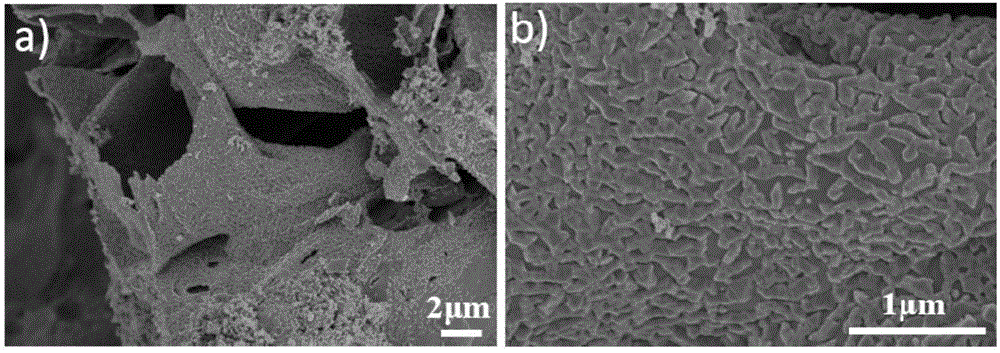
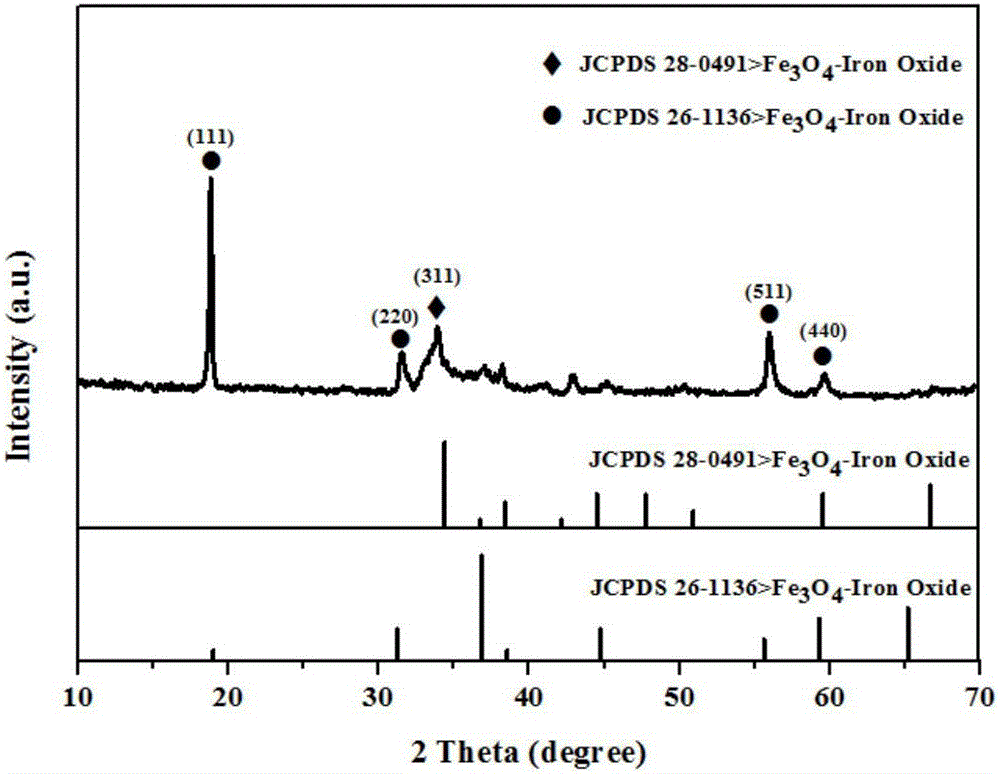
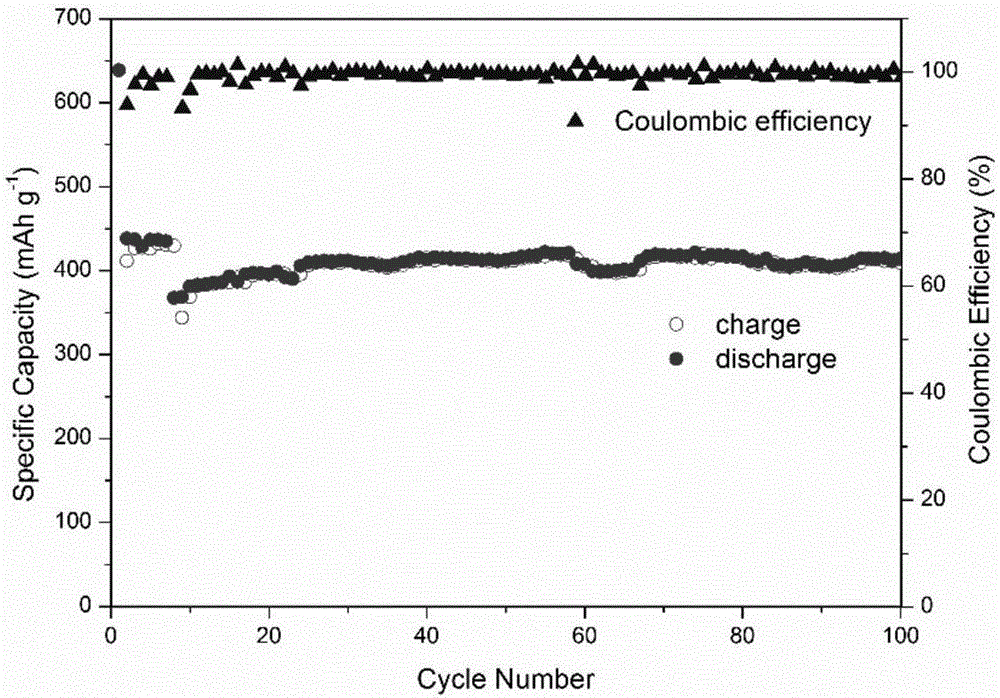
Preparation method of nitrogen-doping carbon substrate-supported Fe3O4 composite material sodium-ion battery negative electrode material
A sodium ion battery and ferric oxide technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of poor conductivity, unstable cycle performance, low current capacity, etc., to improve stability, maintain the original shape, and relieve volume expansion. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1) Weigh urea and ammonium ferric citrate with a mass ratio of 4:1, dissolve the urea and ammonium ferric citrate in deionized water, and ultrasonicate for 30 minutes at a power of 300W to make ammonium ferric citrate with a concentration of 0.8mg / mL suspension A;
[0025] 2) Adjust the pH value of the suspension A to 3, then pour it into a watch glass, put it in the refrigerator and freeze it at -20°C for 12 hours to obtain a solid solid B;
[0026] 3) Put the frozen solid B into a freeze dryer and dry at -50°C for 12 hours to obtain a completely dried product C;
[0027] 4) Pour product C into a quartz crucible, wrap the quartz crucible with tin foil, then put it into a glass tube for oxides, set the temperature and holding time of the vacuum tube furnace to 5°C min -1 The heating rate was increased to 500 °C, and pyrolysis was carried out for 2 h to obtain the final product nitrogen-doped carbon matrix supported Fe 3 o 4 Composite sodium ion battery anode material...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) Weigh urea and ferric acetate with a mass ratio of 4:3, dissolve the urea and ferric acetate in deionized water, and ultrasonicate for 30 min at a power of 300W to prepare a suspension with a ferric acetate concentration of 0.8 mg / mL. Turbid liquid A;
[0031] 2) Adjust the pH value of the suspension A to 3, then pour it into a watch glass, put it in the refrigerator and freeze it at -20°C for 12 hours to obtain a solid solid B;
[0032] 3) Put the frozen solid B into a freeze dryer and dry at -50°C for 12 hours to obtain a completely dried product C;
[0033] 4) Pour the product C into a quartz crucible, wrap the quartz crucible with tin foil, then put it into a glass tube for oxides, set the vacuum tube furnace temperature and holding time at 5°C min -1 The heating rate was increased to 500 °C, and pyrolysis was carried out for 2 h to obtain the final product nitrogen-doped carbon matrix supported Fe 3 o 4 Composite sodium ion battery anode material.
[0034] T...
Embodiment 3
[0036] 1) Dissolve urea and soluble trivalent complex iron salt in deionized water at a mass ratio of 4:1 to 4:4, and sonicate for 10 minutes at a power of 300W to make a soluble trivalent complex iron salt with a concentration of 2mg / mL Suspension A; wherein, the soluble trivalent complex iron salt is ferric ammonium oxalate.
[0037] 2) Adjust the pH value of the suspension A to 5 and freeze it in the refrigerator at -20°C for 24 hours to obtain the solid B;
[0038] 3) freeze-dry solid B in a freeze dryer at -50°C for 24 hours to obtain product C;
[0039] 4) Pour the product C into a quartz crucible, wrap the quartz crucible with tin foil, and then heat it in a vacuum tube furnace at 10°C min -1 The heating rate was increased from room temperature to 400 °C and pyrolyzed for 2 h to obtain a nitrogen-doped carbon matrix supported Fe 3 o 4 Composite sodium ion battery anode material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com