Technology for recycling by-product fluosilicic acid of wet process phosphoric acid
A technology of wet-process phosphoric acid and fluosilicic acid, which is applied in ammonium orthophosphate fertilizers, alkaline orthophosphate fertilizers, applications, etc., can solve the problems of long impurity removal process, high silica gel content, high impurity content, etc., and achieve process feasibility , the fluorine content is controllable, and the effect of improving the ecological environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
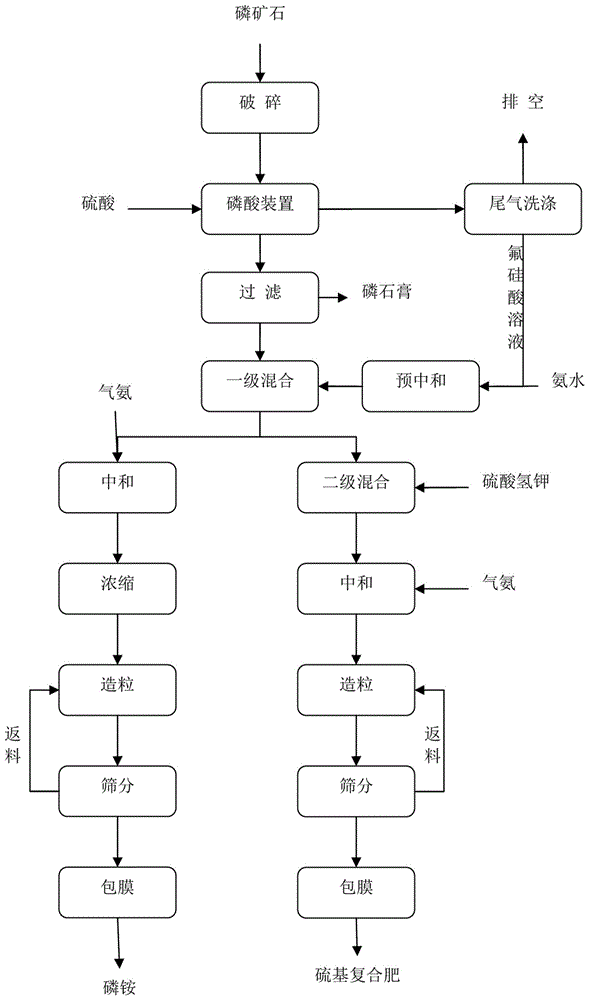
[0035] A process for reusing hydrofluorosilicic acid by-product of wet-process phosphoric acid, said process comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step 1): the fluorine-containing gas in the production process of wet-process phosphoric acid is washed and absorbed to form a fluorosilicate solution;
[0037] Step 2): In step 1), the fluorosilicic acid solution is pre-neutralized with ammonia water to generate an ammonium fluorosilicate solution;
[0038] Step 3): In step 2), the obtained ammonium fluorosilicate solution is mixed with wet-process phosphoric acid to obtain a mixed acid solution;
[0039] Step 4): the mixed acid solution obtained in step 3) is mixed with potassium bisulfate to obtain a compound fertilizer mixed acid slurry;
[0040] Step 5): the compound fertilizer mixed acid slurry obtained in step 4) is neutralized with gas ammonia to obtain the compound fertilizer neutralized slurry;
[0041] Step 6): The compound fertilizer neutralized slurry obtained in s...
Embodiment 2
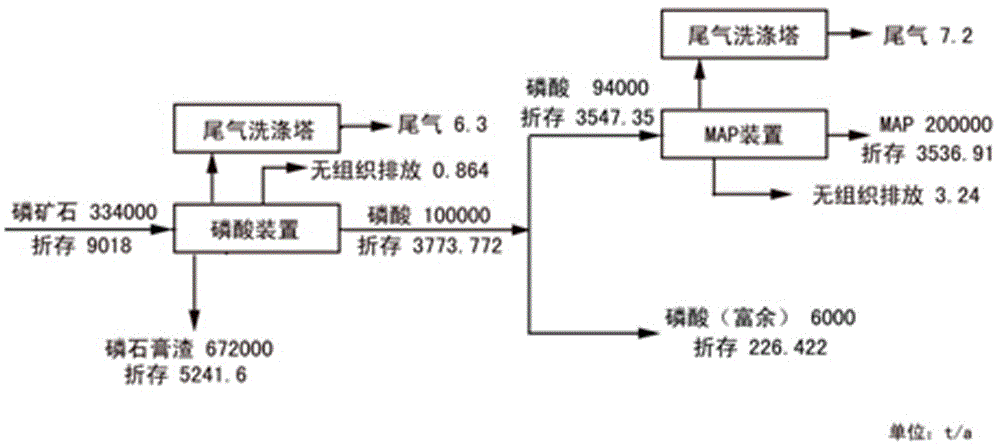
[0050] A process for reusing hydrofluorosilicic acid by-product of wet-process phosphoric acid, said process comprising the following steps:
[0051] Step 1): the fluorine-containing gas in the production process of wet-process phosphoric acid is washed and absorbed to form a fluorosilicate solution;
[0052] Step 2): In step 1), the fluorosilicic acid solution is pre-neutralized with ammonia water to generate an ammonium fluorosilicate solution;
[0053] Step 3): In step 2), the obtained ammonium fluorosilicate solution is mixed with wet-process phosphoric acid to obtain a mixed acid solution;
[0054] Step 4): the mixed acid solution obtained in step 3) is mixed with potassium bisulfate to obtain a compound fertilizer mixed acid slurry;
[0055] Step 5): the compound fertilizer mixed acid slurry obtained in step 4) is neutralized with gas ammonia to obtain the compound fertilizer neutralized slurry;
[0056] Step 6): The compound fertilizer neutralized slurry obtained in ste...
Embodiment 3
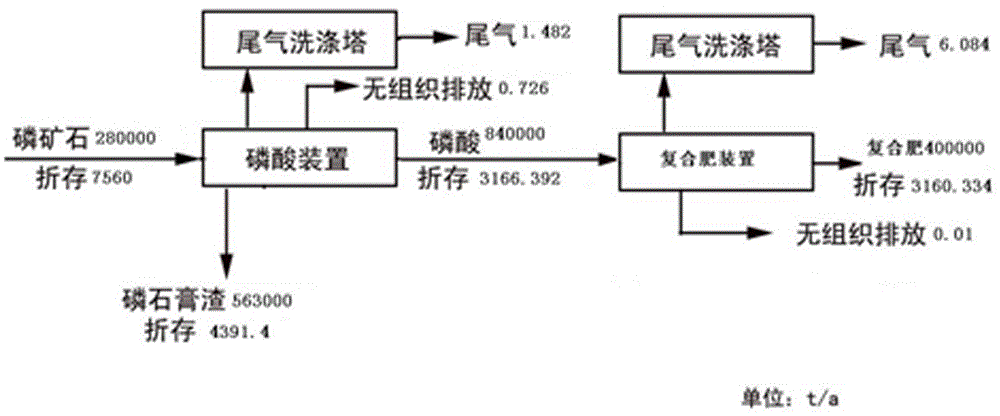
[0064] A process for reusing hydrofluorosilicic acid by-product of wet-process phosphoric acid, said process comprising the following steps:
[0065] Step 1): the fluorine-containing gas in the production process of wet-process phosphoric acid is washed and absorbed to form a fluorosilicate solution;
[0066] Step 2): In step 1), the fluorosilicic acid solution is pre-neutralized with ammonia water to generate an ammonium fluorosilicate solution;
[0067] Step 3): In step 2), the obtained ammonium fluorosilicate solution is mixed with wet-process phosphoric acid to obtain a mixed acid solution;
[0068] Step 4): step polymerization 3) to obtain the neutralization reaction of mixed acid liquid and ammonia gas to obtain ammonium phosphate neutralization slurry;
[0069] Step 5): the ammonium phosphate neutralized slurry obtained in step 4) is concentrated to obtain a concentrated slurry;
[0070] Step 6): The concentrated slurry obtained in step 5) is subjected to spray granul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com