Hydrophilic modification method for polytetrafluoroethylene membrane
A technology of polytetrafluoroethylene film and polytetrafluoroethylene, which is applied in the chemical field, can solve the problems of complex preparation process of chemical treatment methods, decreased thermal and chemical stability of materials, poor hydrophilic stability, etc., and achieves good pollution resistance and light Catalytic performance, remarkable effect of hydrophilic modification, good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
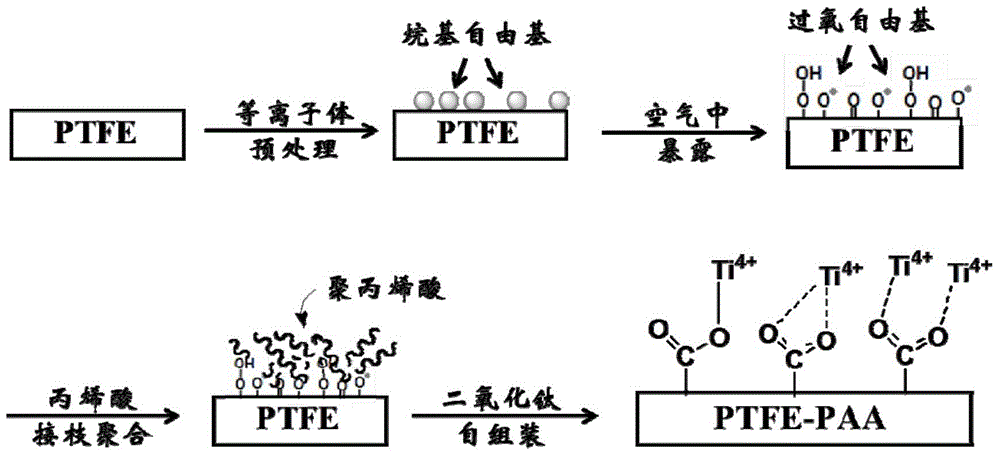
[0047] Embodiment 1: the pretreatment of polytetrafluoroethylene membrane surface plasma
[0048] Using nitrogen as the gas atmosphere, plasma equipment with a voltage of 30 volts, a current of 2 amperes, a discharge distance of 8 mm, and a discharge power of 10,000 Hz, the PTFE film was subjected to plasma pretreatment for 120 seconds. During the treatment process, when high-energy particles such as ions, electrons, and free radicals in the plasma bombard the surface of the membrane, the energy transmitted by them is greater than the bond energy of the chemical bonds C-C and C-F bonds that make up the material molecules, resulting in these chemical bonds under the action of high-energy particles. Cleavage occurs to generate alkyl radicals on the membrane surface. In the process of exposure to air for 10 minutes, these alkyl radicals will react with oxygen and water in humid air to generate relatively stable peroxyl radicals.
[0049] The concentration of free radicals on the...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: thermal graft polymerization of polytetrafluoroethylene film surface acrylic acid solution
[0051] Put the pretreated polytetrafluoroethylene membrane into the prepared acrylic acid (AA) solution and soak it for 5 minutes, take it out, spread the acrylic acid solution on the surface of the membrane evenly with a glass rod, and sandwich the membrane sample between two clean glass plates. In the middle, put it into a vacuum drying oven at 75°C for graft polymerization for 4 hours. Take out the polytetrafluoroethylene film grafted with polyacrylic acid (PAA) on the surface, wash and remove the acrylic acid monomer and homopolymer adsorbed on the film surface with a large amount of deionized water, and dry it to obtain PTFE / PAA polytetrafluoroethylene film. Vinyl grafted film.
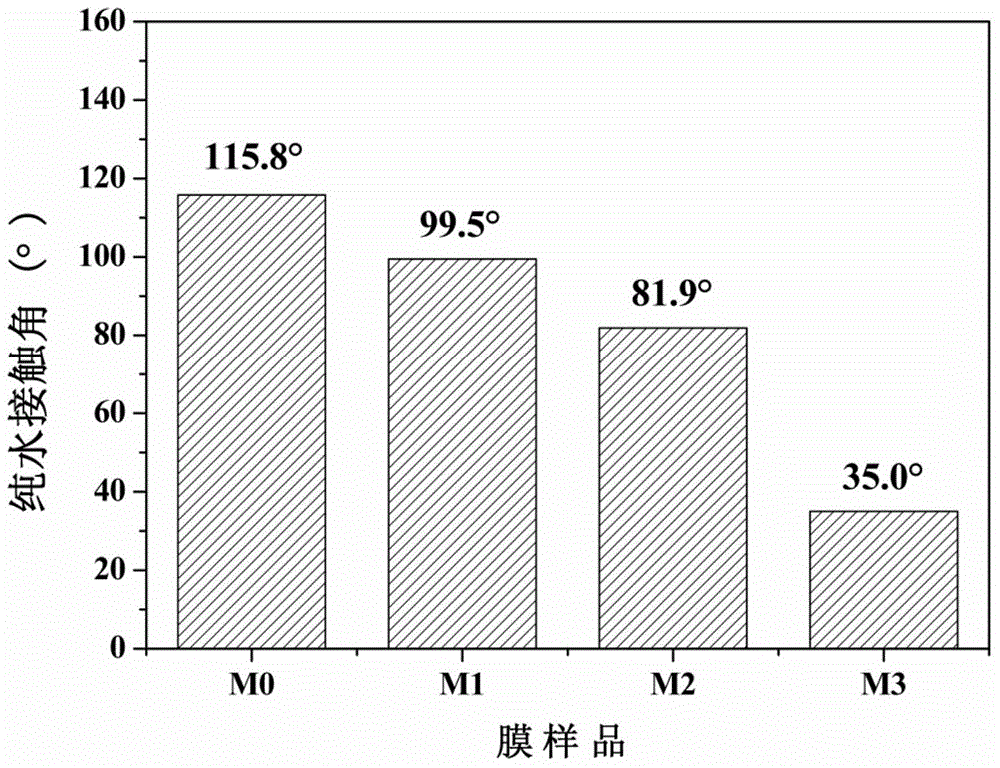
[0052] The surface weight gain rate of the obtained PTFE / PAA polytetrafluoroethylene grafted membrane is 12%. The contact angle of pure water on the surface of the polytetrafluoroet...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Titanium dioxide self-assembly on the surface of polytetrafluoroethylene membrane.
[0054] The PTFE / PAA polytetrafluoroethylene graft film that makes in embodiment 2 is in TiO 2 Static immersion in sol for 20 minutes to make TiO 2 Ti 4+ Coordination with the carboxyl groups on PAA assembles to the surface of the grafted membrane. After washing with deionized water and drying, PTFE / PAA / TiO 2 Hydrophilic modified membrane.
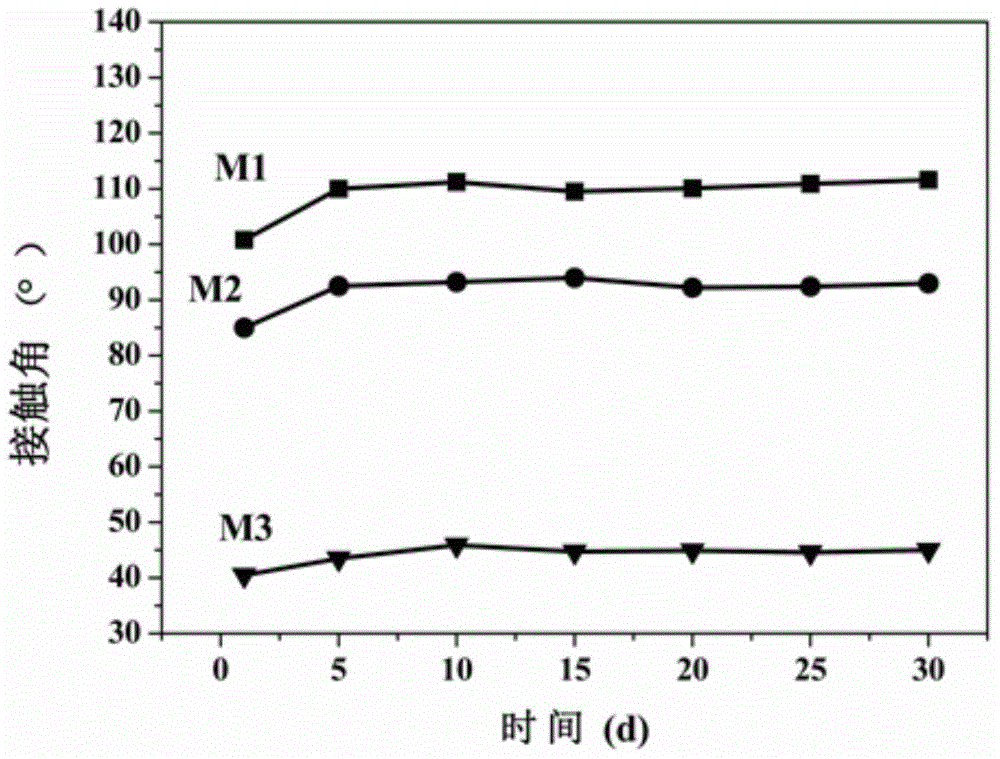
[0055] The resulting PTFE / PAA / TiO 2 The surface weight gain rate of the hydrophilic modified membrane was 21%. The pure water contact angle on the surface of the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane was reduced to 35° on the basis of Example 2. The above-mentioned polytetrafluoroethylene hydrophilic modified membrane was continuously filtered in 1 g / L bovine serum albumin solution for 120 minutes, and the contaminated membrane was subjected to ultraviolet light with an intensity of 500 watts for 15 minutes. The polytetrafluoroethylene pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| photodegradation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com