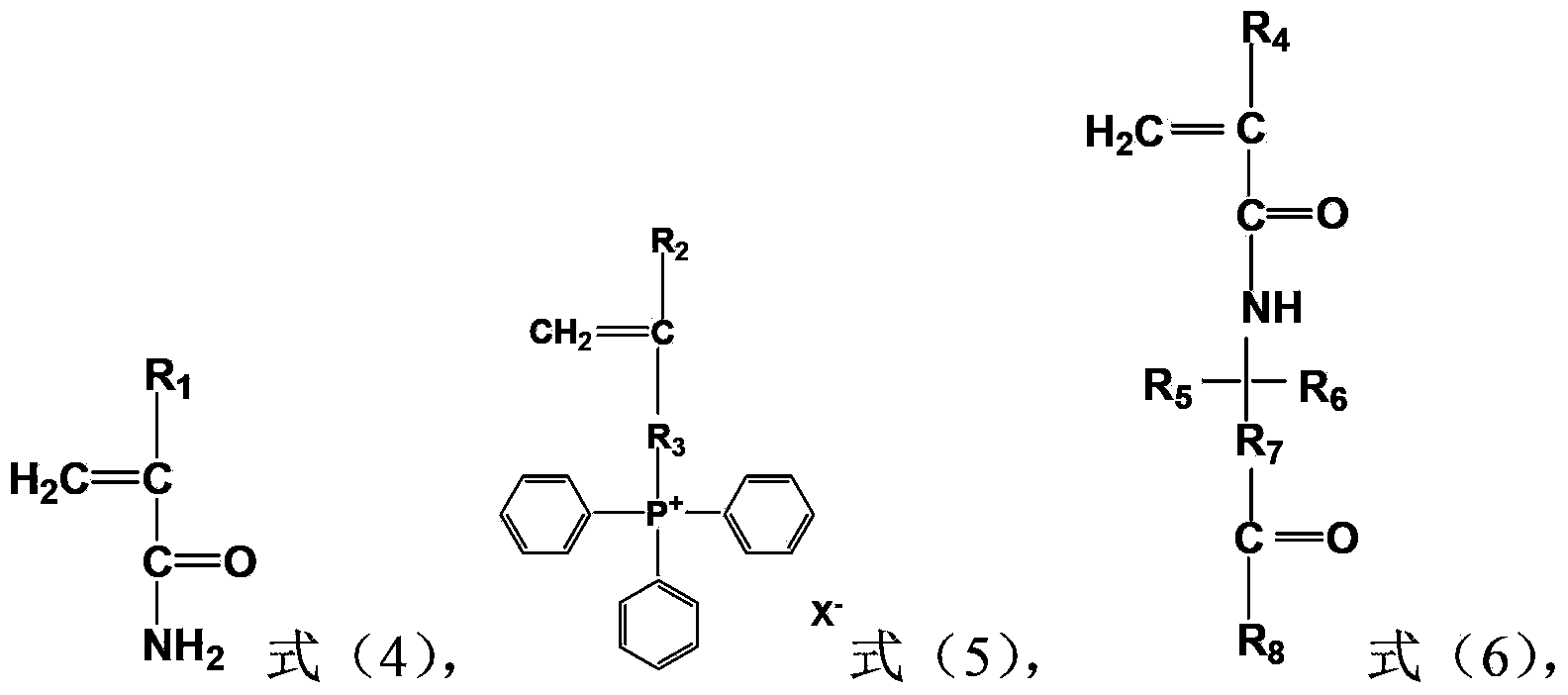
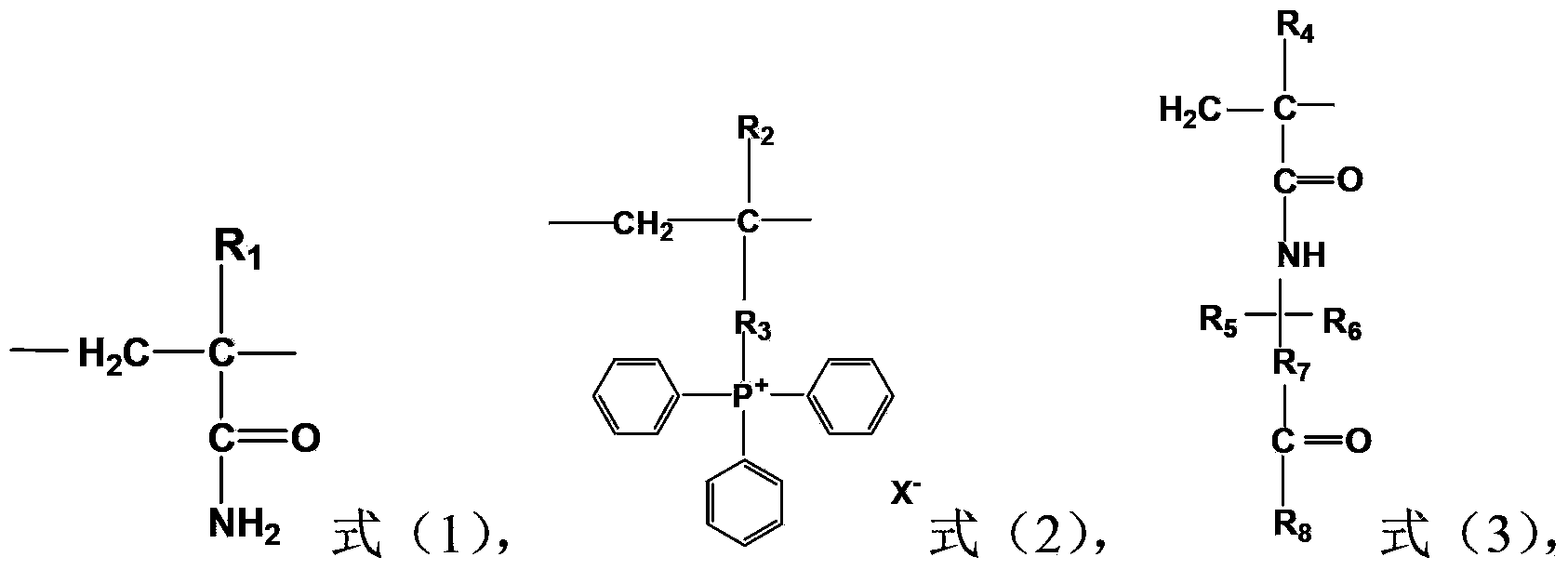
Acrylamide copolymer, preparation method and application thereof
An acrylamide-based, copolymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, drilling compositions, etc., can solve the problems of rapid drop in resistance reduction effect, non-degradable, permanent damage, etc., and achieve simple monomer conversion rate , The effect of low water insoluble content and low formation damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0079] At room temperature, add 21.32 g of acrylamide (AM), 66.40 g of the M1 monomer represented by formula (13) and 20.3 g of diacetone acrylamide (purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, the same below) into the reaction flask , add 612.11g of deionized water, stir to dissolve the monomer completely, and stir evenly. Add 5.5g of 1% by weight of EDTA aqueous solution, 2.1g of 1% by weight of azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution, chain extender N', 0.002g of N-dimethylethylenediamine, and add 0.1 % sodium bisulfite solution 1.1g, urea 0.12g, stir well to make it evenly mixed. The pH was adjusted to 7.5 with 1% by weight sodium hydroxide solution. The initial temperature of the system was controlled to 4°C, and after 30 minutes of nitrogen deoxygenation, 0.75 g of 1% by weight ammonium persulfate aqueous solution w...
Embodiment 2
[0085] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0086] Add 29.85g of AM, 45.94g of M2 monomer represented by formula (15) and 10.15g of diacetone acrylamide into the polymerization bottle, add 200.53g of deionized water, stir to completely dissolve the monomer, and pour Add 4.65g of 1% by weight of EDTA aqueous solution, add 1.23g of 1% by weight of azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution, add 0.002g of chain extender N,N'-dimethylethylenediamine, add 0.1% Add 0.11 g of urea to 1.15 g of sodium bisulfite solution, stir well to make it evenly mixed. The pH was adjusted to 7.1 with 1% by weight sodium hydroxide solution. The initial temperature of the system was controlled to 10°C, and after 30 minutes of deoxygenation with nitrogen, 0.8 g of a 1% by weight ammonium persulfate aqueous solution was added and nitrogen deoxygenation was continued for 10 minutes...
Embodiment 3
[0090] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0091] At room temperature, put 5.11g of methacrylamide, 110.66g of M1 monomer represented by formula (13) and 40.61g of diacetone acrylamide into the polymerization bottle, add 234.57g of deionized water, and stir to make the monomer completely 7.56g of 1% by weight aqueous EDTA solution, 2.13g of 1% by weight azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution, and 0.001% chain extender N', N-dimethylethylenediamine were added to the flask g, add 1.13 g of 0.1% by weight sodium bisulfite solution, add 0.20 g of urea, stir well to make it evenly mixed. The pH was adjusted to 7.3 with 1% by weight sodium hydroxide solution. The initial temperature of the system was controlled to 8°C, and after 30 minutes of nitrogen deoxygenation, 0.9 g of 1% ammonium persulfate aqueous solution was added and nitrogen deoxygenation was c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com