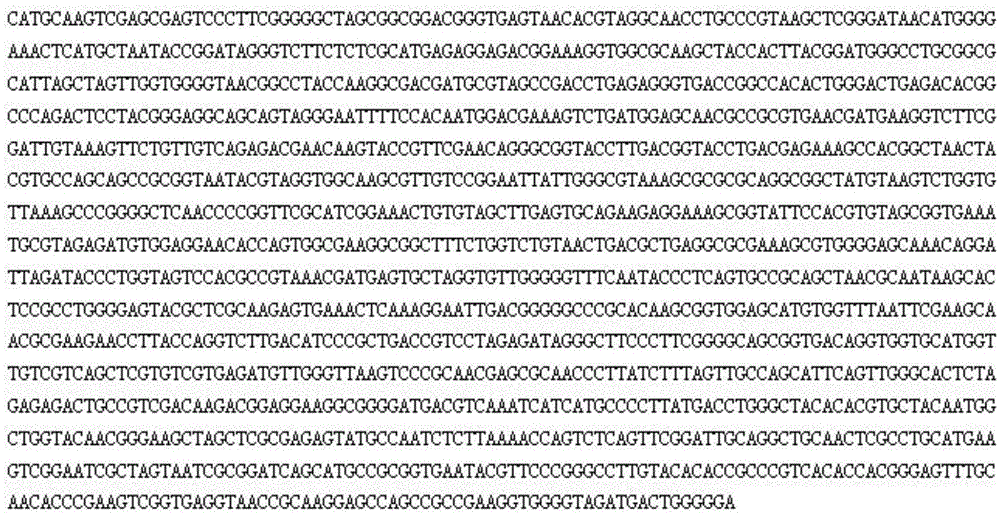High-temperature-resistant garden waste decomposition bacterium FHM1 and application thereof
A technology of garden waste and high temperature resistance, which is applied in the field of environmental biology to speed up the composting process and reduce environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Screening of high-temperature-resistant cellulose-degrading bacterial strains
[0023] Samples were collected from composting of garden waste in an apple orchard in Changping District, Beijing at the early stage of high temperature, middle stage of high temperature, and late stage of high temperature material, and the accumulation of landscaping waste in the afforestation area of Yanqing Plain in Beijing; 10 g of the above fresh samples were weighed and placed in a container containing 10 glass beads. , and filled with 90ml of sterile water in a conical flask, placed in a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm for 30min to fully disperse the samples, and left to enrich and cultivate at 50°C for 24h. Use a sterile pipette to draw 1ml of the supernatant and add it to a test tube containing 9ml of sterile water, which is 10 -1 Sample diluent, again from 10 -1 Take 1ml of the sample and add it to 9ml sterile water, which is 10 -2 sample diluent, and so on, to get 10 -3 、1...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2 FHM1 strain molecular biology identification
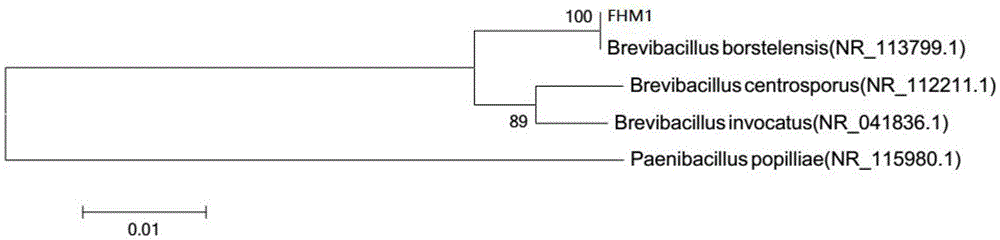
[0027] Molecular identification of the Brevibacillus Potsdamer obtained from the screening was carried out according to the following steps: pick a single colony of the screened strain and inoculate it in liquid LB medium, culture it on a shaker at 50°C and 150 r / min, and take out the culture medium on the second day. Centrifuge at 5000r / min for 1min to take the supernatant, and extract colony DNA according to the bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit (provided by Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.); PCR amplification is carried out on the extracted bacterial DNA with universal primers 27F and 1492R; the sequence of 27F is 5 ′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′; 1492R sequence is 5′-AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3′; the PCR product was sequenced, and the sequencing results were analyzed by BLAST in the NCBI database and compared for homology.
[0028] The 16S rDNA gene sequence of Brevibacillus Potsdam (see figure 2 ) with a l...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3 Brevibacillus Potsdam growth assay
[0030] Brevibacillus Potsdam strain FHM1 was inoculated into CMC liquid medium (CMC-Na15.0g, NH 4 NO 3 1.0g, yeast extract 1.0g, MgSO 4 0.5g, KH 2 PO 4 1.0g, distilled water 1000mL), take the culture solution every 2h, continuously sample for 48h, measure the OD600 value of each period, take the culture time as the abscissa, and the OD600 value of each sampling point as the ordinate, draw the growth curve of the bacteria , the growth assay of the bacteria. It can be seen from the measurement results that 0-8h is the lag phase, 9-16h is the logarithmic growth phase, 16-24h is the stable phase, and >26h is the decline phase. The strains in the logarithmic phase grow rapidly and have strong vitality. Therefore, in the subsequent fermentation enzyme production experiments, the 12-hour fermentation liquid should be used as the seed liquid for inoculation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com