Electrochemical Treatment Method for Improving the Surface Properties of CuZnSnS Thin Films
A technology of copper-zinc-tin-sulfur and surface properties, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of high cost and serious environmental pollution, and achieve the effects of low production cost, simple process and improved performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 This embodiment is electrochemical treatment copper zinc tin sulfur thin film surface
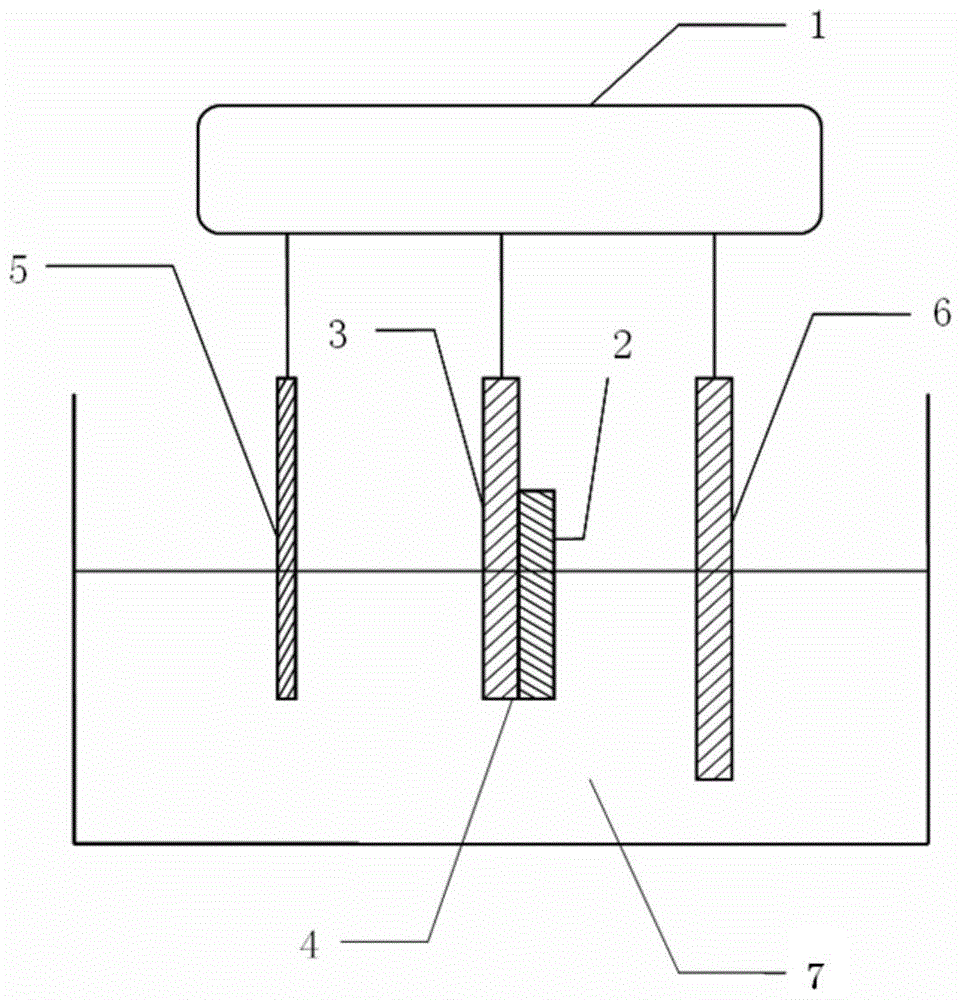
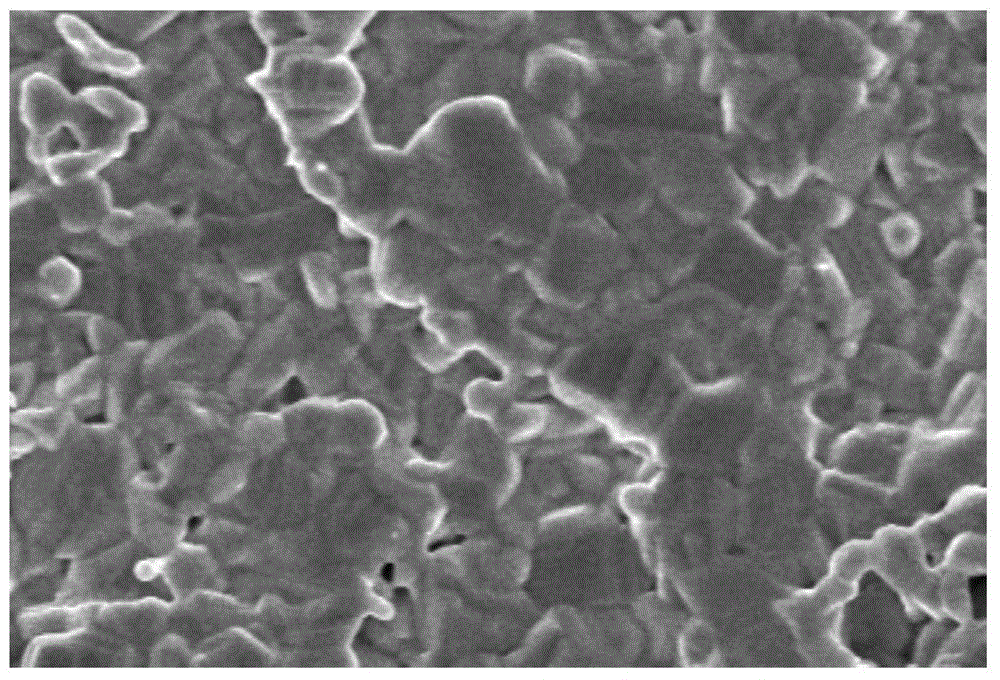
[0045] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film 2 with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
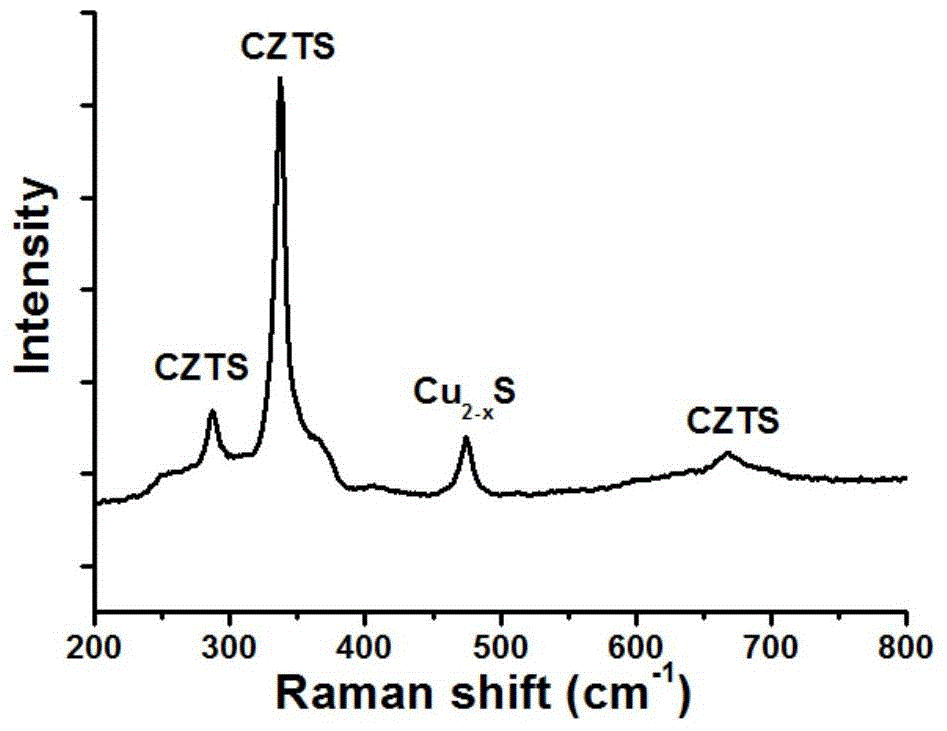
[0046] Step (1): Put the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material 2 in a quartz tube furnace for selenization (or sulfide) annealing. Surface Raman diagram of CuZnSnS film 2 after annealing figure 2 shown. The annealed copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1, and the connection part is only Mo4 and the substrate 3;
[0047] Step (2): Soak the connected copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film 2 in absolute ethanol for 1 to 2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0048] Step (3): Put ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2 This embodiment is the electrochemical treatment of copper zinc tin sulfur film surface
[0052] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
[0053] Step (1): placing the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film material in a quartz tube furnace for selenization (or sulfide) annealing. The annealed copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1, and the connection part is only Mo4 and the substrate 3;
[0054] Step (2): Soak the connected copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film 2 in absolute ethanol for 1 to 2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0055] Step (3): Put the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film 2 cleaned in step (2) into the treatment ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3 This embodiment is electrochemically treating the surface of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film
[0059] Metal Mo with a thickness of 1 μm is deposited on the soda-lime glass substrate as a back electrode, and a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film with a thickness of 1-2 μm is deposited on the Mo layer 4 by electrochemical deposition, which is a prefabricated layer.
[0060] Step (1): placing the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film material in a quartz tube furnace for selenization (or sulfide) annealing. The annealed copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film material is connected to the working electrode of the electrochemical workstation 1, and the connection part is only Mo4 and the substrate 3;
[0061] Step (2): Soak the connected copper-zinc-tin-sulfur film 2 in absolute ethanol for 1 to 2 minutes, remove surface particles and impurities, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen;
[0062] Step (3): Put the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur thin film 2 cleaned in step (2) into the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com