A method for increasing the proportion of fetal free DNA in the plasma free DNA sequencing library of pregnant women
A technology for plasma and pregnant women, applied in the field of biotechnology genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low sequencing throughput, low fetal DNA content, and high detection cost, and achieve the effects of improving detection throughput, improving sequencing sample throughput, and accurate detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
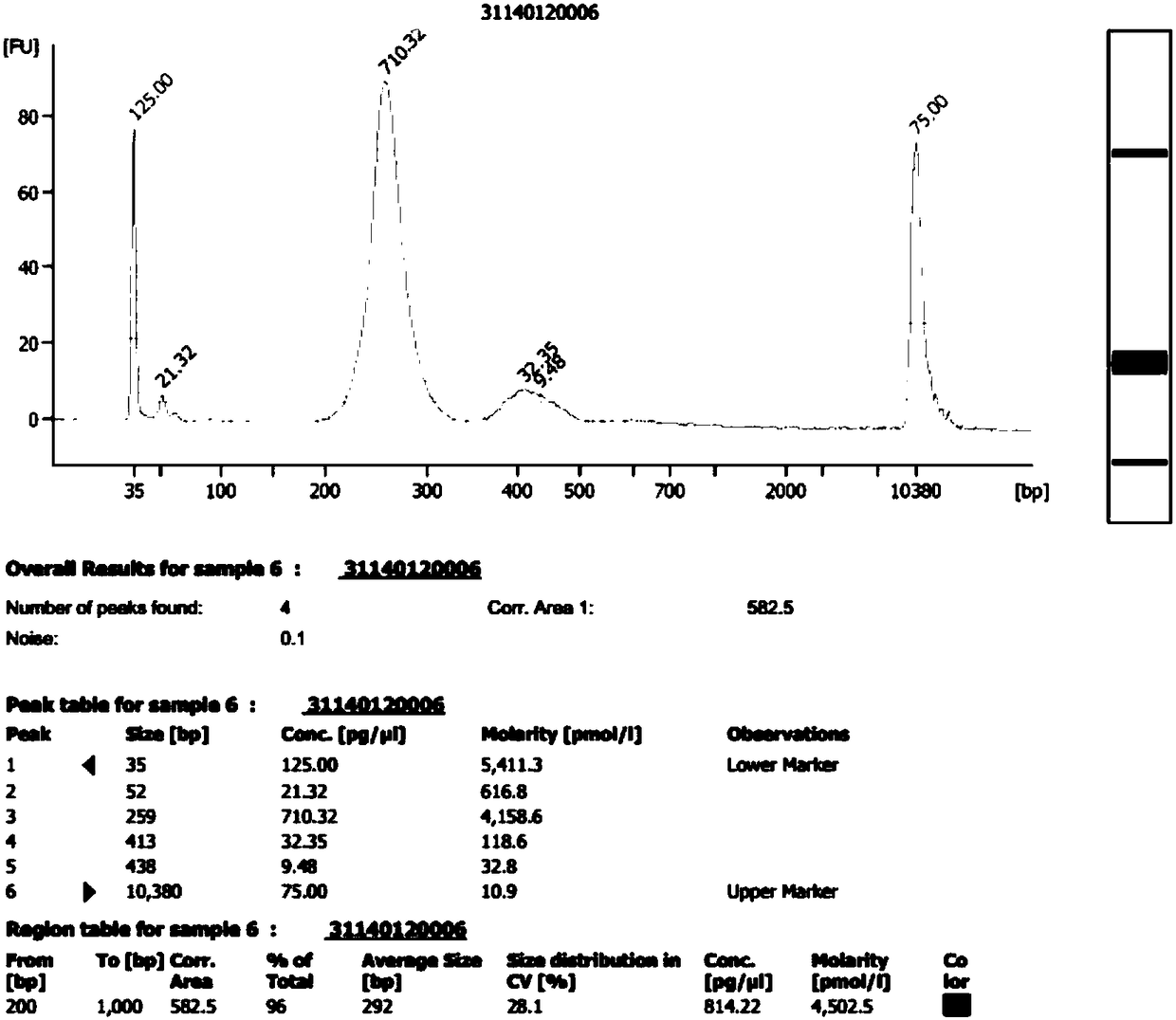
[0055] Comparison of mixed sequencing data volumes of different quantities of original libraries
[0056] experimental method
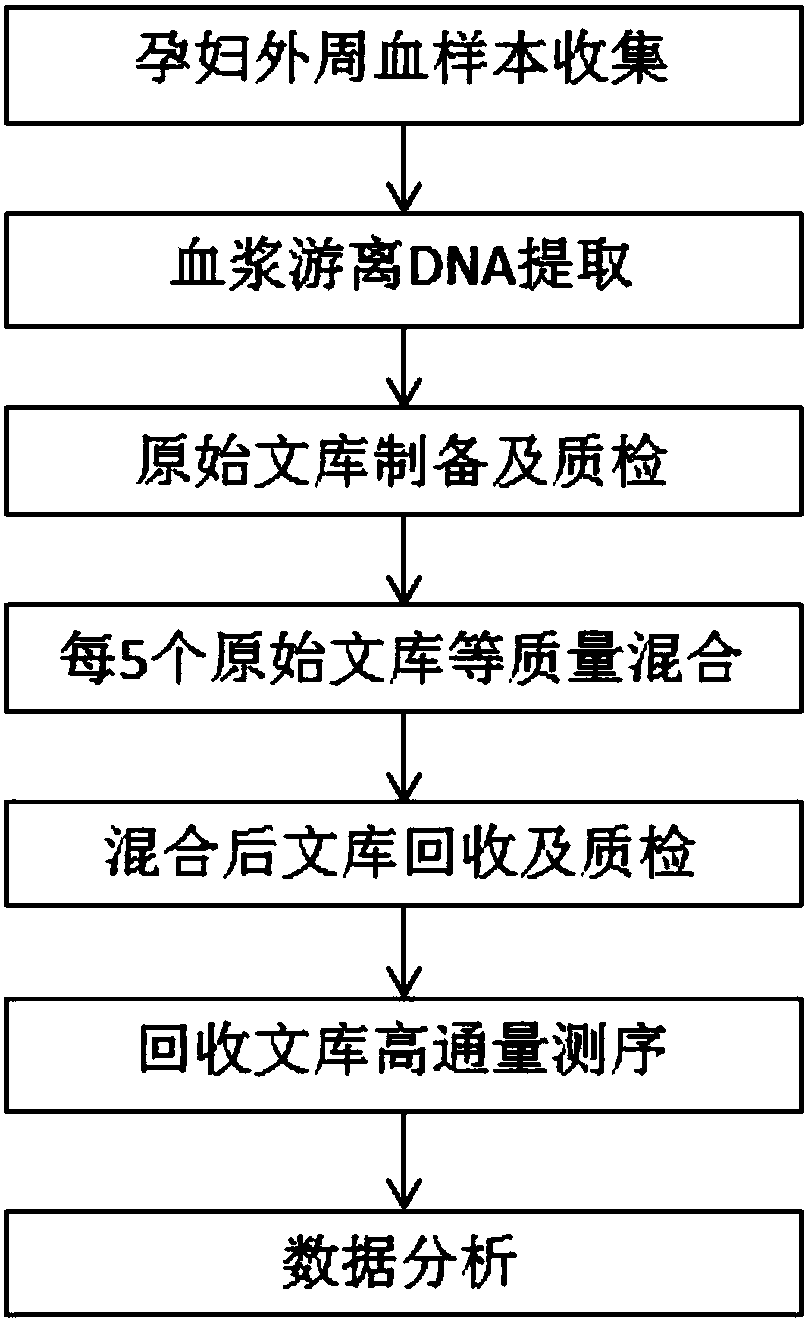
[0057] 1. Collect plasma samples from 54 pregnant women and perform cell-free DNA extraction
[0058] (1) Use EDTA anticoagulant blood collection tubes to extract 5ml of venous blood from pregnant women with a gestational age of 12-24 weeks, centrifuge the EDTA anticoagulant blood collection tubes at 4°C at 1600×g for 10 minutes; absorb all the upper plasma Dispense into 2ml centrifuge tubes, centrifuge the plasma obtained from the first centrifugation at 16000×g for 10 min at room temperature, carefully draw the upper plasma obtained from the second centrifugation into a new centrifuge tube for free DNA extraction ;
[0059] (2) Draw 600 μl of the plasma sample that has been centrifuged twice into a new 2ml centrifuge tube;
[0060] (3) Add 1000 μl Lysis Buffer, 60 μl Magnetic beads, 35 μl Proteinase K, 14 μl Acryl Carrier to 600 μl plasma in turn...
Embodiment 2
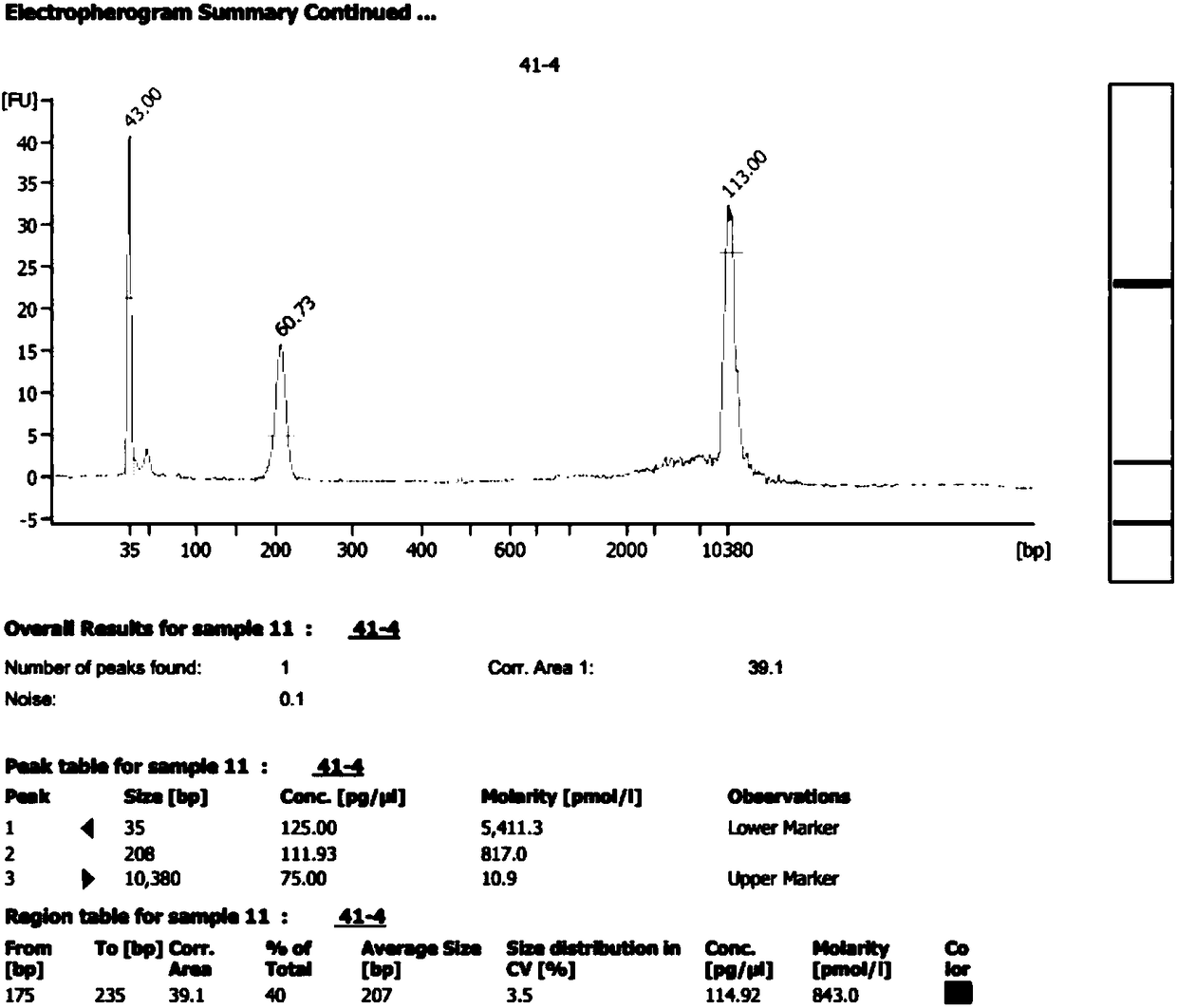
[0104]Using high-throughput sequencing technology and data analysis system to analyze and compare the proportion of fetal free DNA in the original library of plasma free DNA in pregnant women and the recovered library constructed according to the method of the present invention
[0105] experimental method
[0106] 1. Plasma sample preparation and DNA extraction
[0107] Collect 14 cases of peripheral blood samples from pregnant women who are pregnant with male fetuses, perform plasma separation and free DNA extraction according to the method in Example 1, use 1ul solution samples containing free DNA to carry out Qubit quantitative detection, and detect qualified plasma free DNA. The next step is library preparation.
[0108] 2. Library Preparation
[0109] Same as the library preparation in Example 1.
[0110] 3. Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of the original library
[0111] Same as the original library in Example 1 for on-machine sequencing and bioinformatics an...
Embodiment 3
[0122] The method of the present invention is sensitive to the detection sensitivity of fetal cell-free DNA with different content proportions in the plasma of pregnant women
[0123] experimental method
[0124] 1. Plasma sample preparation and cell-free DNA extraction
[0125] Collect the plasma samples of pregnant women whose karyotype is known to be trisomy 21 and a male fetus after sequencing, and the content of fetal cell-free DNA in the plasma has been determined by high-throughput sequencing technology in the early stage, using the known fetal DNA content Plasma samples and non-pregnant plasma samples were mixed in different proportions to prepare mixed plasma with fetal cell-free DNA content accounting for 2%, 3%, 4%, 5% and 10% respectively. The preparation of mixed plasma is shown in Table 8 below:
[0126] Table 8
[0127]
[0128]
[0129] The mixed plasma in Table 8 was extracted according to the extraction method in Example 1, and 1 μl of the solution s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com