Low-yield high-grade alcohol high-yield ethyl lactate saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and construction method thereof
A strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the technology of ethyl lactate, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low ability to synthesize ethyl lactate and high content of higher alcohols, and achieve the effect of overcoming uncoordinated flavors, excellent flavors, and broad market prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with low production of higher alcohols and high production of ethyl lactate
[0033] The main construction process of the strain is as follows:
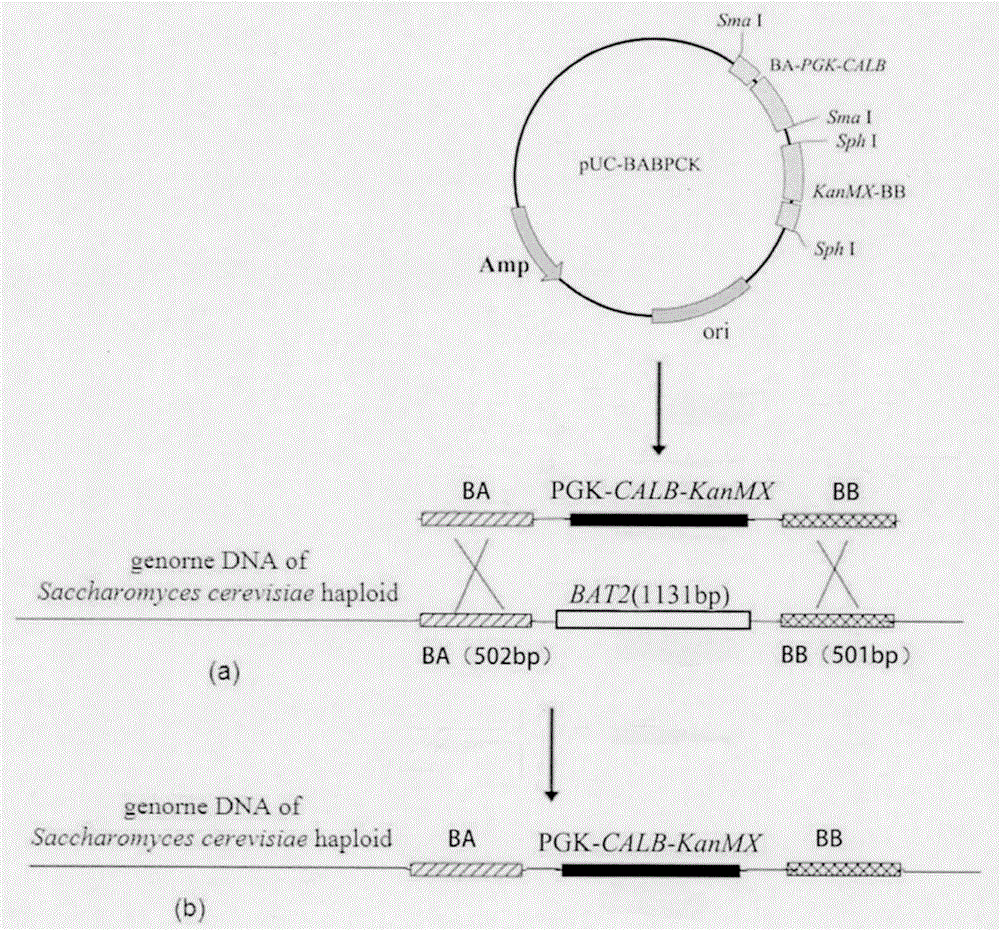
[0034] 1) Construction of pUC-BABPCK plasmid
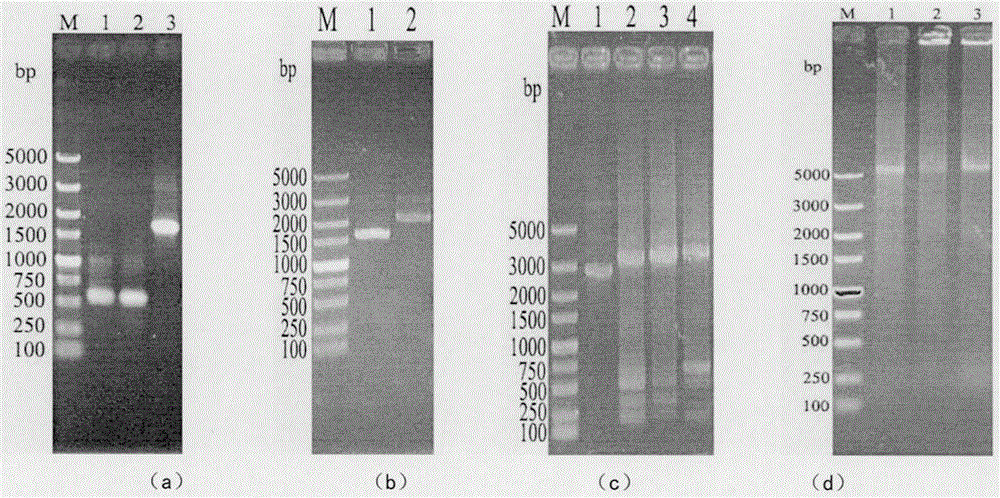
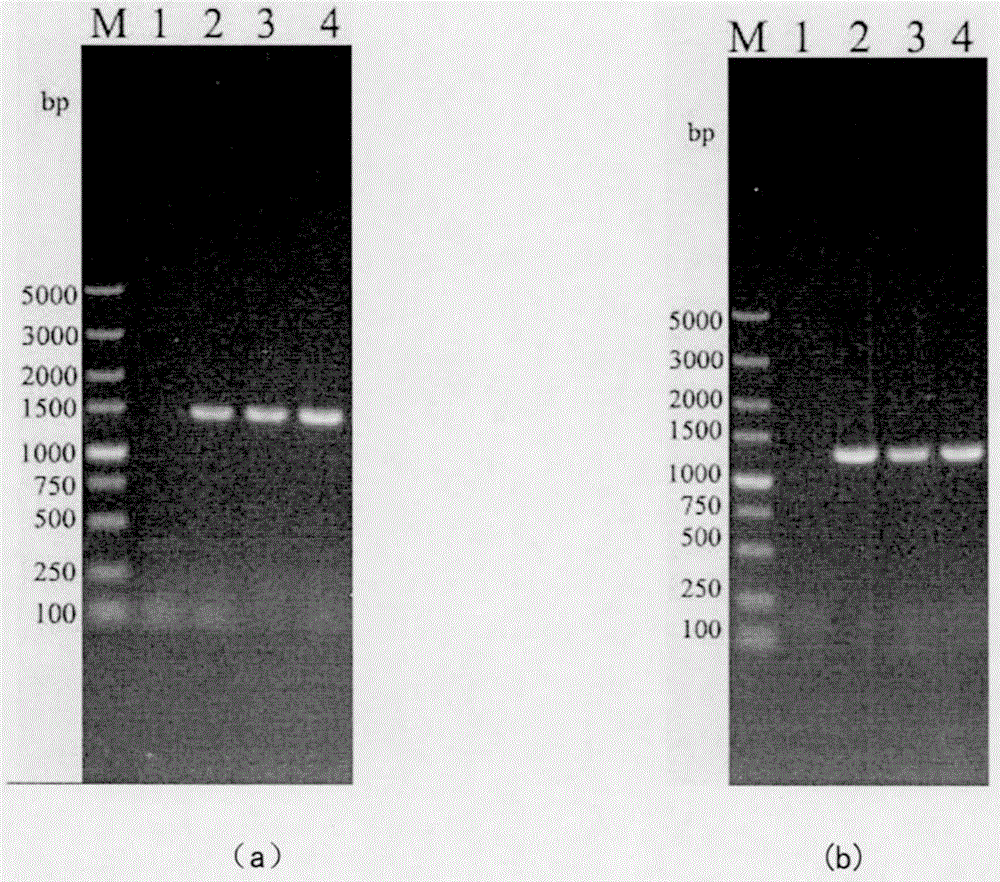
[0035] Using pUC-19 as the base plasmid to construct the homologous recombination plasmid pUC-BABPCK, the construction process is as follows: figure 1 As shown (the strain construction method is basically the same), using Saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC32315 haploid α5 as a template, using primers BA-U (SEQ NO: 3) and BA-D (SEQ NO: 4) PCR amplification to obtain a 502bp upstream homology Arm BA and 501 bp downstream homology arm BB of BB-U (SEQ NO: 5) and BB-D (SEQ NO: 6). Using the pMD20-T-CALB-2 plasmid donated by South China University of Technology as a template, three target gene upstream primers Ci-U (SEQNO: 7), Cn-U (SEQNO: 8), Cα-U (SEQNO: 9 ) and downstream primers C-D (SEQ NO: 10) PCR amplification to obtain th...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Fermentation experiment of sorghum raw material semi-solid liquor with INU strain containing inulinase signal peptide
[0050] 1) Fermentation process route:
[0051] Sorghum → soaking → liquefaction → saccharification → cooling → mixing koji, inoculation with lactic acid bacteria → cultivation for 12 hours → fermentation → distillation
[0052] 2) Process conditions: soaking conditions: 60-70°C, fully absorb water; cooking conditions: 115°C for about 30 minutes; liquefaction conditions: 85-90°C, high temperature resistant α-amylase, liquefaction for 60 minutes; saccharification conditions: 55-60°C , add glucoamylase, saccharification for 20min; fermentation conditions: 30°C, 7 days; wine steaming conditions: 100mL fermentation broth, add 100mL water, steam 100mL wine sample.
[0053] 3) Ingredients: sorghum flour: 78g; add water 200mL; high temperature resistant α-amylase: 25μL; glucoamylase: 45μL; acid protease: 1.2mL;
[0054] Carry out semi-solid Daqu l...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: Fermentation experiment of sorghum raw material semi-solid liquor with CalB self-signal peptide nsB strain
[0064] 1) Fermentation process route:
[0065] The fermentation process is consistent with 1) in Example 2.
[0066] 2) Process conditions: consistent with 2) in Example 2.
[0067] 3) batching: consistent with 3) in embodiment 2.
[0068]Carry out semi-solid Daqu liquor fermentation experiments on Saccharomyces cerevisiae starting strain α5 and selected strain α5CALBn according to the above-mentioned fermentation process; during the fermentation period, shake and weigh every 12 hours, and record the weight loss; after the fermentation is over, stop the cultivation and weigh; Residual sugar concentration, alcohol content and content of main aroma components. The comprehensive performance was characterized by fermentation capacity, residual sugar concentration and product production, and the results are shown in Table 4.
[0069] Table 4 Fermentatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com