Method for strengthening Cr(VI) electroreduction by virtue of small molecular inorganic acid
A small molecule organic acid and inorganic acid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and limit the feasibility of industrial application, and achieve electric energy Low consumption, easy to promote and use on a large scale, and the effect of adding less
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
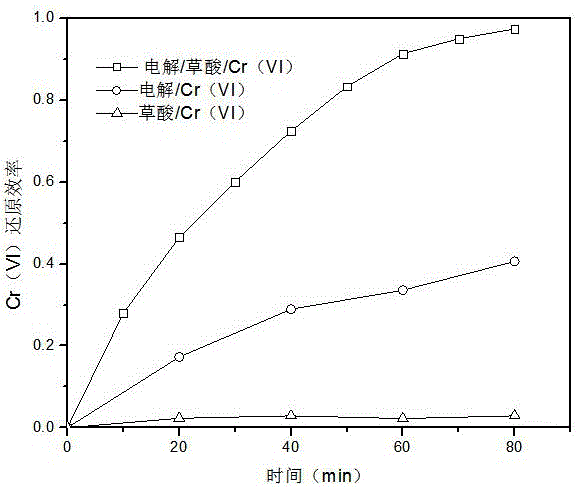
[0022] Add 0.5mM oxalic acid to the water body with a Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1mM (mmol / L, the same below), adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL, and use a low-voltage DC power supply to conduct electrolysis with a constant current I=20mA. The anode used is flake graphite, iron or platinum (1cm×1cm), and the cathode is a sheet Activated carbon fiber, glassy carbon, metal platinum or graphite (3cm×3cm), during this process, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the electrolyte to mix evenly.
[0023] Comparative Experiment 1: Add 0.5mM oxalic acid to water with a Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1mM, adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL. Under the condition of no electricity, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution to make it uniform....
Embodiment 2
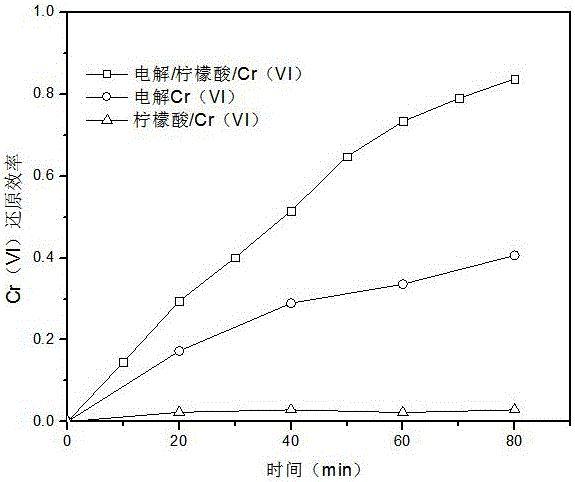
[0026] Add 0.5mM citric acid to water with a Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1mM, adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL, and use a low-voltage DC power supply to conduct electrolysis with a constant current I=20mA. The anode used is flake graphite, iron or platinum (1cm×1cm), and the cathode is a sheet Activated carbon fiber, glassy carbon, metal platinum or graphite (3cm×3cm), during this process, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the electrolyte to mix evenly.
[0027] Comparative Experiment 1: Add 0.5mM citric acid to water with a Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1mM, adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL. Under the condition of no electricity, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution to make it uniform.
[0028] Comparative experiment ...
Embodiment 3
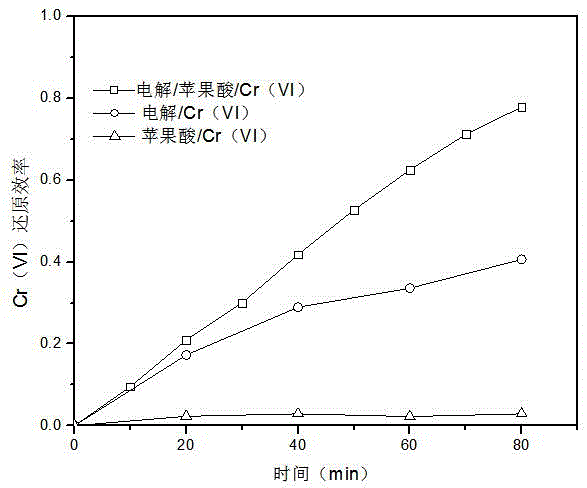
[0030] Add 1 mM malic acid to the water body with Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1 mM, adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL, and use a low-voltage DC power supply to conduct electrolysis with a constant current I=20mA. The anode used is flake graphite, iron or platinum (1cm×1cm), and the cathode is a sheet Activated carbon fiber, glassy carbon, metal platinum or graphite (3cm×3cm), during this process, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the electrolyte to mix evenly.
[0031] Comparative experiment 1: Add 1 mM malic acid to water with a Cr(VI) concentration of 0.1 mM, adjust the pH value to 3 with sulfuric acid, and use Na 2 SO 4 Adjust the conductivity of the electrolyte to about 3ms / cm, so that the mixed solution reaches 200mL. Under the condition of no electricity, use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution to make it uniform.
[0032]Comparative experim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com