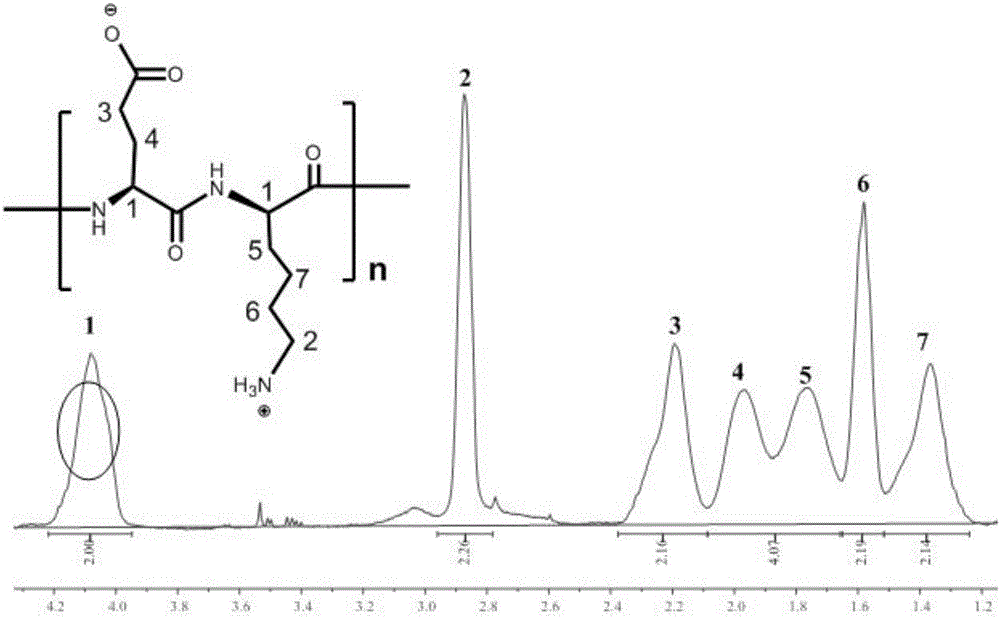
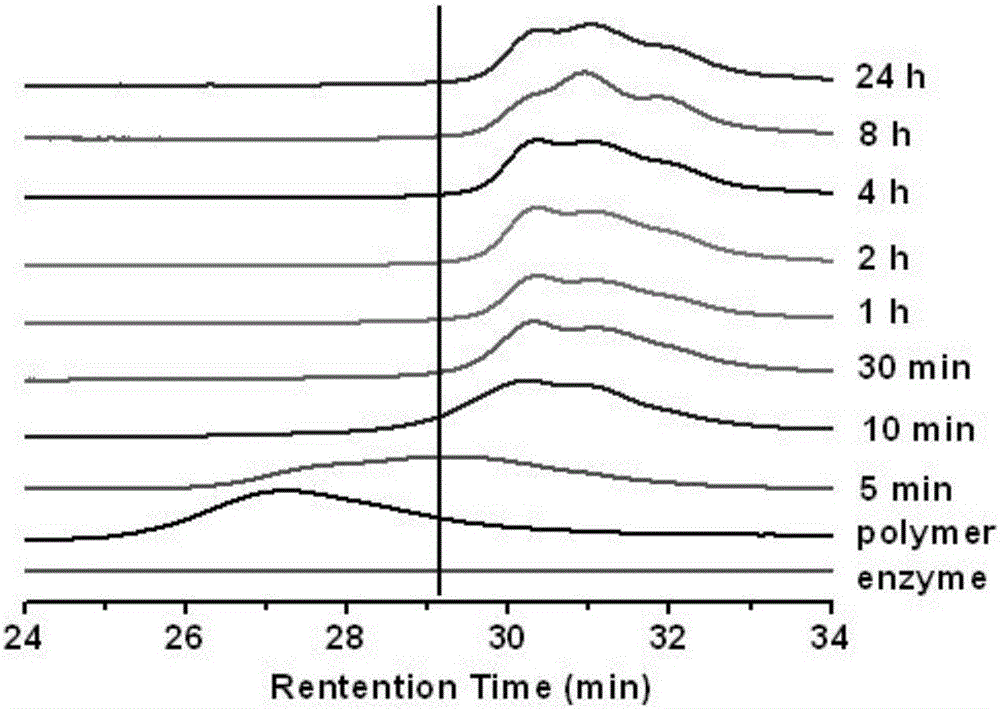
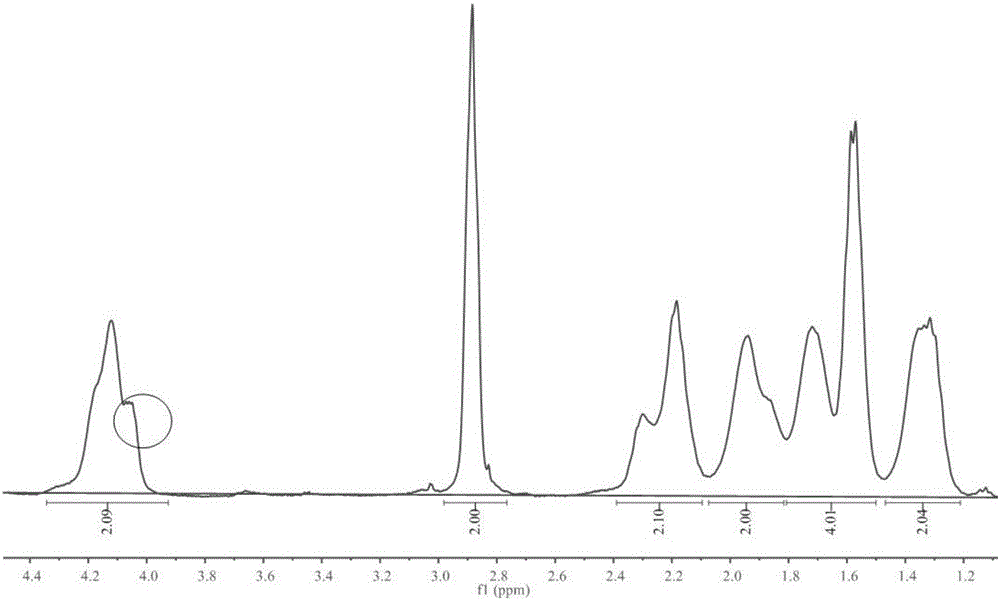
Enzyme degradation-controllable anti-nonspecific protein adsorption polypeptide and monomer and preparation method thereof
A technology of monomers and inhibitors, applied in the field of peptides and their preparation, can solve the problems of large impact on the size of biomolecules, abnormal cell death, loss of protein non-adsorption, etc., achieve broad application prospects, and improve resistance to non-specific proteins The effect of adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0072] The following exemplifies the preparation method of the anti-non-specific protein adsorption polypeptide with controllable enzymatic degradation of the present invention, preferably including the following parts:
[0073] (1) Condensation synthesis of dipeptide monomers with side chain protection
[0074] Through the condensation of glutamic acid and lysine with different protecting groups, such as γ-benzyl-N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-glutamic acid and N ε -Condensation of benzyloxycarbonyl-α-tert-butyl-L-lysine, and through selective deprotection, a dipeptide with side chains protected by benzyl and benzyloxycarbonyl was obtained, and purified by separation and used for The next step of polycondensation. The advantage of this method is that it can avoid directly protecting amino acids with two side chains (eg, γ-benzyl-L-glutamic acid and N ε -benzyloxycarbonyl--L-lysine) polycondensation after mixing produces the problem of uneven distribution of positively and negative...
Embodiment 1
[0090] 1) polycondensation
[0091] Take the first monomer (structural formula shown in formula I) 200mg (0.4mmol), then add 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC.HCl) 115mg ( 0.6mmol) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) 81mg (0.6mmol). After adding 2 mL of anhydrous N, N-diformamide (DMF) to the system, seal it with a rubber stopper, bubble it with nitrogen for 30 min, and then react in a closed room at room temperature for 48 h. After the reaction, about 18 mL of anhydrous ether was added to the reaction system for precipitation. After standing still for about 20 minutes, the solvent was poured off to obtain an oily non-deprotected zwitterionic polypeptide with alternating glutamic acid and lysine residues.
[0092] 2) deprotection group
[0093] After completely dissolving the above oil with about 2mL of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), add about 2mL of 33% (33wt.%) hydrobromic acetic acid (HBr / HOAc) solution for deprotection, and the reaction system wi...
Embodiment 2
[0097] 1) polycondensation
[0098] Take the first monomer (its structural formula is shown in formula I) 100mg (0.2mmol) and the second monomer (its structural formula is shown in formula III) 20mg (0.04mmol), add 1-ethyl-(3-dimethyl Aminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC.HCl) (86.4mg, 0.45mmol) and 1-hydroxy-7-azobenzotriazole (HOAt) (61.3mg, 0.45mmol), and 0.004 mmol of cysteine protected by aminobenzyloxycarbonyl group protected by end-capping agent. After adding about 2 mL of anhydrous DMF to the system, seal it with a rubber stopper, bubble it with nitrogen for 30 minutes, and then react in a closed room at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction is over, add about 18 mL of anhydrous ether to the reaction system for precipitation. After standing still for about 20 minutes, pour off the solvent to obtain an oily undeprotected polypeptide (the molar ratio of the first monomer to the second monomer is 5: 1).
[0099] 2) deprotection group
[0100] Afte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com