Light-emitting diode structure with indium-containing conductive layer and preparation method therefor
A technology of light-emitting diodes and conductive layers, applied in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor InGaN quantum well crystal quality, large lattice mismatch, low internal quantum efficiency, etc., to improve spontaneous radiation recombination. rate, improve crystal quality, improve the effect of crystal quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 , A light-emitting diode epitaxial structure with n-type and p-type InGaN conductive layers
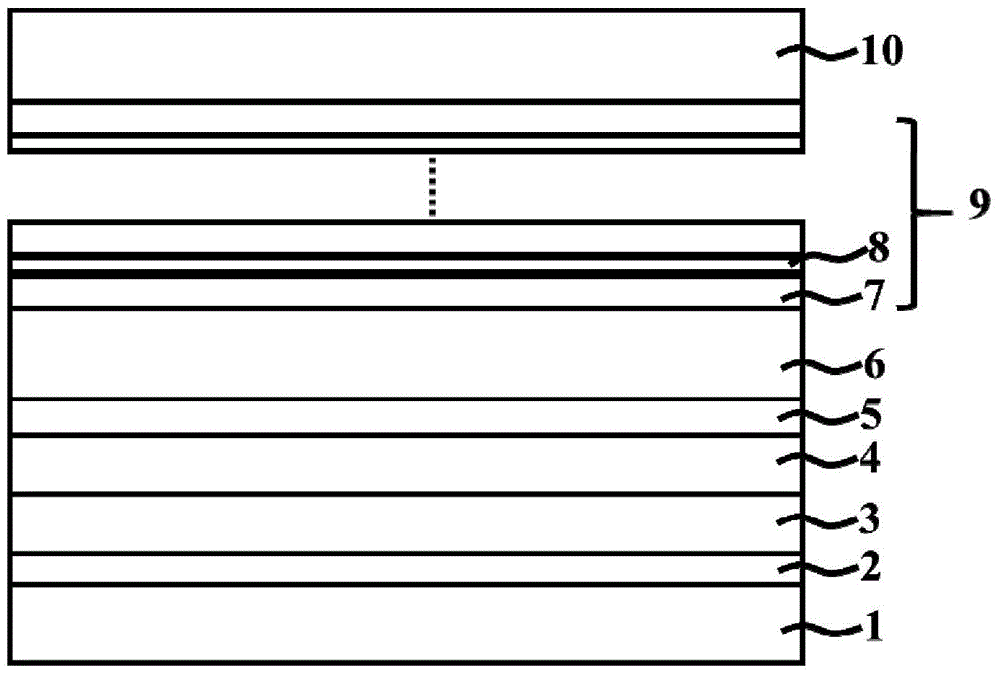
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the light-emitting diodes are sapphire substrate 1, GaN nucleation layer 2, unintentionally doped GaN layer 3, N-type GaN conductive layer 4, In composition graded InGaN layer 5, N-type InGaN layer from bottom to top. Conductive layer 6, multi-quantum well active region 9 and P-type InGaN conductive layer 10.
[0043] The epitaxial growth steps are as follows:
[0044] (1). Put the sapphire substrate into the metal-organic chemical vapor phase chemical deposition equipment, pass in hydrogen, raise the temperature of the reaction chamber to 1300 degrees Celsius, and perform high-temperature cleaning on the substrate.
[0045] (2). The temperature is lowered to 550 degrees Celsius, and the reaction chamber is filled with ammonia gas, hydrogen gas and trimethylgallium, and a 30 nm GaN nucleation layer is grown on the substrate descri...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 , A light-emitting diode epitaxial structure with n-type and p-type InGaN conductive layers
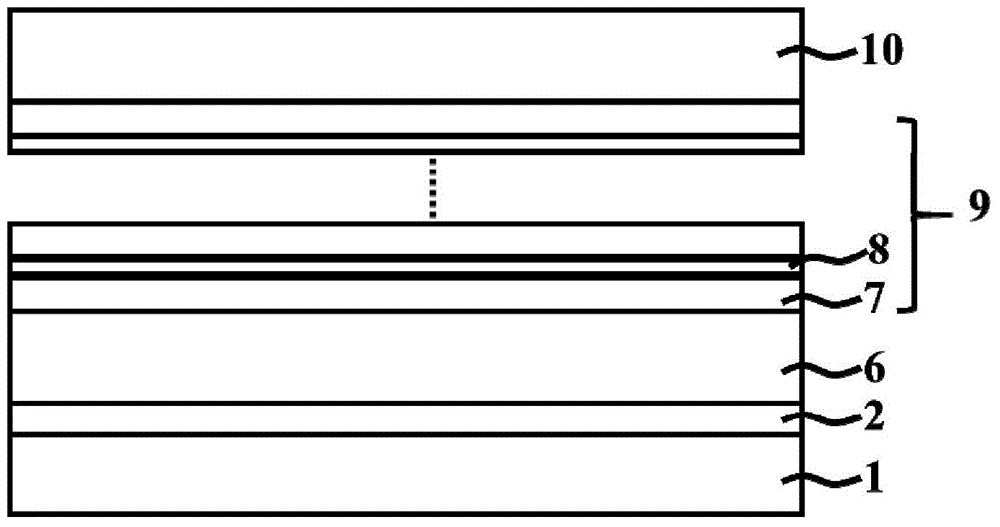
[0057] Such as figure 2 As shown, the light-emitting diode is sequentially composed of a sapphire substrate 1, a GaN nucleation layer 2, an N-type InGaN conductive layer 6, a multi-quantum well active region 9, and a P-type InGaN conductive layer 10 from bottom to top. The preparation method is as follows: As in Example 1, the difference is:
[0058] After the growth on the nucleation layer described in step (2) is completed, directly enter step (6), the reaction chamber is fed with silane, ammonia, hydrogen trimethylgallium and trimethylindium, and the temperature is kept at 800 degrees Celsius. ) on the sample described above, grow an N-type doped InGaN conductive layer with a thickness of 2.5 um and a doping concentration of 8×10 18 cm -3 .
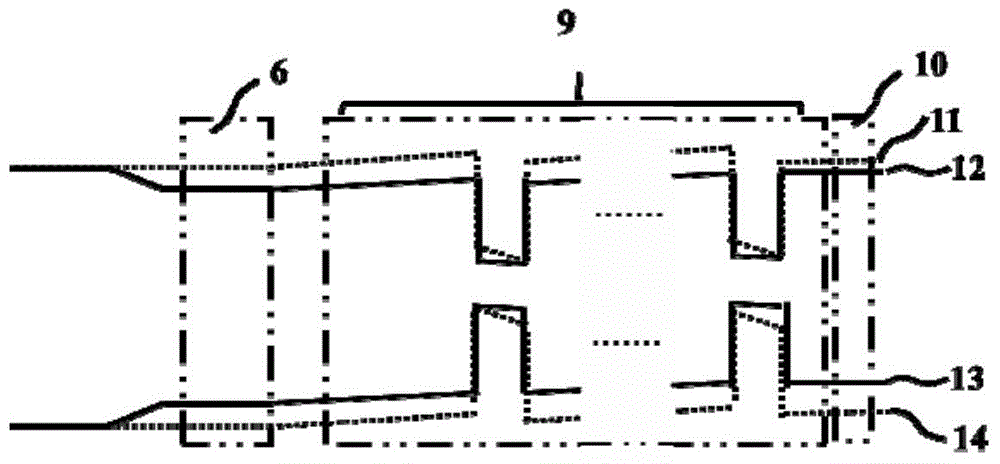
[0059] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the figure includes a P-type InGaN conductive layer 10; a conduction b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com