High-temperature resistant flavonoid aglycone invertase and applications thereof
A flavonoid aglycone converting enzyme and high temperature resistant technology, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering technology and biomedicine, can solve the problems of unsatisfied catalytic conditions, unsatisfactory β-glucosidase catalytic efficiency, etc., and achieves strong catalytic conversion ability and thermal stability. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The preparation method of the high-temperature-resistant flavone aglycone converting enzyme described in the present invention, the separation and purification of induced expression specifically includes inducing and cultivating the expression host bacteria containing the recombinant plasmid at a suitable concentration of the inducer (IPTG) at 30°C, collecting the bacteria and ultrasonically crushing them, and taking The fusion protein was obtained by affinity chromatography of the supernatant.
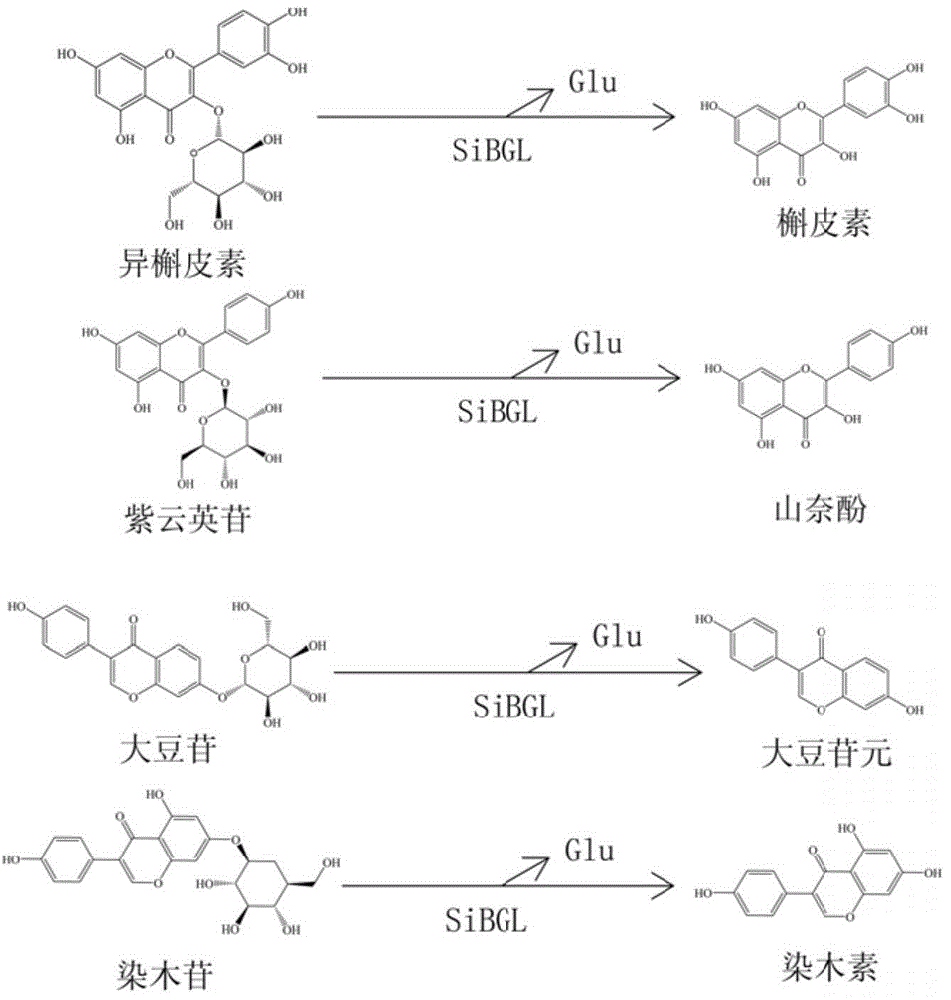
[0040] The present invention also provides a method for preparing flavone aglycone, specifically, the high-temperature-resistant flavone aglycone converting enzyme of the present invention enzymatically hydrolyzes four typical flavone glycosides (isoquercetin, Astragalin, daidzin, genistin) were hydrolyzed to prepare corresponding flavonoid aglycones (quercetin, kaempferol, daidzein and genistin).
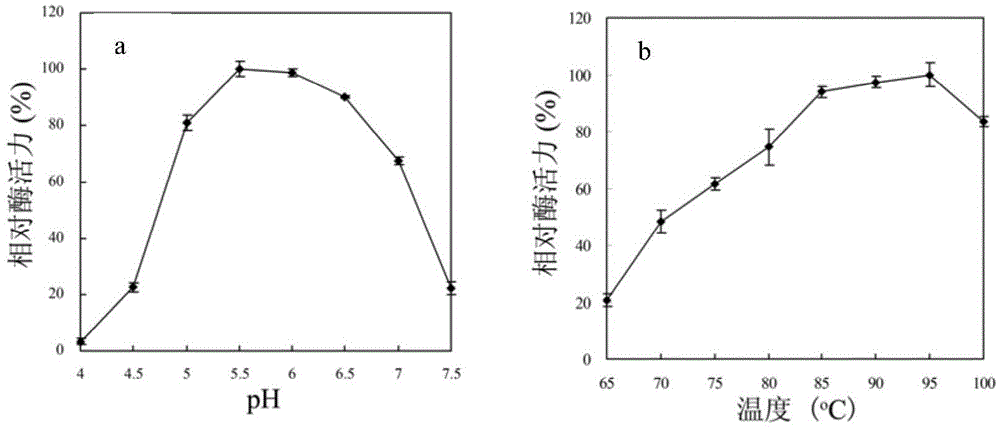
[0041] The high-temperature-resistant flavone aglycon converting enzyme SiBGL o...
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Acquisition of high temperature resistant flavone aglycone converting enzyme gene of the present invention and construction of recombinant plasmid pET-SiBGL
[0044] Codon optimization of high temperature resistant flavone aglycon converting enzyme SiBGL gene and construction of recombinant plasmid pET-SiBGL
[0045] according to known Sulfolobus islandicus The whole genome sequence (accession number: NC_012588.1) was screened to obtain the gene fragment encoding the high-temperature-resistant flavone aglycone converting enzyme SiBGL of the present invention. Due to the codon preference of this extreme thermophile and the expression host Escherichia coli BL21(DE3 ) have a certain difference, which may affect the high-efficiency expression of the extremely heat-resistant flavone aglycone convertase protein, so we optimized the codons of the gene encoding the target protein according to the codon preference of the host bacteria, and optimized the coding The m...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Preparation of the high temperature resistant flavonoid aglycon converting enzyme SiBGL of the present invention
[0047] The recombinant plasmid pET-SiBGL was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109(DE3) host bacteria (purchased from Novagen), on LB plates containing kanamycin (50 μg / mL) (LB medium: tryptone 10 g / L, yeast Extract 5 g / L, NaCl 5 g / L, agar 15 g / L) after culturing overnight at 37°C, pick the transformants into 200 mL of LB medium (50 μg / mL kanamycin) at 37°C, Shake culture at 200 rpm until OD600 is 0.6, add a final concentration of 0.5 mM isopropyl β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) inducer, culture at 30°C for 6 h, and use a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge to distill the culture solution Centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C to collect the cells.
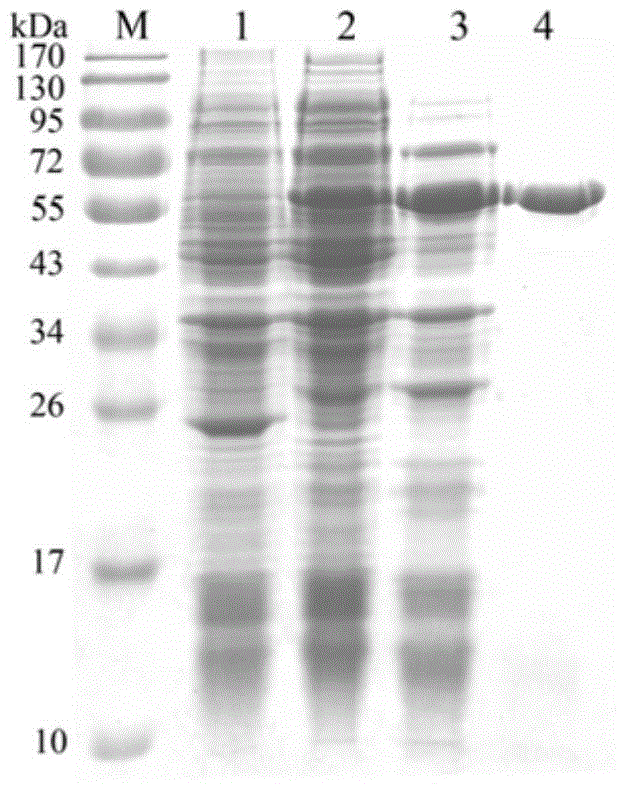
[0048] Since the recombinant plasmid pET-SiBGL contains a His-tag tag, it was purified by His·Bind Purification Kit (purchased from Novagen) to obtain a purified recombinant enzyme. Specific ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com