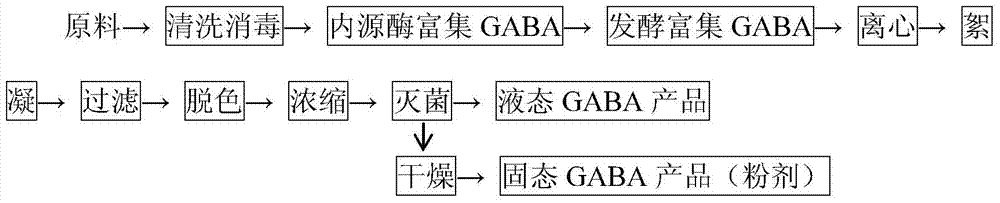
Method for preparing γ-aminobutyric acid by fermentation of compound strains
A technology of compound strains and aminobutyric acid, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems such as the method for preparing γ-aminobutyric acid by fermentation and the low content of GABA which have not been seen yet, To achieve the effect of low price of raw materials, simple formula and increased concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Isolation, identification, mycological characteristics and other microorganism-related information of Rhizopus sp. zsm-005
[0040] 1. Isolation, identification and preservation of Rhizopus sp. zsm-005
[0041] The applicant isolated a strain of rhizopus (Rhizopus sp.) zsm-005 strain from the distiller's koji of folk traditional sweet rice wine in Xiaogan area, Hubei Province, and named it Rhizopus sp.zsm-005.
[0042] Specific steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Separation method (dilution plate method)
[0044] Under aseptic conditions, take 10.0g of folk traditional sweet rice wine koji from Xiaogan City, Hubei Province, add it to a triangular bottle of 90ml sterile water (a certain number of small glass beads are placed in the bottle in advance), vibrate and shake for 30min, and then Carry out gradient dilution, choose the diluent whose dilution is 10-3, 10-4, 10-5. Under sterile conditions, take 1ml of the diluted sample solution, transfer it to a petri ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2 Utilizes the example of composite bacterial strain fermentation method to produce GABA
[0075] (1) Cleaning and disinfection of raw materials: fresh brown rice is cleaned, broken grains, moldy grains and heterochromatic grains are removed, disinfected with 1% sodium hypochlorite solution, and cleaned with tap water to obtain clean brown rice;
[0076] (2) GABA enrichment
[0077] 1) Using endogenous enzymes to enrich GABA
[0078] Soak the clean brown rice with 1% calcium chloride solution at a volume ratio of 1:2 (brown rice: calcium chloride solution) at 30°C for 6 hours, then wash it with distilled water for 3 times, drain the water, and place it at 35°C Cultivate for 16 hours to germinate. During the cultivation process, nutrient solution (formula: calcium lactate 110mg / L, sodium glutamate 2000mg / L) is used in the form of water mist (refer to Huang Hanying, Zhao Siming, Yin Tao, etc. for the specific method. An intelligent system suitable for sprout ...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3 Fermentation condition test
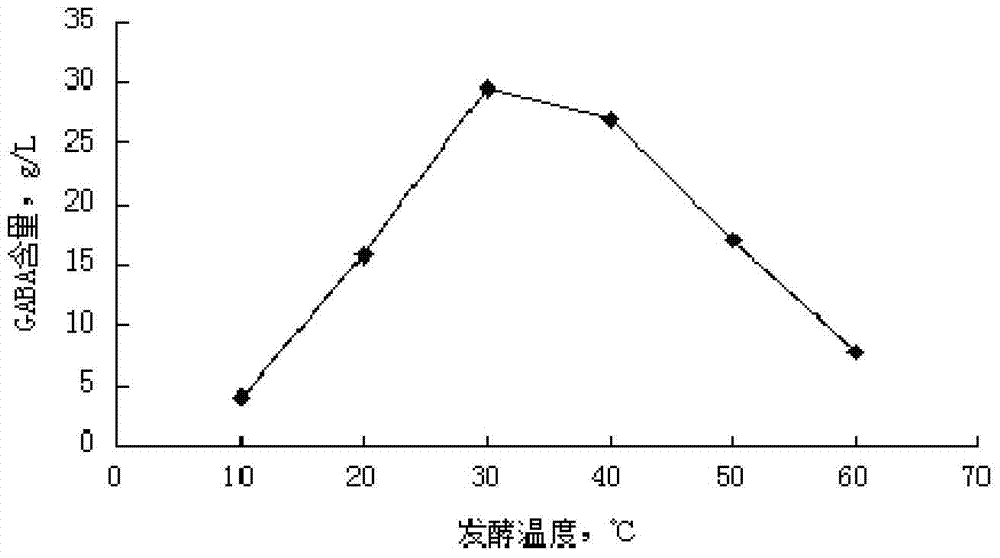
[0092] (1) Determination of suitable fermentation temperature
[0093] The composite strain (Lactobacillus plantarum ZSM-002: Brettanomyces castellum ZSM-001: Rhizopus zsm-005 strain by volume ratio = 2:2:1) is 3 according to the volume ratio of the composite strain and the fermentation medium Inoculate the compound strain into the fermentation medium (fermentation medium formula: L-sodium glutamate 50g / L, glucose 40g / L, rice bran 60g / L, replenish water to 1L) in the inoculum of % inoculum, respectively in 10 ℃ , 20°C, 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, and 60°C were fermented for 70 hours, and the content of GABA in the fermentation broth was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The results show that the temperature for producing GABA by compound bacterial strain fermentation is advisable with 30°C (see figure 2 ).
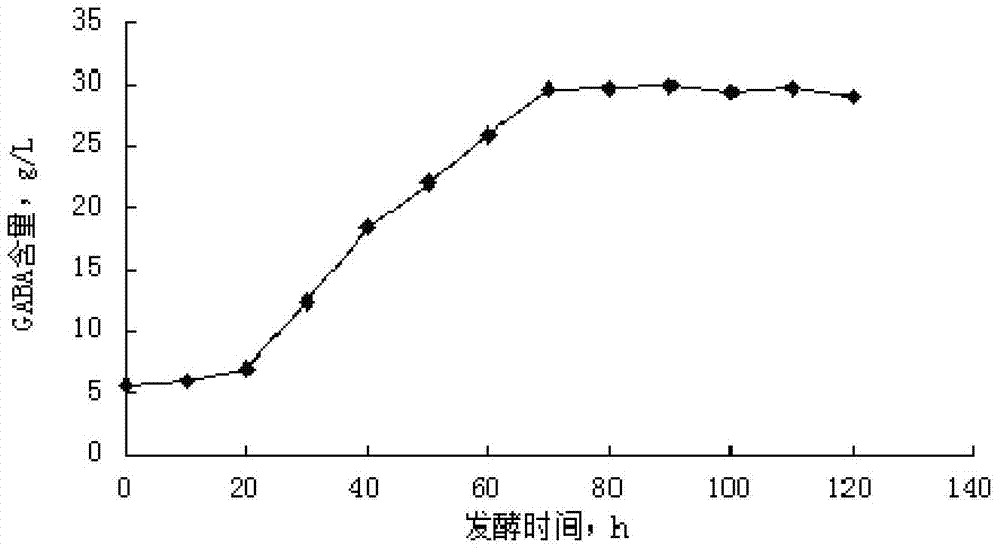
[0094] (2) Determination of suitable fermentation time
[0095] Inoculate the compound strain (ZSM-002: ZS...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com