Preparation method of iron and nitrogen doped carbon nanoparticle photocatalyst
A carbon nanoparticle and photocatalyst technology, which is applied in the field of chemical and nanomaterial preparation, can solve the problems of high equipment cost, difficulty in obtaining solids doped with carbon nanoparticles, and unsuitability for industrialization requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
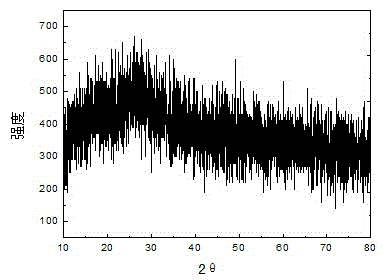
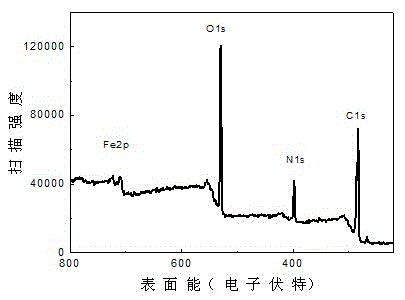
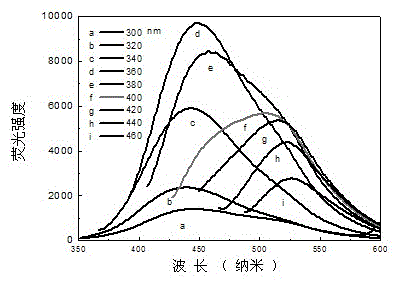
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) Mixing of materials: Weigh 1.0 g of citric acid and 1.0 g of ammonium oxalate, add 0.1 g of ferric chloride to a 250 ml beaker, and dissolve with a small amount of distilled water to obtain a purple mixed solution.
[0029] (2) Formation of iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles: Pour the above mixed solution into a 250 ml beaker, place in a constant temperature drying oven and heat at 210°C for 2 hours. Take out the beaker and let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and a brown-yellow foamy solid is obtained in the beaker, which is an iron-nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle photocatalyst.
[0030] (3) Photocatalytic effect evaluation: The photocatalytic performance of the catalyst was evaluated by using the commercial dye MB as a simulated pollutant degradation template, and using an iodine-tungsten lamp as a light source to simulate sunlight. Take 1.0 ml of 1.0 mg / ml MB solution, put it in a 100 ml beaker, add 20 mg of the synthesized catalyst, add 0...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Dissolution of materials: Weigh 1.0 g of malic acid and 1.0 g of ammonium oxalate into a 250 ml beaker, add 0.1 g of ferric chloride, and add a small amount of distilled water to dissolve to obtain a purple mixed solution.
[0033] (2) Formation of iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles: Pour the above mixed solution into a 250 ml beaker, place in a constant temperature drying oven and heat at 210°C for 2 hours. Take out the beaker and let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and a brown-yellow foamy solid is obtained in the beaker, which is an iron-nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle photocatalyst.
[0034] (3) The photocatalytic photocatalytic performance of the catalyst was evaluated by using the photocatalytic commercial dye MO as a simulated pollutant degradation template, and using an iodine-tungsten lamp as a light source to simulate sunlight. Take 1.0 mL of 1.0 mg / mL MO solution, put it in a 100 mL beaker, add 20 mg of the synthesized catalyst, a...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Dissolution of materials: Weigh 1.0 g of tartaric acid and 1.0 g of ammonium oxalate, add 0.1 g of ferric chloride to a 250 ml beaker, and dissolve with a small amount of distilled water to obtain a purple mixed solution.
[0037] (2) Formation of iron and nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles: Pour the above mixed solution into a 250 ml beaker, place in a constant temperature drying oven and heat at 210°C for 2 hours. Take out the beaker and let it cool down to room temperature naturally, and a brown-yellow foamy solid is obtained in the beaker, which is an iron-nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle photocatalyst.
[0038] (3) The photocatalytic commercial dye RB was used as the template for simulating the degradation of pollutants, and the iodine tungsten lamp was used as the light source to simulate sunlight to evaluate the photocatalytic performance of the catalyst. Take 1.0 ml of 1.0 mg / ml RB solution, put it in a 100 ml beaker, add 20 mg of the synthesized catalyst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com